Entropy increases as temperature increases. An increase in temperature means that the particles of the substance have greater kinetic energy. The faster moving particles have more disorder than particles that are moving more slowly at a lower temperature.
Q. What is the relationship between entropy and heat transfer?
The second law states that there exists a useful state variable called entropy. The change in entropy (delta S) is equal to the heat transfer (delta Q) divided by the temperature (T). For a given physical process, the entropy of the system and the environment will remain a constant if the process can be reversed.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is the relationship between entropy and heat transfer?
- Q. What is the relationship between entropy and the second law of thermodynamics?
- Q. What is the equation for the change in entropy?
- Q. Can change in entropy be negative?
- Q. Does entropy change in a reversible process?
- Q. How does entropy change with pressure?
- Q. Does entropy increase with compression?
- Q. Why Does entropy increase with volume?
- Q. Does entropy depend on temperature?
- Q. Does dissolving increase entropy?
- Q. Does dissolving salt release energy?
- Q. What will happens to entropy when water freezes?
- Q. How do you know if entropy increases or decreases?
- Q. Why does entropy decrease?
- Q. Does entropy increase with disorder?
- Q. Why is entropy irreversible?
- Q. Does entropy decrease when ice melts?
- Q. What happens to entropy when ice melts?
Q. What is the relationship between entropy and the second law of thermodynamics?
Explanation: Second law of thermodynamics tells about the degradation of energy caused due to entropy generation during heat transfer between system & surrounding through a finite temperature difference. The entropy is a property of thermodynamic system which is measure of randomness in a system.
Q. What is the equation for the change in entropy?
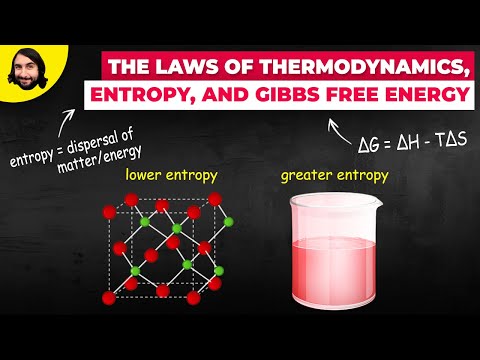
Entropy changes (ΔS) are estimated through relation ΔG=ΔH−TΔS for finite variations at constant T.
Q. Can change in entropy be negative?
A negative change in entropy indicates that the disorder of an isolated system has decreased. For example, the reaction by which liquid water freezes into ice represents an isolated decrease in entropy because liquid particles are more disordered than solid particles.
Q. Does entropy change in a reversible process?
Entropy is the loss of energy available to do work. Another form of the second law of thermodynamics states that the total entropy of a system either increases or remains constant; it never decreases. Entropy is zero in a reversible process; it increases in an irreversible process.
Q. How does entropy change with pressure?
energy within a system. The entropy of a substance increases with its molecular weight and complexity and with temperature. The entropy also increases as the pressure or concentration becomes smaller. Entropies of gases are much larger than those of condensed phases.
Q. Does entropy increase with compression?
When compressing an ideal gas volume, the entropy increases since the molecules collide more times per second with each other. Similarly, as the molecules have more room to move, the entropy decreases when expanding an ideal gas.
Q. Why Does entropy increase with volume?
As well, increasing the volume of a substance increases the number of positions where each molecule could be, which increases the number of microstates. Therefore, any change that results in a higher temperature, more molecules, or a larger volume yields an increase in entropy.
Q. Does entropy depend on temperature?
Affecting Entropy If you increase temperature, you increase entropy. (1) More energy put into a system excites the molecules and the amount of random activity. (2) As a gas expands in a system, entropy increases. This one is also easy to visualize.
Q. Does dissolving increase entropy?
Dissolution of a solute normally increases the entropy by spreading the solute molecules (and the thermal energy they contain) through the larger volume of the solvent.
Q. Does dissolving salt release energy?
When salt dissolves in water, sodium and chloride ions are pulled apart to form new weak bonds with water molecules. Pulling them apart takes energy, while forming new bonds with the water molecules releases energy.
Q. What will happens to entropy when water freezes?
When water freezes its entropy decreases. This does not violate the second law of thermodynamics. The second law does not say that entropy can never decrease anywhere. Entropy can decrease somewhere, provided it increases somewhere else by at least as much.
Q. How do you know if entropy increases or decreases?
A decrease in the number of moles on the product side means lower entropy. An increase in the number of moles on the product side means higher entropy. If the reaction involves multiple phases, the production of a gas typically increases the entropy much more than any increase in moles of a liquid or solid.
Q. Why does entropy decrease?
The entropy is decreasing because a gas is becoming a liquid. The entropy is increasing because a gas is being produced and the number of molecules is increasing. The entropy is decreasing because four total reactant molecules are forming two total product molecules. All are gases.
Q. Does entropy increase with disorder?
A measure of disorder; the higher the entropy the greater the disorder. In thermodynamics, a parameter representing the state of disorder of a system at the atomic, ionic, or molecular level; the greater the disorder the higher the entropy.
Q. Why is entropy irreversible?
In science, a process that is not reversible is called irreversible. This concept arises frequently in thermodynamics. An irreversible process increases the entropy of the universe. Because entropy is a state function, the change in entropy of the system is the same, whether the process is reversible or irreversible.
Q. Does entropy decrease when ice melts?
When ice melts, the change is endothermic ( H is positive), and entropy increases ( S is positive) as the water molecules lose ordered arrangement of ice crystals.
Q. What happens to entropy when ice melts?
Entropy is a measure of the disorder or randomness of the system. The greater the randomness in a system, greater is its entropy. The randomness is greater in liquid state as compared to solid state so the entropy increases when ice melts into water.