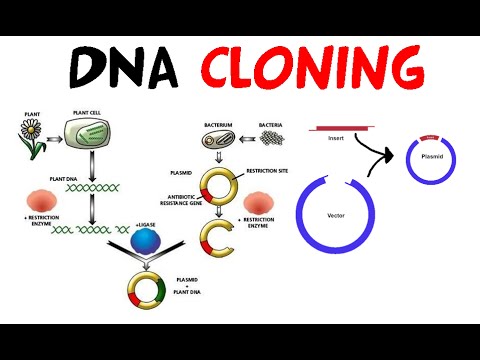
Q. What is the purpose of cloning a gene?
The first motive for cloning genes may be to gain information about the nucleotide sequence of the gene. DNA sequencing or restriction enzyme cutting analysis can be used to study a gene or compare versions of a gene from different sources. A second motive would be to manipulate a gene.
Q. What is gene cloning and why do we need to clone a gene?
Gene cloning, also known as molecular cloning, refers to the process of isolating a DNA sequence of interest for the purpose of making multiple copies of it. The recombinant DNA can then be inserted into another cell, such as a bacterial cell, for amplification and possibly production of the resulting protein.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is the purpose of cloning a gene?
- Q. What is gene cloning and why do we need to clone a gene?
- Q. What is gene cloning and expression?
- Q. Why cloning is not allowed in humans?
- Q. What are the implications of cloning humans?
- Q. Is cloning moral or immoral?
- Q. Is cloning ethical is it safe to use clones in the food supply?
- Q. What are some of the ethical problems with cloning?
- Q. Does cloning cause faster aging?
- Q. Why cloning animals has such a high failure rate?
- Q. Why is reproductive cloning wrong?
Q. What is gene cloning and expression?
Genetic cloning, or the replication of DNA fragments, and their protein expression utilize a variety of molecular cloning techniques. The products of cloning and expression are commonly used in biotechnology research for the production of antibodies, small molecule identification, and functional studies.
Q. Why cloning is not allowed in humans?
Human beings should not be cloned for several reasons that are going to be further discussed in this op-ed: cloning is a risky, imperfect procedure, it does not create an exact copy of an individual, and it poses ethical concerns by using human beings as a means to an end, opening up possibilities for abuse and …
Q. What are the implications of cloning humans?
The cloning in human may produce certain psychological problems like psychological distress that affects the uniqueness and individuality of an organism. Moreover, it may cause certain issues in earlier or later twin’s growth.
Q. Is cloning moral or immoral?
In the United States today, no federal law prohibits human cloning, either for purposes of reproduction or for purposes of biomedical research. This is not because most people favor reproductive cloning.To the contrary, public opinion and almost all elected officials oppose it.
Q. Is cloning ethical is it safe to use clones in the food supply?
We have not identified any food safety concerns, and we have found no material difference in food from clones as compared to food from conventionally bred animals. Therefore, there is no science-based reason to use labels to distinguish between milk derived from clones and that from conventional animals.
Q. What are some of the ethical problems with cloning?
Cloning raises many ethical controversies. One of the greatest concerns the production and destruction of a two-to-four-day-old embryo to make a line of embryonic stem cells. Another concern is assuring that women donating eggs for research give proper informed consent.
Q. Does cloning cause faster aging?
The study confirms that if cloned animals survive through the fetal development and the first few years of life, they won’t age any faster than other animals.
Q. Why cloning animals has such a high failure rate?
RNA-sequencing highlights problems with gene expression in clones. In a study published Dec. Using RNA sequencing, the researchers found multiple genes whose abnormal expression could lead to the high rate of death for cloned embryos, including failure to implant in the uterus and failure to develop a normal placenta.
Q. Why is reproductive cloning wrong?
Reproductive cloning is inherently unsafe. At least 95% of mammalian cloning experiments have resulted in failures in the form of miscarriages, stillbirths, and life-threatening anomalies; some experts believe no clones are fully healthy.