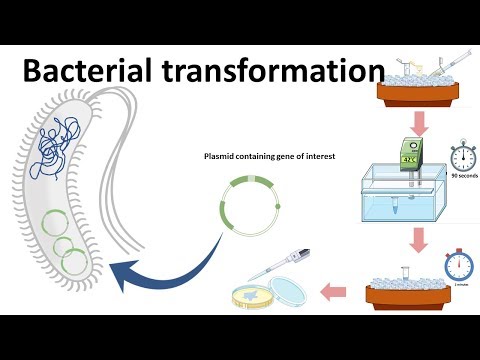
Q. What is the process of adding foreign DNA to a bacterial cell called?
Bacteria can take up foreign DNA in a process called transformation. Transformation is a key step in DNA cloning. It occurs after restriction digest and ligation and transfers newly made plasmids to bacteria.
Q. How is DNA inserted into a cell?
Physical methods such as electroporation or microinjection actually pokes holes in the cell membrane so DNA can be introduced directly into the cell. Microinjection requires the use of a fine needle to deliver nucleic acids to individual cells.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is the process of adding foreign DNA to a bacterial cell called?
- Q. How is DNA inserted into a cell?
- Q. Which process incorporates genes from other species?
- Q. What is the difference between conjugation and transduction?
- Q. What is the most important difference between transduction and conjugation?
- Q. Which bacteria form is shown in the image?
- Q. What is the definition of cocci?
- Q. What does it mean to have gram-positive cocci?
- Q. What antibiotics treat gram positive cocci?
- Q. Is Gram positive cocci contagious?
- Q. Where does gram positive cocci come from?
- Q. Is Gram positive cocci curable?
- Q. Is Gram positive cocci the same as MRSA?
- Q. What disease does Gram positive bacteria cause?
- Q. What color is Gram positive bacteria?
- Q. Is Gram positive bacteria good?
Q. Which process incorporates genes from other species?
Horizontal gene transfer also known as lateral gene transfer is the process by which an organism incorporates genetic material from another organism without mating.
Q. What is the difference between conjugation and transduction?
Conjugation is the transfer of circular DNA called plasmids through cell to cell contact. Transformation is the uptake of ‘free’ DNA from the environment. Transduction is the transfer of DNA by bacteria-specific viruses called bacteriophage.
Q. What is the most important difference between transduction and conjugation?
In transduction, DNA is accidentally moved from one bacterium to another by a virus. In conjugation, DNA is transferred between bacteria through a tube between cells. Transposable elements are chunks of DNA that “jump” from one place to another.
Q. Which bacteria form is shown in the image?
Answer: The microscopic image shown in the figure is a coccus.
Q. What is the definition of cocci?
Definitions of cocci. noun. any spherical or nearly spherical bacteria. synonyms: coccus.
Q. What does it mean to have gram-positive cocci?
noun, singular: gram-positive coccus. A group of spherical bacteria that retains the violet stain following gram staining. Supplement. Gram staining is a useful method for the rapid identification of bacterial species, especially those that are causing disease.
Q. What antibiotics treat gram positive cocci?
Most infections due to Gram-positive organisms can be treated with quite a small number of antibiotics. Penicillin, cloxacillin, and erythromycin should be enough to cover 90 per cent of Gram-positive infections.
Q. Is Gram positive cocci contagious?
However, it is known that given the right circumstances, even if the staph infection arises from organisms present on one’s body, if another person has direct contact with the infectious staph bacteria and has a break in the skin or mucous membranes, the organisms and potentially the disease can be contagious.
Q. Where does gram positive cocci come from?
The origin of these organisms is most probably the vaginal and cervical flora. BSI with anaerobic gram-positive cocci and microaerophilic streptococci often is associated with septic abortion. Anaerobic gram-positive cocci generally are found along with Prevotella species.
Q. Is Gram positive cocci curable?
In two clinical trials of HAP due to Gram-positive pathogens, particularly MRSA, treatment with telavancin achieved higher cure rates in patients with monomicrobial Staphylococcus aureus infection and cure rates comparable to vancomycin in patients with MRSA infection [96].
Q. Is Gram positive cocci the same as MRSA?
MRSA refers to particular strains of gram-positive bacteria Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) that are resistant to methicillin. S. aureus is common and frequently present in or on human skin.
Q. What disease does Gram positive bacteria cause?
Some Gram-positive bacteria cause disease….Gram-positive cocci cause certain infections, including the following:
- Pneumococcal infections.
- Staphylococcal aureus infections.
- Streptococcal infections.
- Toxic shock syndrome.
Q. What color is Gram positive bacteria?
Hans Christian Gram developed the staining method in 1884. The staining method uses crystal violet dye, which is retained by the thick peptidoglycan cell wall found in gram-positive organisms. This reaction gives gram-positive organisms a blue color when viewed under a microscope.
Q. Is Gram positive bacteria good?
Gram-positive bacteria, those species with peptidoglycan outer layers, are easier to kill – their thick peptidoglycan layer absorbs antibiotics and cleaning products easily.