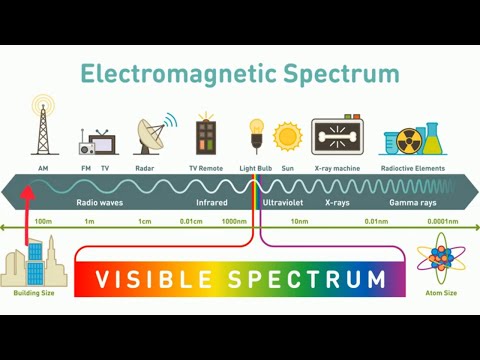
The electromagnetic spectrum is the term used by scientists to describe the entire range of light that exists. From radio waves to gamma rays, most of the light in the universe is, in fact, invisible to us! Light is a wave of alternating electric and magnetic fields.
Q. What is the electromagnetic spectrum simple definition?
Electromagnetic spectrum, the entire distribution of electromagnetic radiation according to frequency or wavelength. The electromagnetic spectrum comprises the span of all electromagnetic radiation and consists of many subranges, commonly referred to as portions, such as visible light or ultraviolet radiation.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is the electromagnetic spectrum simple definition?
- Q. What is the electromagnetic spectrum and why is it important?
- Q. What is the most important electromagnetic spectrum?
- Q. Why are electromagnetic waves important to humans?
- Q. How many types of rays are there?
- Q. What type of radiation does a Geiger counter measure?
- Q. What is a dangerous level of radiation on a Geiger counter?
- Q. How do film badges detect radiation?
- Q. Who should wear dosimeter badges?
- Q. Are dosimeter badges required?
- Q. Where do you wear your TLD badge?
Q. What is the electromagnetic spectrum and why is it important?
These observations enable astronomers to determine certain physical characteristics of objects, such as their temperature, composition and velocity. The electromagnetic spectrum consists of much more than visible light. It includes wavelengths of energy that human eyes can’t perceive.
Q. What is the most important electromagnetic spectrum?
visible light
Q. Why are electromagnetic waves important to humans?
They are also responsible for transmitting energy in the form of microwaves, infrared radiation (IR), visible light (VIS), ultraviolet light (UV), X-rays, and gamma rays. Each region of this spectrum plays an important part in our lives, and in the business involving communication technology.
Q. How many types of rays are there?
630 different species
Q. What type of radiation does a Geiger counter measure?
A Geiger counter (Geiger-Muller tube) is a device used for the detection and measurement of all types of radiation: alpha, beta and gamma radiation. Basically it consists of a pair of electrodes surrounded by a gas. The electrodes have a high voltage across them. The gas used is usually Helium or Argon.
Q. What is a dangerous level of radiation on a Geiger counter?
Radiation exposure
| Event | Radiation reading, millisievert (mSv) |
|---|---|
| Single dosage which would cause radiation sickness, including nausea, lower white blood cell count. Not fatal | 1,000.00 |
| Accumulated dosage estimated to cause a fatal cancer many years later in 5% of people | 1,000.00 |
Q. How do film badges detect radiation?
There is a lightproof packet of photographic film inside the badge. The more radiation this absorbs, the darker it becomes when it is developed. To get an accurate measure of the dose received, the badge contains different materials that the radiation must penetrate to reach the film.
Q. Who should wear dosimeter badges?
Who needs a dosimeter? Radiation workers who operate x-ray machines, flouroscopy units, certain unsealed and sealed radioisotopes or are exposed to other sources of gamma or high energy beta radiation are generally required to wear one or more dosimeters.
Q. Are dosimeter badges required?
Failure to Use Dosimeter as Required When badges are required, it is both the individual and the supervisor’s responsibility to ensure that they are worn.
Q. Where do you wear your TLD badge?
Thermoluminescent dosimetry (TLD)
- Wear the badge at chest or waist level, and if a lead apron is used in an X-ray area, under the apron.
- Wear only the badge assigned to you.
- Replace the badge in the rack at the end of each day – this should be in a low radiation background area.