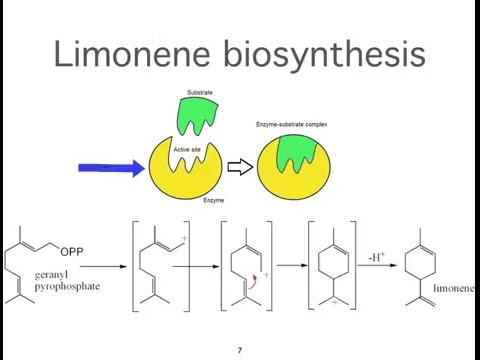
Simple lipids are present in essential oils such as menthol, camphor, limonene, β- pinene, geraniol, etc.
Q. Where are lipids found in food?
Introduction. In foods, lipids are mainly found in the form of triacylglycerols (triacylglycerides) (TAG), which make up to 99% of lipids of plant and animal origin (Fennema, 1996). Phospholipids (PL) are important structural lipids in foods and cell membranes.
Table of Contents
- Q. Where are lipids found in food?
- Q. Where are lipids and oils found in a plant?
- Q. What kind of lipids do plants make and what use do they have?
- Q. What are the two main functions of lipids in plants?
- Q. Is starch found in animal cells?
- Q. What do humans use plant lipids for?
- Q. How do lipids affect the human body?
- Q. What is a lipid and what does it do?
- Q. What is the difference between fats and lipids?
- Q. What is the difference between lipids and cholesterol?
- Q. What are the two major differences between proteins and lipids?
- Q. Is glucose a lipid carbohydrate or protein?
- Q. What are the similarities between lipids and carbohydrates?
- Q. What is the connection between lipids and proteins?
- Q. What do lipids and proteins do?
- Q. Where do the lipids and proteins constituting the cell?
- Q. Which of the following is simple lipid?
Q. Where are lipids and oils found in a plant?
Essential oils are located in the flowers and leaves of plants and citrus fruits. More generally in plants, lipids are most often concentrated in the seeds and fruits.
Q. What kind of lipids do plants make and what use do they have?
Lipids function as the structural components of cell membranes, which serve as permeable barriers to the external environment of cells. In plants, lipids play especially important roles as signaling and energy storage compounds. Plant lipids include triacylglycerols, phospholipids, galactolipids, and sphingolipids.
Q. What are the two main functions of lipids in plants?
Lipids are ubiquitous in plants, serving many important functions, including storage of metabolic energy, protection against dehydration and pathogens, the carrying of electrons, and the absorption of light. Lipids also contribute to the structure of membranes.
Q. Is starch found in animal cells?
Animals do not store starch. Instead, they store carbohydrates in the form of the polysaccharide glycogen. However, only small quantities of glycogen can be stored. It is mostly stored in the cells in the liver and the muscles.
Q. What do humans use plant lipids for?
The plant oil and lipids find various industrial and technology applications in coatings and polymers, printing inks, lubricants, cosmetics/pharmaceuticals, leather processing, surfactants, solvents, hydraulic fluids, pesticide/herbicide adjuvants, glycerin (glycerol), and as fuels.
Q. How do lipids affect the human body?
Within the body, lipids function as an energy reserve, regulate hormones, transmit nerve impulses, cushion vital organs, and transport fat-soluble nutrients. Fat in food serves as an energy source with high caloric density, adds texture and taste, and contributes to satiety.
Q. What is a lipid and what does it do?
A lipid is any of various organic compounds that are insoluble in water. They include fats, waxes, oils, hormones, and certain components of membranes and function as energy-storage molecules and chemical messengers.
Q. What is the difference between fats and lipids?
Fats are divided into unsaturated fats and saturated fats. Trans fats and cis fats come under the category of unsaturated fats. Lipids are hydrophobic in nature….Lipids vs Fats.
| Lipids | Fats |
|---|---|
| These are structural components and energy molecules in the body. | This serves as a source of energy. |
Q. What is the difference between lipids and cholesterol?
Cholesterol is a type of blood fat, and blood fats are known as lipids. Cholesterol and other lipids are carried in the blood attached to proteins, forming tiny spheres, or “parcels” known as lipoproteins. So, lipoproteins are lipids plus proteins.
Q. What are the two major differences between proteins and lipids?
Some are commonly found together in certain foods, such as beef, pork, and any other meat. Also, they are both organic substances, having lots of carbon-hydrogen bonds. The difference is that lipids contain fatty acids and glycerol, while proteins contain amino acids, which have nitrogen.
Q. Is glucose a lipid carbohydrate or protein?
Part A.
| 1. carbohydrate | Starch | Polysaccharide |
|---|---|---|
| 5. protein | enzyme | Cellulose |
| 6. lipid | saturated fat | amino acid |
| 7. protein | polypeptide chain | unsaturated fatty acid |
| 8. carbohydrate | Glucose |
Q. What are the similarities between lipids and carbohydrates?
Similarities: Complex carbohydrates (e.g. polysaccharides) and lipids both contain a lot of chemical energy and can be used for energy storage. Complex carbohydrates and lipids are both insoluble in water – they are not easily transported.
Q. What is the connection between lipids and proteins?
The structures of the solvent lipid molecules are important in determining the conformational state of a membrane protein, and hence its activity, through charge and hydrogen bonding interactions between the lipid headgroups and residues in the protein, and through hydrophobic matching between the protein and the …
Q. What do lipids and proteins do?
The body uses three main nutrients to function— carbohydrate, protein, and fat. Carbohydrates are used for energy (glucose). Fats are used for energy after they are broken into fatty acids. Protein can also be used for energy, but the first job is to help with making hormones, muscle, and other proteins.
Q. Where do the lipids and proteins constituting the cell?
Where do the lipids and proteins constituting the cell membrane get synthesized? Answer: Lipids are synthesized in the Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER), and the proteins are synthesized in the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER).
Q. Which of the following is simple lipid?
The main simple lipids are triglycerides (also known as triacylglycerols), steryl esters, and wax esters. Hydrolysis of these lipids yields glycerol and fatty acids, sterols and fatty acids, and fatty alcohols plus fatty acids, respectively.