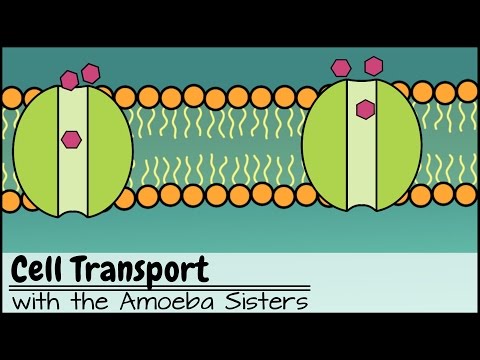
Q. What is the process that moves materials through a membrane against a concentration difference?
The main way that active transport differs from diffusion is that in active transport the material has to go against the concentration, unlike diffusion.
Q. What process moves materials through a cell membrane against the concentration gradient?
Secondary Active Transport: An electrochemical gradient, created by primary active transport, can move other substances against their concentration gradients, a process called co-transport or secondary active transport.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is the process that moves materials through a membrane against a concentration difference?
- Q. What process moves materials through a cell membrane against the concentration gradient?
- Q. What is the process that moves material?
- Q. What is the movement of materials from a low concentration to high concentration called?
- Q. Is the movement of molecules from a low concentration to a high concentration?
- Q. Which way will the water tend to move in terms of sugar concentration )?
- Q. What moves molecules in and out of cells?
- Q. Do gases move in and out of cells?
- Q. What are 2 differences between active and passive transport?
Q. What is the process that moves material?
Materials move within the cell’s cytosol by diffusion, and certain materials move through the plasma membrane by diffusion (Figure 1).
Q. What is the movement of materials from a low concentration to high concentration called?
Diffusion
Q. Is the movement of molecules from a low concentration to a high concentration?
Active transport This occurs when molecules are moved across the cell membrane from an area where they are at a low concentration to an area where they are at a high concentration by specific transport proteins. This movement is against the concentration gradient so the transport proteins require an energy supply.
Q. Which way will the water tend to move in terms of sugar concentration )?
Water will tend to move across the membrane to the left until equilibrium is reached. At that point, the concentrations of water and sugar will be the same on both sides of the membrane.
Q. What moves molecules in and out of cells?
Water, carbon dioxide, and oxygen are among the few simple molecules that can cross the cell membrane by diffusion (or a type of diffusion known as osmosis ). Diffusion is one principle method of movement of substances within cells, as well as method for essential small molecules to cross the cell membrane.
Q. Do gases move in and out of cells?
Dissolved or gaseous substances have to pass through the cell membrane to get into or out of a cell. This is true in gases and for particles dissolved in solutions – but diffusion does not occur in solids.
Q. What are 2 differences between active and passive transport?
Active transport requires energy for the movement of molecules whereas passive transport does not require energy for the movement of molecules. In active transport, the molecules move against the concentration gradient whereas in passive transport, the molecules move along the concentration gradient.