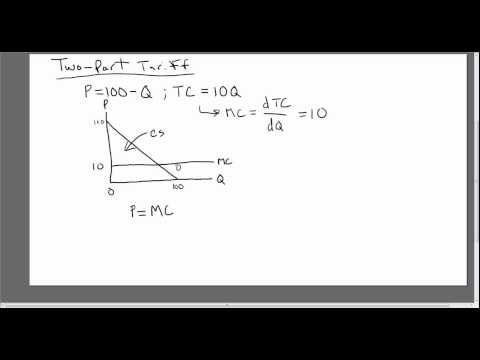
This refers to an unconventional pricing technique where a business first charges an upfront fee from consumers for its product and later charges them additional fees based on their per unit usage.
Q. What is the main disadvantage of two-part tariff?
Q4. What is the main disadvantage of two port tariff? a. He has to pay semi fixed charges.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is the main disadvantage of two-part tariff?
- Q. Is there deadweight loss in a two-part tariff?
- Q. Why is a two part tariff important?
- Q. What is the difference between two part tariff and maximum demand tariff?
- Q. What is perfect price discrimination?
- Q. What is the difference between maximum demand tariff and two part tariff?
- Q. What all are included in the three-part tariff?
- Q. Which tariff is most ideal for the consumer?
- Q. Which tariff is used by small commercial consumers?
- Q. Which tariff is used in industry?
- Q. Which type of tariff is used for domestic consumers?
- Q. Which of following is correct statement about simple tariff?
- Q. What is a specific tariff?
- Q. What is the main objective of tariff?
- Q. What are the main points to be considered while fixing the tariff?
- Q. Which is not desirable characteristic of tariff?
- Q. How do tariffs impact the economy?
- Q. Are trade wars good or bad for the economy?
- Q. What impact has the tire tariff have on the economy overall?
- Q. What is the main disadvantage of tariff?
Q. Is there deadweight loss in a two-part tariff?
Let us now become a little more concrete about the incentives implied by the use of two-part tariffs by a single (monopoly) seller. The result would be a socially efficient allocation (that is, no deadweight loss) with the entire surplus being captured by the seller.
Q. Why is a two part tariff important?
The purpose of a two-part tariff is to extract more of the consumer surplus, by using a pricing scheme made up of two parts: • A fixed, one-time fee charged to each user that entitles the person to make further purchases. It may be also called entry fee, set-up charge, or enrollment fee.
Q. What is the difference between two part tariff and maximum demand tariff?
Maximum Demand Tariff: It is similar to the two-part tariff with the only difference that the maximum demand is actually measured by installing maximum demand meter in the premises of the consumer. It is mostly applied to big consumers. It is not suitable for small consumer as a separate maximum demand meter is …
Q. What is perfect price discrimination?
First-degree discrimination, or perfect price discrimination, occurs when a business charges the maximum possible price for each unit consumed. Because prices vary among units, the firm captures all available consumer surplus for itself, or the economic surplus.
Q. What is the difference between maximum demand tariff and two part tariff?
What is the difference between two part tariff and maximum demand tariff? A separate maximum demand meter is used. c. Semi fixed charges are also included.
Q. What all are included in the three-part tariff?
Definition:When the total charges to be made from the consumer is split into three parts, fixed charge, semifixed charge and running charge, it is known as three-part tariff.
Q. Which tariff is most ideal for the consumer?
Right Answer is: B Three-Part Tariff: When the total charge to be made from the consumer is split into three parts, it is known as a three-part tariff.
Q. Which tariff is used by small commercial consumers?
Maximum demand tariff
Q. Which tariff is used in industry?
Maximum demand tariff The max demand is calculated by a maximum demand meter. This removes any conflict between the supplier and the consumer as it were the two part tariff. It is similar to two-part tariff. Generally applied to large industrial consumers.
Q. Which type of tariff is used for domestic consumers?
Straight-line Meter rate tariff. Block meter Rate tariff. Two-part tariff. Power factor tariff.
Q. Which of following is correct statement about simple tariff?
Which statement about simple tariff is true? Explanation: In simple tariff cost of energy is charged on the basis of unit consumed cost per KWh is given by summing annual fixed cost and annual operating cost and dividing it by total number of units applied to the consumer per annum.
Q. What is a specific tariff?
A “unit” or specific tariff is a tax levied as a fixed charge for each unit of a good that is imported – for instance $300 per ton of imported steel. An “ad valorem” tariff is levied as a proportion of the value of imported goods.
Q. What is the main objective of tariff?
Tariff means the schedule of rates or charges. Tariff, in case of electric supply, means the schedule or rates framed for supply of electrical energy to different classes of consumers. The main objective of the tariff is to distribute equitably the cost of supplying energy among the various classification of use.
Q. What are the main points to be considered while fixing the tariff?
Under these guidelines, tariffs are fixed on a cost plus return model, that is, all the admissible costs and a 16 per cent return is considered while fixing the tariff. The estimates for the next three years are also considered for tariff fixation and tariff revision takes place every three years.
Q. Which is not desirable characteristic of tariff?
The advantage of tariff is that the consumer gets an incentive to consume more electrical energy. This increases the load factor of the system and hence the cost of generation is reduced. However, its principal defect is that it lacks a measure of the consumer’s demand.
Q. How do tariffs impact the economy?
Tariffs Raise Prices and Reduce Economic Growth One possibility is that a tariff may be passed on to producers and consumers in the form of higher prices. Tariffs can raise the cost of parts and materials, which would raise the price of goods using those inputs and reduce private sector output.
Q. Are trade wars good or bad for the economy?
In a global economy, a trade war can become very damaging to the consumers and businesses of both nations, and the contagion can grow to affect many aspects of both economies. A trade war that begins in one sector can grow to affect other sectors.
Q. What impact has the tire tariff have on the economy overall?
From an economic standpoint, the impact of tire tariffs was mixed. The tire tariff initiative saved about 1,200 jobs in the tire manufacturing industry, but at a cost of approximately $1.1 billion to domestic consumers in the form of higher prices.
Q. What is the main disadvantage of tariff?
One of the major disadvantages of tariffs is that they raise the price of imports, leading to a decrease in consumer surplus. Tariffs discourage competition, leading to decreases in product quality. In addition, high tariffs may lead to trade wars between nations.