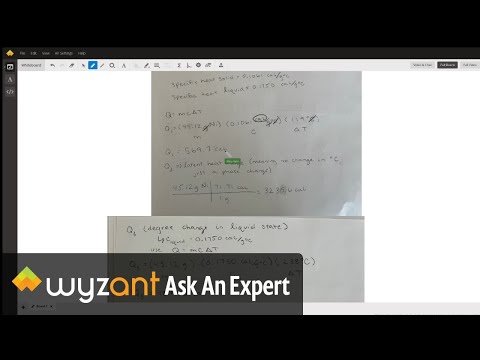
Q. What is the specific heat capacity for nickel?
0.444
Specific Heats (Csp)
| Substance | Formula | Csp (J/goC) |
|---|---|---|
| Magnesium | Mg | 1.017 |
| Mercury | Hg | 0.138 |
| Neon | Ne | 1.03 |
| Nickel | Ni | 0.444 |
Q. What is the heat of lead?
Specific heat of Lead is 0.13 J/g K. Latent Heat of Fusion of Lead is 4.799 kJ/mol. Latent Heat of Vaporization of Lead is 177.7 kJ/mol.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is the specific heat capacity for nickel?
- Q. What is the heat of lead?
- Q. What is the latent heat of fusion for nickel?
- Q. What does nickel oxide react with?
- Q. What is the specific heat capacity of lead?
- Q. What is the specific heat capacity of the metal?
- Q. What is specific heat capacity of lead?
- Q. What is the heat of fusion of lead?
- Q. What is nickel oxide used for?
- Q. Where is nickel oxide used?
- Q. Which is the principal metal oxide of nickel?
- Q. What’s the boiling point of lead in liquid?
- Q. What happens when you heat nickel oxide with carbon monoxide?
Q. What is the latent heat of fusion for nickel?
17.2
Metals and their latent heat of fusion
| Metal | Symbol | Latent Heat of Fusion |
|---|---|---|
| (kJ/mol) | ||
| Nickel | Ni | 17.2 |
| Niobium | Nb | 26.8 |
| Osmium | Os | 31 |
Q. What does nickel oxide react with?
In the first step of the process, nickel oxide is reacted with water gas, a mixture of H2 and CO, at atmospheric pressure and a temperature of 50 °C. Reaction of this impure material with residual carbon monoxide gives the toxic and volatile compound, nickel tetracarbonyl, Ni(CO)4.
Q. What is the specific heat capacity of lead?
Heat Capacities for Some Select Substances
| Substance | specific heat capacity Cp,s (J/g °C) | molar heat capacity Cp,m (J/mol °C) |
|---|---|---|
| graphite | 0.710 | 8.53 |
| helium | 5.1932 | 20.786 |
| iron | 0.450 | 25.09 |
| lead | 0.129 | 26.4 |
Q. What is the specific heat capacity of the metal?
| Specific Heat Capacity of Metals Table Chart | ||
|---|---|---|
| Metal | Btu/(lb-°F) | J/(g-°C) |
| Calsium | 0.150 | 0.62802 |
| Carbon Steel | 0.120 | 0.502416 |
| Cast Iron | 0.110 | 0.460548 |
Q. What is specific heat capacity of lead?
0.128Jg⋅K.
Q. What is the heat of fusion of lead?
Molar ΔH (kJ/mol)
| Substance | heat of fusion ΔHfus (kJ/mol) | heat of vaporization ΔHvap (kJ/mol) |
|---|---|---|
| lead | 4.64 | 180.5 |
| methane | 0.946 | 8.61 |
| mercury | 2.33 | 5.92 |
| methanol | 3.17 | 35.2 |
Q. What is nickel oxide used for?
The applications of Nickel oxide (NiO) today is found in semiconductors, capacitor-inductor devices, tuned circuits, transparent heat mirrors, thermistors and varistors, batteries, micro-supercapacitors, electrochromic and chemical or temperature sensing devices.
Q. Where is nickel oxide used?
Nickel oxide has a range of applications such as: For making electrical ceramics such as thermistors and varistors e.g. ferrites (nickel zinc ferrite) Pigments for ceramic, glasses and glazes.
Specific Heat Capacity of Metals Table Chart Metal Btu/ (lb-°F) J/ (kg-K) J/ (g-°C) Btu/ (lb-°C) Lanthanum 0.047 196.7796 0.1967796 0.0846 Lead 0.030 125.604 0.125604 0.054 Lead Liquid 0.037 154.9116 0.1549116 0.0666 Lithium 0.850 3558.78 3.55878 1.53
Q. Which is the principal metal oxide of nickel?
It is the principal oxide of nickel. It is classified as a basic metal oxide. Several million kilograms are produced annually of varying quality, mainly as an intermediate in the production of nickel alloys. The mineralogical form of NiO, bunsenite, is very rare.
Q. What’s the boiling point of lead in liquid?
Boiling points and specific heat of liquid metals Metal Vapor Pressure (atm) Vapor Pressure (atm) Specific Heat of Liquid Specific Heat of Liquid Iron 2093 1594 0.197 0.82 Lead 1230 889 0.033 0.14 Magnesium 857 638 0.32 1.34 Manganese 1495 1131 0.20 0.84
Q. What happens when you heat nickel oxide with carbon monoxide?
Heating nickel oxide with either hydrogen, carbon, or carbon monoxide reduces it to metallic nickel. It combines with the oxides of sodium and potassium at high temperatures (>700 °C) to form the corresponding nickelate.