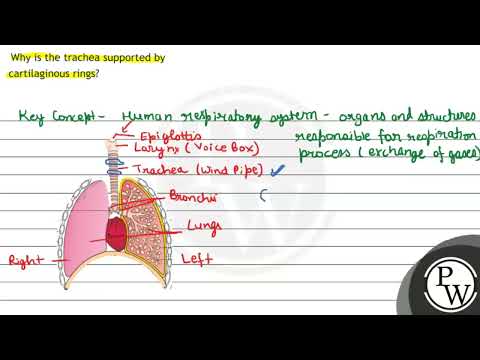
In the trachea, or windpipe, there are tracheal rings, also known as tracheal cartilages. Cartilage is strong but flexible tissue. The tracheal cartilages help support the trachea while still allowing it to move and flex during breathing.
Q. What is another name for the windpipe?
The airway that leads from the larynx (voice box) to the bronchi (large airways that lead to the lungs). Also called trachea.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is another name for the windpipe?
- Q. Why does the trachea have C shaped cartilage?
- Q. What is the role of rings of cartilage present in throat?
- Q. Why is the trachea ribbed?
- Q. What is the main function of trachea?
- Q. Is the trachea part of the lungs?
- Q. Can you live without a trachea?
- Q. Is BiPAP considered high flow?
- Q. Is CPAP a vapotherm?
- Q. Is vapotherm like BiPAP?
- Q. How high can vapotherm go?
Q. Why does the trachea have C shaped cartilage?
The cartilaginous rings are C-shaped to allow the trachea to collapse slightly at the opening so that food can pass down the esophagus. The esophagus lies posteriorly to the trachea. The mucocilliary escalator helps prevent pathogens from entering the lungs.
Q. What is the role of rings of cartilage present in throat?
Rings of cartilage are present in the throat as it helps the throat from collapsing when there is a low amount of air present. It also helps them to expand when food or water passes through it. Thus it plays an important role in supporting the throat during air blockage and helps in smooth air flow.
Q. Why is the trachea ribbed?
C-shaped cartilaginous rings reinforces the anterior and lateral sides of the trachea to protect and maintain the airway open. (The cartilaginous rings are incomplete because this allows the trachea to collapse slightly to allow food to pass down the esophagus.)
Q. What is the main function of trachea?
The trachea serves as passage for air, moistens and warms it while it passes into the lungs, and protects the respiratory surface from an accumulation of foreign particles. The trachea is lined with a moist mucous-membrane layer composed of cells containing small hairlike projections called cilia.
Q. Is the trachea part of the lungs?
The trachea, also known as the windpipe, is a cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all air-breathing animals with lungs….
| Trachea | |
|---|---|
| TA98 | A06.3.01.001 |
| TA2 | 3213 |
| FMA | 7394 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Q. Can you live without a trachea?
The condition is called tracheal agenesis, and it is extremely rare. Fewer than 200 cases have been identified in more than a century. The lifespan of an infant born without a trachea is measured in minutes. Such a baby dies silently, having never drawn a breath.
Q. Is BiPAP considered high flow?
High-flow oxygen therapy as effective as BiPAP in preventing reintubation. 1. In this study, high flow nasal cannula (HFNC) was found to be non-inferior to bilevel positive airway pressure (BiPAP) in reducing reintubation rates after cardiothoracic surgery.
Q. Is CPAP a vapotherm?
Evidence from these clinical trials suggests Vapotherm Hi-VNI Technology is the only mask-free form of non-invasive ventilation for spontaneously breathing patients shown to be as clinically effective as CPAP/Bi-Level and NiPPV as a tool for primary non-invasive management of preterm infants with RDS.
Q. Is vapotherm like BiPAP?
Vapotherm high velocity therapy is Mask-Free NIV® for spontaneously breathing patients and as such a viable alternative to NiPPV (e.g. BiPAP®). Unlike pressure-based respiratory support modalities, it achieves oxygenation and ventilatory support through a high velocity flush of the patient’s end-expiratory gas.
Q. How high can vapotherm go?
While clinicians should titrate flow to clinical effect, Vapotherm high velocity therapy generally achieves clinical efficacy between 25-35 L/min in adults and 6-8 L/min in neonates and for pediatric patients it is recommended to set the flow at 1.5-2 L/min per kilogram of bodyweight, up to 8kg.