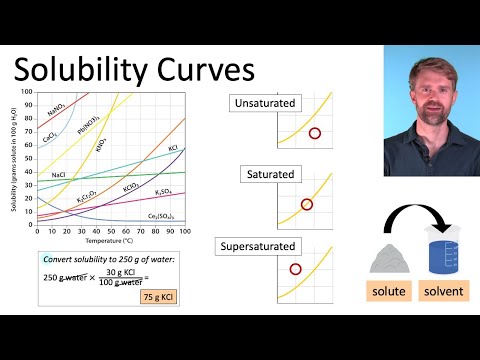
Q. What is the solubility of NaNO3 at 10 degrees?
Based on the literature, at 10∘C 10 ∘ C , 80 g of sodium nitrate can be dissolved in 100 g of water.
Q. What is the solubility of NaCl at room temperature?
0.36 g/ml
Table of Contents
- Q. What is the solubility of NaNO3 at 10 degrees?
- Q. What is the solubility of NaCl at room temperature?
- Q. Why solubility of NaCl is not affected by temperature?
- Q. How does increasing acidity affect solubility?
- Q. What is the effect of branching on solubility?
- Q. How do you interpret a solubility curve?
- Q. What are the application of solubility curve?
- Q. How does temperature affect solubility?
- Q. What is the effect of temperature on solubility class 6?
- Q. Will increasing temperature always increase solubility?
- Q. What is the effect of temperature and pressure on solubility?
- Q. What is the effect of change of temperature on the solubility of a salt?
- Q. What is the effect of change of temperature on the solubility of a salt in water class 9?
- Q. What is the effect of change of temperature?
Q. Why solubility of NaCl is not affected by temperature?
The heat of solution of NaCl is very small as the heat of ionization is nearly equal to the heat of hydration. Therefore, temperature doesn’t affect the dissolution of NaCl as the heat of hydration almost equalizes heat of dissolution.
Q. How does increasing acidity affect solubility?
The Effect of Acid–Base Equilibria the Solubility of Salts. As more acid is added to a suspension of Mg(OH)2, the equilibrium shown in Equation 16.4. 6 is driven to the right, so more Mg(OH)2 dissolves. Sparingly soluble salts derived from weak acids tend to be more soluble in an acidic solution.
Q. What is the effect of branching on solubility?
The linear polysaccharides with highly regular conformation that can form crystalline or partial crystalline structures are mostly insoluble in water, while branching structure could increase the solubility for two reasons: (1) the branching structure could weaken the intramolecular interaction due to the steric …
Q. How do you interpret a solubility curve?
Trace the solubility of a substance with increasing temperature.
- The curved line represents saturation.
- Below the curve, the solution is unsaturated.
- Above the curve the solution is supersaturated. This means there is more solute than the solution can hold.
Q. What are the application of solubility curve?
The solubility process of a given substance at any temperature can be determined. The solubility curve helps us to predict which substance will crystallize out first from a solution containing two or more solutes. The solubility curve helps us to compare the solubilities of different substances at the same temperature.
Q. How does temperature affect solubility?
For many solids dissolved in liquid water, the solubility increases with temperature. The increase in kinetic energy that comes with higher temperatures allows the solvent molecules to more effectively break apart the solute molecules that are held together by intermolecular attractions.
Q. What is the effect of temperature on solubility class 6?
The solubility of a substance in water increases on increasing the temperature. Larger amount of a substance can be dissolved in a given amount of water on heating it. The solubility of a substance decreases on lowering the temperature.
Q. Will increasing temperature always increase solubility?
Increasing the temperature will therefore increase the solubility of the solute. An example of a solute whose solubility increases with greater temperature is ammonium nitrate, which can be used in first-aid cold packs.
Q. What is the effect of temperature and pressure on solubility?
The solubility of a solid may increase or decrease with increasing temperature, whereas the solubility of a gas decreases with an increase in temperature and a decrease in pressure.
Q. What is the effect of change of temperature on the solubility of a salt?
If we heat the solvent, the average kinetic energies of its molecules increases. Hence, the solvent is able to dislodge more particles from the surface of the solute. Thus, increasing the temperature increases the solubilities of substances. For example, sugar and salt are more soluble in water at higher temperatures.
Q. What is the effect of change of temperature on the solubility of a salt in water class 9?
(d) The solubility of most of the salts increases in with increase in temperature. But for same salts like sodium chloride there is no effect of temperature on the solubility. For same salts like Cerium sulphate the solubility decreases with increase in temperature.
Q. What is the effect of change of temperature?
Effect of change of temperature on matter: On increasing the temperature of solids, the kinetic energy of the particles increases. Due to the increase in kinetic energy, the particles start vibrating with greater speed. The energy supplied by heat overcomes the forces of attraction between the particles.