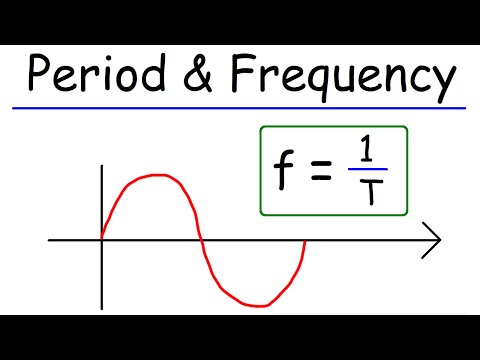
Q. What is the symbol of period of a wave?
symbol T
Q. What symbol is used for period in physics?
Period is usually represented by the symbol T. Figure 1: The period of a periodically varying quantity may be measured between successive equivalent points on a plot of the quantity over time.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is the symbol of period of a wave?
- Q. What symbol is used for period in physics?
- Q. How do you find the period of a wave equation?
- Q. What is the period of a wave measured in?
- Q. How do you calculate water waves?
- Q. How fast do waves travel in water?
- Q. What is the period of water wave?
- Q. What is the speed of water wave?
- Q. What is a speed wave?
- Q. How do waves move in water?
- Q. How fast are sound waves?
- Q. Can sound waves travel in vacuum?
- Q. What can sound not travel through?
- Q. Which material does sound travel fastest?
- Q. Does sound travel faster in water?
- Q. Does sound travel faster than light?
- Q. What materials can sound travel through?
- Q. What materials absorb the most sound?
- Q. Which material did you hear the sound best through?
- Q. What materials vibrate the best?
- Q. Can we minimize vibration?
- Q. Does foam reduce vibration?
- Q. How can vibration be reduced?
- Q. What are the materials used to reduce vibration stress?
- Q. Does sand absorb vibration?
- Q. What are the main causes of vibration?
- Q. How do you classify vibration?
- Q. What is excessive vibration?
- Q. What are the two types of vibration?
Q. How do you find the period of a wave equation?
- To find the amplitude, wavelength, period, and frequency of a sinusoidal wave, write down the wave function in the form y(x,t)=Asin(kx−ωt+ϕ).
- The amplitude can be read straight from the equation and is equal to A.
- The period of the wave can be derived from the angular frequency (T=2πω).
Q. What is the period of a wave measured in?
seconds
Q. How do you calculate water waves?
Question of the Day: Ocean Waves #2
- Facts:
- The formula for travel time is: time (secs) =distance (km)/speed (km/sec)
- A wave is a deep water wave if the depth > wavelength/2.
- A wave is a shallow water wave if depth < wavelength/20. To figure out whether it’s a deep or shallow water wave, you need to find its wavelength. a) The formula for wavelength vs.
Q. How fast do waves travel in water?
While they are in deep water, far offshore, the slowest wave components with the shortest period and the smallest distance between crests could be traveling at less than 5 miles per hour. The components with the longest periods could be moving at more than 35 miles per hour.
Q. What is the period of water wave?
Wave period is the distance between two waves passing through a stationary point, measured in seconds. When it comes reading forecast graphs, swell period is definitely the magic number.
Q. What is the speed of water wave?
In the case of a wave, the speed is the distance traveled by a given point on the wave (such as a crest) in a given interval of time. In equation form, If the crest of an ocean wave moves a distance of 20 meters in 10 seconds, then the speed of the ocean wave is 2.0 m/s.
Q. What is a speed wave?
Summary. Wave speed is the distance a wave travels in a given amount of time, such as the number of meters it travels per second. Wave speed is related to wavelength and wave frequency by the equation: Speed = Wavelength x Frequency.
Q. How do waves move in water?
Waves are created by energy passing through water, causing it to move in a circular motion. The ocean is never still. Waves transmit energy, not water, across the ocean and if not obstructed by anything, they have the potential to travel across an entire ocean basin. Waves are most commonly caused by wind.
Q. How fast are sound waves?
approximately 332 metres per second
Q. Can sound waves travel in vacuum?
Sound waves are travelling vibrations of particles in media such as air, water or metal. So it stands to reason that they cannot travel through empty space, where there are no atoms or molecules to vibrate.
Q. What can sound not travel through?
vacuum
Q. Which material does sound travel fastest?
solids
Q. Does sound travel faster in water?
While sound moves at a much faster speed in the water than in air , the distance that sound waves travel is primarily dependent upon ocean temperature and pressure. This causes the speed of sound to increase and makes the sound waves refract upward.
Q. Does sound travel faster than light?
The speed of sound through air is about 340 meters per second. Light will travel through a vacuum at 300 million meters per second. So they’re totally different scales. No information can propagate faster than the speed of light.
Q. What materials can sound travel through?
Sound is a type of energy made by vibrations. These vibrations create sound waves which move through mediums such as air, water and wood. When an object vibrates, it causes movement in the particles of the medium.
Q. What materials absorb the most sound?
In general, soft, pliable, or porous materials (like cloths) serve as good acoustic insulators – absorbing most sound, whereas dense, hard, impenetrable materials (such as metals) reflect most.
Q. Which material did you hear the sound best through?
Sound travels fastest through solids, slower through liquids and slowest through gases.
Q. What materials vibrate the best?
The best materials for carrying sound waves include some metals such as aluminum, and hard substances like diamond.
Q. Can we minimize vibration?
The following precautions help to reduce whole-body vibration exposure: Mechanically isolate the vibrating source or surface to reduce exposure. Ensure that equipment is well maintained to avoid excessive vibration. Install vibration damping seats.
Q. Does foam reduce vibration?
thick, can substantially reduce structure-borne vibrations before they produce annoying sound or destructive resonance. It also reduces vibration. Vibration dampers and sound-absorbing foam should be selected so they both absorb in the same low-frequency range produced by the machinery.
Q. How can vibration be reduced?
Unlike pure viscous- or elastic-based materials, Sorbothane reduces vibrations over millions of cycles without degrading. Because it’s a visco-elastic material, it absorbs, isolates, and reduces vibrations simultaneously.
Q. What are the materials used to reduce vibration stress?
They are necessary in systems that convey high-temperature substances such as steam or exhaust gases, or to absorb movement and vibration. The most common type of bellows is made of metal (most commonly stainless steel), plastic (such as PTFE), fabric (such as glass fiber), or an elastomer such as rubber.
Q. Does sand absorb vibration?
Sand is commonly used in the construction of suspended floors for example, to dampen low frequency vibration and to isolate one recording environment from another. Sand is one of the best materials available for isolation using the MAM principle.
Q. What are the main causes of vibration?
Vibration can be caused by one or more factors at any given time, the most common being imbalance, misalignment, wear and looseness. Imbalance – A “heavy spot” in a rotating component will cause vibration when the unbalanced weight rotates around the machine’s axis, creating a centrifugal force.
Q. How do you classify vibration?
Classification of vibration
- First classification: Free and Forced Vibrations.
- Free vibrations.
- Forced vibrations – are vibrations of the system that is subjected to an external force, the resulting vibration is known as forced vibration.
- Second Classification: Undamped and Damped Vibration.
Q. What is excessive vibration?
As the vibration exposure continues, the pain may develop into an injury or disease. Vibration can cause changes in tendons, muscles, bones and joints, and can affect the nervous system. Collectively, these effects are known as Hand-Arm Vibration Syndrome (HAVS).
Q. What are the two types of vibration?
There are two types of vibration: whole body vibration and hand-arm vibration – both can cause ill health.