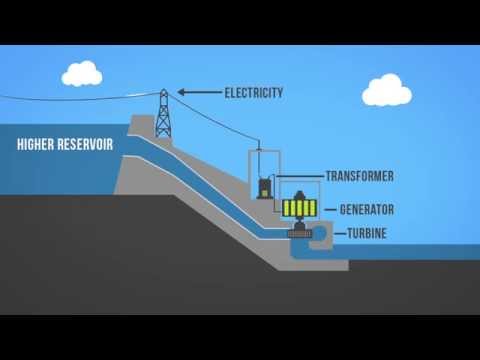
Q. What is the working of hydroelectric power plant?
Water when stored at a height in the dam has a large amount of potential energy which gets converted into the kinetic energy of flowing water when it is allowed to fall on the turbines it gets converted into mechanical energy of the turbine and finally gets converted into the electric energy by the generator.
Q. What is hydroelectric power plant PDF?
It’s a form of energy … a renewable resource. Hydroelectric power plants do not use up resources to create electricity nor do they pollute the air, land, or water, as other power plants may. Hydroelectric power has played an important part in the development of this Nation’s electric power industry.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is the working of hydroelectric power plant?
- Q. What is hydroelectric power plant PDF?
- Q. What is hydro electric power station what are its elements discuss them one by one with neat sketches?
- Q. What are the three main components of hydroelectric power plant?
- Q. What is the function of penstock?
- Q. What are the components of powerhouse?
- Q. What are the major components of a hydroelectric power plant?
- Q. What are the components of hydroelectric power plant explain briefly?
- Q. How many types of hydroelectric power are there?
- Q. How do we use hydroelectric energy?
- Q. How many homes can 1 MW of hydropower?
- Q. What is a FERC permit?
- Q. What is the difference between FERC and NERC?
- Q. Does FERC regulate intrastate pipelines?
- Q. What is a FERC pipeline?
Q. What is hydro electric power station what are its elements discuss them one by one with neat sketches?
Penstock: A penstock is a huge steel pipe which carries water from the reservoir to the turbine. Potential energy of the water is converted into kinetic energy as it flows down through the penstock due to gravity. Water Turbine: Water from the penstock is taken into the water turbine.
Q. What are the three main components of hydroelectric power plant?
A typical hydroelectric plant is a system with three parts: a power plant where the electricity is produced, a dam that can be opened or closed to control water flow, and a reservoir where water is stored. The water behind the dam flows through an intake and pushes against blades in a turbine, causing them to turn.
Q. What is the function of penstock?
A penstock is a sluice or gate or intake structure that controls water flow, or an enclosed pipe that delivers water to hydro turbines and sewerage systems. The term is inherited from the earlier technology of mill ponds and watermills.
Q. What are the components of powerhouse?
ADVERTISEMENTS: Read this article to learn about the following six components of hydro power plant, i.e., (1) Forebay and Intake Structures, (2) Head Race or Intake Conduits, (3) Surge Tank, (4) Turbines and Generators, (5) Power House, and (6) Trail Race and Draft Tube.
Q. What are the major components of a hydroelectric power plant?
What are the major components of a Hydroelectric Power Plant?
- Head race tunnels/channels.
- Surge shaft/surge chambers.
- Pressure shaft/Penstock.
- Underground and surface power house.
- Tailrace channel or tailrace tunnel.
Q. What are the components of hydroelectric power plant explain briefly?
A hydroelectric plant consists of a reservoir for storage of water, a diversion dam, an intake structure for controlling and regulating the flow of water, a conduit system to carry the water from the intake to the waterwheel, the turbines coupled with generators, the draft tube for conveying water from waterwheel to …
Q. How many types of hydroelectric power are there?
Hydropower systems There are four main types of hydropower projects. These technologies can often overlap. For example, storage projects can often involve an element of pumping to supplement the water that flows into the reservoir naturally, and run-of-river projects may provide some storage capability.
Q. How do we use hydroelectric energy?
Hydroelectric power for the Nation Water flowing through the dams spin turbine blades (made from metal instead of leaves) which are connected to generators. Power is produced and is sent to homes and businesses. Hydropower is the most important and widely-used renewable source of energy.
Q. How many homes can 1 MW of hydropower?
With 1 MW enough to power 750-1,000 average American homes according to Electric Power Supply Association, that’s enough generating capacity to produce electricity for roughly 75 to 101 million homes.
Q. What is a FERC permit?
During the term of the permit, a permittee prepares an application for an original hydropower license. What is an “original” hydropower license? A new license, also called a relicense, authorizes the continued operation of an existing (previously licensed) project, and the license term may be 30 to 50 years.
Q. What is the difference between FERC and NERC?
The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission is a federal agency that regulates the interstate transmission of electricity, natural gas and oil. FERC oversees NERC in the United States, as do provincial governments in Canada. What type of legal structure does NERC have? NERC is a 501(c)(6) not-for-profit corporation.
Q. Does FERC regulate intrastate pipelines?
Interstate pipelines are managed by the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) and the U.S. Department of Transportation (DOT). The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission regulates pipelines, storage, natural gas transportation in interstate commerce, and liquefied natural gas facility construction.
Q. What is a FERC pipeline?
The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission, or FERC, is an independent agency that regulates the interstate transmission of electricity, natural gas, and oil. FERC also reviews proposals to build liquefied natural gas (LNG) terminals and interstate natural gas pipelines as well as licensing hydropower projects.