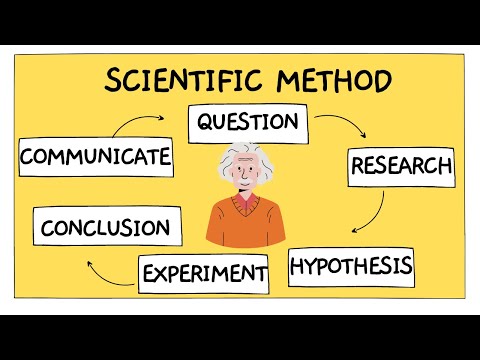
Conduct an Experiment The experiment is one of the most important steps in the scientific method, as it is used to prove a hypothesis right or wrong, and to formulate scientific theories.
Q. What property do hypotheses and theories have in common?
Answer and Explanation: One major factor that a scientific hypothesis, theory, and law have in common is that they are all based on observations.
Table of Contents
- Q. What property do hypotheses and theories have in common?
- Q. Why do scientists use variables?
- Q. What is the difference between religious truth and scientific truth?
- Q. Does science tell us the truth?
- Q. Is science concerned with truth?
- Q. What is the meaning of objective truth?
- Q. What is religious truth?
- Q. What is the difference between a hypothesis and a theory?
- Q. What comes first a hypothesis or theory?
- Q. What are examples of theory?
- Q. Which of the following best describes a controlled experiment?
- Q. Which of the following best differentiates a theory from a hypothesis?
- Q. Which of the following statements best distinguishes a law from a theory quizlet?
- Q. Which of the following is the quality of a good scientific hypothesis?
- Q. What are the common features of life?
- Q. What are the 10 characteristics of all living things?
- Q. What are the 5 characteristics of cells?
- Q. What are the 10 characteristics of life?
- Q. What are the 12 characteristics of life?
- Q. What are examples of the 7 characteristics of life?
- Q. What are the 5 requirements of life?
- Q. What are the requirements that support life?
- Q. What are the functional requirement of life?
- Q. What are the four requirements of life?
- Q. Is reproduction a functional requirement of life?
- Q. What is required for cellular life in humans?
- Q. What do cells need to be considered living?
- Q. Can life exist without cells?
- Q. How complex is a cell?
Q. Why do scientists use variables?
In science, a variable is any item, factor, or condition that can be controlled or changed. Using these variables correctly helps scientists measure cause and effect in scientific experiments and allows scientists to manipulate cause and effect to produce desired outcomes.
Q. What is the difference between religious truth and scientific truth?
Put differently, the world of science tends to equate fact with truth, while the world of religion tends to equate truth with fact. There is another distinction between fact and truth that needs to be recognized. Truths, on the other hand, being interpretations of facts, are in human minds.
Q. Does science tell us the truth?
Science is the process of building and testing these models based on experimental evidence. But at the end of the day, these are still just models. They aren’t The Truth. In fact, the only way to know if a model is absolutely true would be to test every possible case that applies to the model.
Q. Is science concerned with truth?
The purpose of science Scientific realists claim that science aims at truth and that one ought to regard scientific theories as true, approximately true, or likely true. Realists often point to the success of recent scientific theories as evidence for the truth (or near truth) of current theories.
Q. What is the meaning of objective truth?
The words objective truth are a reminder that the truth of a belief or statement is entirely a matter of how things are with its object, and has nothing to do with the state of its subject – the person who has the belief or makes the statement1.
Q. What is religious truth?
Truth of religion is here identified with religious truth understood as knowledge orientated towards the ultimate deepest reality called by various names: God, Dharma, Tao, the Sacred, etc. A religion is true in the sense that it states that the transcendent, supernatural, sacred reality exists.
Q. What is the difference between a hypothesis and a theory?
Hypothesis: What’s the Difference? A hypothesis proposes a tentative explanation or prediction. A theory, on the other hand, is a substantiated explanation for an occurrence. Theories rely on tested and verified data, and scientists widely accepted theories to be true, though not unimpeachable.
Q. What comes first a hypothesis or theory?
In scientific reasoning, a hypothesis is constructed before any applicable research has been done. A theory, on the other hand, is supported by evidence: it’s a principle formed as an attempt to explain things that have already been substantiated by data.
Q. What are examples of theory?
The definition of a theory is an idea to explain something, or a set of guiding principles. Einstein’s ideas about relativity are an example of the theory of relativity. The scientific principles of evolution that are used to explain human life are an example of the theory of evolution.
Q. Which of the following best describes a controlled experiment?
A controlled experiment is a scientific test that tests the effect of a single independent variable at a time.
Q. Which of the following best differentiates a theory from a hypothesis?
Hypotheses must be testable and falsifiable. The best statement, which distinguishes hypotheses from theories in science is “Hypotheses usually are relatively narrow in scope; theories have broad explanatory power.”
Q. Which of the following statements best distinguishes a law from a theory quizlet?
Which of the following statements best distinguishes a law from a theory? A law is the result of inductive reasoning based on repeated, confirmed observations, while a theory is an explanatory statement or set of statements derived from facts and confirmed hypotheses. You just studied 14 terms!
Q. Which of the following is the quality of a good scientific hypothesis?
In order for a hypothesis to be able to be used in science, which of the following must be true? It is testable and falsifiable. A hypothesis can be supported or rejected through experimentation.
Q. What are the common features of life?
All living organisms share several key characteristics or functions: order, sensitivity or response to the environment, reproduction, growth and development, regulation, homeostasis, and energy processing. When viewed together, these characteristics serve to define life.
Q. What are the 10 characteristics of all living things?
These characteristics become the criteria for scientists to separate the living elements in nature from the non-living ones.
- Cells and DNA.
- Metabolic Action.
- Internal Environment Changes.
- Living Organisms Grow.
- The Art of Reproduction.
- Ability to Adapt.
- Ability to Interact.
- The Process of Respiration.
Q. What are the 5 characteristics of cells?
Also it can protect the cell. Cell Wall- The cell wall belongs in this section because it will give protection to the plant cells, only if they are in danger. Cytoplasm- The cytoplasm belongs in this section because it will give the cell its shape….They are:
- Grow and develop.
- reproduce.
- use energy.
- respond.
Q. What are the 10 characteristics of life?
Plants use photosynthesis to capture light energy and store that energy as sugar.
- Homeostasis. .
- Adaptation. .
- Regulation. .
- Sensitivity / response to stimuli. .
- Metabolism. .
- Reproduction. .
- Order. .
- Growth and development. .
Q. What are the 12 characteristics of life?
Terms in this set (11)
- Reproduction. the process by which organisms are given rise to offspring.
- metabolism. is the process of energy generation and use.
- homeostasis.
- Survival.
- evolution.
- development.
- growth.
- Autonomy.
Q. What are examples of the 7 characteristics of life?
The seven characteristics of life include:
- responsiveness to the environment;
- growth and change;
- ability to reproduce;
- have a metabolism and breathe;
- maintain homeostasis;
- being made of cells; and.
- passing traits onto offspring.
Q. What are the 5 requirements of life?
Cells = Living things have one or more cells.
- Homeostasis = The maintenance of a relatively stable internal environment.
- Reproduction = The ability to form a new offspring.
- Metabolism = The ability to obtain and use. energy for growth and movement.
- DNA/Heredity = Genetic material that is passed on during reproduction.
Q. What are the requirements that support life?
Living organisms require the following to survive:
- energy.
- gases.
- water.
- soil.
- favourable temperatures.
Q. What are the functional requirement of life?
Interrelationships, maintaining boundaries, movement, responsiveness, digestion, metabolism, excretion, reproduction, and growth.
Q. What are the four requirements of life?
It is useful to categorize the requirements for life on Earth as four items: energy, carbon, liquid water, and various other elements.
Q. Is reproduction a functional requirement of life?
Explanation: All life forms must be able to uptake or produce energy to survive (metabolism), grow, and reproduce to propagate the species. While having a safe place to live is an ideal for most species, it is not a requirement of life. These criteria can be tested by thinking of a single cell.
Q. What is required for cellular life in humans?
Every cell in your body needs oxygen to help it metabolize (burn) the nutrients released from food for energy. Cells that do the same job combine together to form body tissue, such as muscle, skin, or bone tissue. Groups of different types of cells make up the organs in your body, such as your heart, liver, or lungs.
Q. What do cells need to be considered living?
Q. Can life exist without cells?
And while some cells can live on their own, others need to be part of a larger group of cells to survive. So, to answer your question after all that, you can’t be truly alive without cells.
Q. How complex is a cell?
The cell is the most complex and most elegantly designed system man has ever witnessed. The reason is that organic molecules are so complex that their formation cannot possibly be explained as being coincidental and it is manifestly impossible for an organic cell to have been formed by chance.