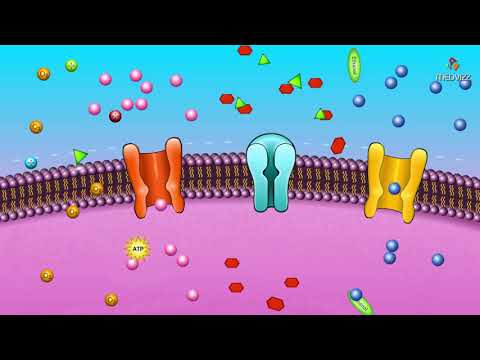
Q. What make a cell membrane selectively permeable?
The membrane is selectively permeable because substances do not cross it indiscriminately. Some molecules, such as hydrocarbons and oxygen can cross the membrane. Many large molecules (such as glucose and other sugars) cannot. Water can pass through between the lipids.
Q. What is permeable rock?
Definition: Some rocks have pores in them, which are empty spaces. If these pores are linked, then fluid, like water, can flow through the rock. If fluid can flow through the rock, then the rock is permeable. Permeable. Porous.
Table of Contents
- Q. What make a cell membrane selectively permeable?
- Q. What is permeable rock?
- Q. What is an example of a permeable rock?
- Q. What is the least permeable rock?
- Q. Is Chalk easily eroded?
- Q. What are the characteristics of chalk?
- Q. How is natural chalk formed?
- Q. Is Chalk hard?
- Q. Can u eat chalk?
- Q. What is the importance of chalk?
- Q. What is a piece of chalk made up of can you break it into smaller particles?
- Q. Which has more force of attraction chalk or rubber band?
- Q. What is a piece of chalk made up of?
- Q. Why can a piece of chalk be broken into small particles?
- Q. What happen if you hammer the chalk?
Q. What is an example of a permeable rock?
Permeable rocks include sandstone and fractured igneous and metamorphic rocks and karst limestone. Impermeable rocks include shales and unfractured igneous and metamorphic rocks.
Q. What is the least permeable rock?
The least permeable rocks are unfractured intrusive igneous and metamorphic rocks, followed by unfractured mudstone, sandstone, and limestone.
Q. Is Chalk easily eroded?
Chalk is a sedimentary rock because it is formed of compressed sediment. It is also permeable because water can pass through it. Because chalk is sedimentary and porous it can be easily eroded and weathered by wind, rain and waves which means the chalk cliffs are often unstable.
Q. What are the characteristics of chalk?
Chalk is a non-clastic carbonate sedimentary rock that is form of limestone compesed of the mineral calcite. It is soft, fine-grained and easily pulverized. Color is white-to-grayish variety of limestone rock. It is composed of the shells of such minute marine organisms as foraminifera, coccoliths, and rhabdoliths.
Q. How is natural chalk formed?
They’re formed from the skeletal remains of minute planktonic green algae that lived floating in the upper levels of the ocean. When the algae died, their remains sank to the bottom of the ocean and combined with the remains of other creatures to form the chalk that shapes the cliffs today.
Q. Is Chalk hard?
Chalk is highly porous, with typical values of porosity ranging from 35 to 47 per cent. While it is similar in appearance to both gypsum and diatomite, chalk is identifiable by its hardness, fossil content, and its reaction to acid (it produces effervescence on contact).
Q. Can u eat chalk?
While chalk is minimally toxic, not poisonous in small amounts, and may not hurt you, it’s never a good idea to eat chalk. A pattern of eating chalk is a different story, however. Eating chalk often can disrupt your digestive system and cause damage to your internal organs.
Q. What is the importance of chalk?
chalk Mineral, mainly calcium carbonate (CaCO 3), formed from the shells of minute marine organisms. It varies in properties and appearance; pure forms, such as calcite, contain up to 99% calcium carbonate. It is used in making putty, plaster and cement, and harder forms are occasionally used for building.
Q. What is a piece of chalk made up of can you break it into smaller particles?
Hammering
Q. Which has more force of attraction chalk or rubber band?
Answer: the force of attraction of iron will be the highest then the rubber band nd at last the chalk..
Q. What is a piece of chalk made up of?
Chalk, soft, fine-grained, easily pulverized, white-to-grayish variety of limestone. Chalk is composed of the shells of such minute marine organisms as foraminifera, coccoliths, and rhabdoliths. The purest varieties contain up to 99 percent calcium carbonate in the form of the mineral calcite.
Q. Why can a piece of chalk be broken into small particles?
Complete answer: Intermolecular force of attraction of chalk particles is weaker in respect to the intermolecular force of iron particles. This is the reason a chalk piece breaks into small particles by hammering but not iron pieces.
Q. What happen if you hammer the chalk?
WHEN WE HAMMER A PIECE OF CHALK, THE CHALK WILL BREAK INTO PIECES BECAUSE THE INTER MOLECULAR SPACE IS LESS IN COMPARISION WITH OTHER SOLIDS.IN THE CASE OF BRICK IT WILL NOT BREAK SO EASILY LIKE CHALK ,BUT THE INTER MOLECULAR SPACE IS MORE THAN CHALK.IN THE CASE OF IRON NAIL , IT WILL NOT BREAK , BUT IT CAN BEND A …