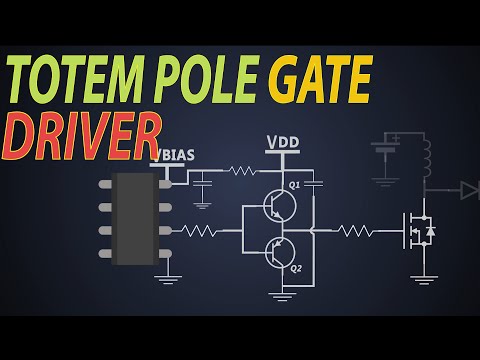
Totem-pole output, also known as a push-pull output, is a type of electronic circuit and usually realized as a complementary pair of transistors. The High and Low level of the output are determined.
Q. What do totem poles represent?
A totem pole or monumental pole is a tall structure created by Northwest Coast Indigenous peoples that showcases a nation’s, family’s or individual’s history and displays their rights to certain territories, songs, dances and other aspects of their culture. Totem poles can also be used as memorials and to tell stories.
Table of Contents
- Q. What do totem poles represent?
- Q. What totem means?
- Q. What is a totem pole driver?
- Q. What do you mean by an active pull up or totem pole output?
- Q. What is a TTL input?
- Q. Why wired and connection is not possible in totem pole configuration?
- Q. Why is the TTL output circuitry called totem pole?
- Q. What is the standard TTL noise margin?
- Q. What TTL should I use?
- Q. What is TTL 64?
- Q. What is the purpose of TTL?
- Q. What is mean by TTL?
- Q. What is TTL 255 in ping?
- Q. What is the default TTL value in Windows?
- Q. What happens when TTL is 0?
- Q. What is the lowest TTL setting?
- Q. What is TTL 63 in Ping?
- Q. What is a good TTL Ping?
- Q. What is TTL Ping?
- Q. What is the meaning of TTL 128?
- Q. What is ping size?
- Q. How do you reduce TTL?
- Q. What is the minimum TTL for DNS?
- Q. How do I find out what my DNS server is?
- Q. How do I know if my DNS is static or dynamic?
- Q. Should I use static DNS?
Q. What totem means?
Totemism, system of belief in which humans are said to have kinship or a mystical relationship with a spirit-being, such as an animal or plant. The entity, or totem, is thought to interact with a given kin group or an individual and to serve as their emblem or symbol.
Q. What is a totem pole driver?
A totem pole driver or output stage is a loose term used to mean that the output is driven actively in both the high and low directions….
Q. What do you mean by an active pull up or totem pole output?
Totem Pole Output Totem Pole means the addition of an active pull up the circuit in the output of the Gate which results in a reduction of propagation delay. Totem Pole Output TTL. Logic operation is the same as the open collector output.
Q. What is a TTL input?
TTL inputs are the emitters of bipolar transistors. In the case of NAND inputs, the inputs are the emitters of multiple-emitter transistors, functionally equivalent to multiple transistors where the bases and collectors are tied together. The output is buffered by a common emitter amplifier. Inputs both logical ones.
Q. Why wired and connection is not possible in totem pole configuration?
Q. Why totem pole outputs cannot be connected together? connection are used, then a large current from supply +V will flows to ground through high state gate transistor and low state gate transistor. Thus, large current will flow which damages the output transistors of totem pole TTL arrangement.
Q. Why is the TTL output circuitry called totem pole?
The output circuitry of this particular gate is commonly referred to as “totem-pole,” because the two output transistors are stacked one above the other like figures on a totem pole. TTL gates equipped with totem-pole output circuitry are able to both source and sink load current.
Q. What is the standard TTL noise margin?
It should be obvious from these figures that CMOS gate circuits have far greater noise margins than TTL: 1.45 volts for CMOS low-level and high-level margins, versus a maximum of 0.7 volts for TTL.
Q. What TTL should I use?
If you set your TTL to a number lower than 30 seconds, results are likely not to be favorable in the long run. For records that rarely change—such as TXT or MX records—it’s best to keep the TTL somewhere between an hour (3600s) and a day (86400s)….
Q. What is TTL 64?
Up vote 0. 64 is the number of hops that the packet can travel before it is dropped. Hard to reach hosts that are across many hops of the Internet benefit from a larger TTL on packets. In multicast protocols 64 is used to restrict the packet to the same physical region. You may be seeing a multicast protocol.
Q. What is the purpose of TTL?
The purpose of the TTL field is to avoid a situation in which an undeliverable datagram keeps circulating on an Internet system, and such a system eventually becoming swamped by such “immortals”.
Q. What is mean by TTL?
Time to live
Q. What is TTL 255 in ping?
1.1) the ttl is 255. since the default original ttl value by ping is 255, as it reaches a router (hop), it decrements the ttl value by 1 and becomes 254. Let’s look at what the RFC has to say: When a router forwards a packet, it MUST reduce the TTL by at least one….
Q. What is the default TTL value in Windows?
Default TTL (Time To Live) Values of Different OS
| Device / OS | Version | TTL |
|---|---|---|
| Windows | Vista | 128 |
| Windows | 7 | 128 |
| Windows | Server 2008 | 128 |
| Windows | 10 | 128 |
Q. What happens when TTL is 0?
If the TTL is 0, the packet is discarded, and never reaches the host. It’s the router that discards it. When an IP packet is sent, its TTL is usually 255 and is then decremented by 1 at each hop. If the TTL reaches 0, the packet is dropped….
Q. What is the lowest TTL setting?
30 seconds
Q. What is TTL 63 in Ping?
TTL is Time To Live. Each hop decrements this field by one, and if it reaches 0 it is dropped (usually this happens only in loop situations). This makes sure that data packets are not congesting a network if there is a IP routing loop present. 63 is the number of hops that the packet can travel before it is dropped.
Q. What is a good TTL Ping?
The TCP/IP specification recommends setting the TTL field for IP packets to 64, but many systems use smaller values (4.3BSD uses 30, 4.2BSD used 15). And to quote RFC 1700: The current recommended default time to live (TTL) for the Internet Protocol (IP) is 64. The maximum TTL is 255, but it is not the default.
Q. What is TTL Ping?
Time To Live
Q. What is the meaning of TTL 128?
So, for each switch/router/computer your traffic passes through en route to the destination, that counts as 1 hop, and the TTL to your destination will decrease by each hop. So, when you PING something on your LAN, the TTL will be 128, since all machines on your same subnet (192.168. 1.0/24) are all just 1 hop away.
Q. What is ping size?
A correctly-formed ping packet is typically 56 bytes in size, or 64 bytes when the ICMP header is considered, and 84 including Internet Protocol version 4 header.
Q. How do you reduce TTL?
Click the domain you want to edit. Under DNS & ZONE FILES, click on Edit DNS Zone File. Scroll down to the Additional Zone Actions tool, click on the Lower TTL button. This will lower the TTL value to 5 minutes.
Q. What is the minimum TTL for DNS?
DNS TTL Minimum Value Never set your DNS TTL to 0. The number 0 is not defined in the standard, and it may cause your DNS information to be ignored or rejected. 3600 (1 hour) is a good minimum value. It is low enough for changes to take effect quickly, but not so low that the DNS servers get overloaded….
Q. How do I find out what my DNS server is?
To view the DNS being used by Windows, run a Command Prompt, and type “ipconfig /all” followed by Enter. “DNS Servers” will be listed in the information displayed. The easiest way to determine what DNS server you’re using is via Windows Command Prompt.
Q. How do I know if my DNS is static or dynamic?
- Static record — is a record that doesn’t have timestamp information (it will instead have the word “static” printed on its timestamp properties). Static record can only be updated or deleted from the DNS server on-command by the administrator or another program.
- Dynamic record — is a record with timestamp information.
Q. Should I use static DNS?
Static DNS settings will never update on their own and will remain the same, until you decide to update them. Static DNS settings are very useful, since they provide a stable service with no interruptions, and can increase the overall speed of your website.