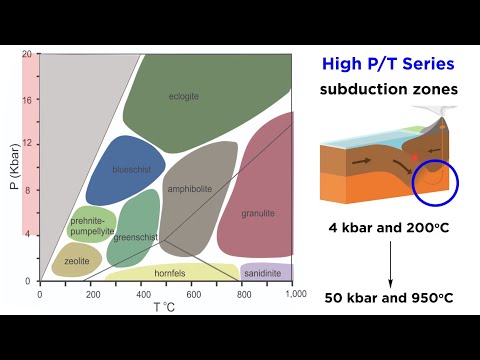
Q. What metamorphic rocks form in subduction zones?
My students and I study the metamorphic products of subduction: rocks called eclogite and blueschist. These rocks begin their lives as basalt the igneous rock that makes up oceanic crust…. think Hawaiian volcanoes) and are then subducted, or pulled under another tectonic plate.
Q. Which of the following factors describes the conditions at a zone where contact metamorphism?
Which of the following best describes the conditions of contact metamorphism? Pressures are fairly low, the rock may be in the upper part of the crust, and heat is supplied from a nearby magma body such as a pluton dike, or sill.
Table of Contents
- Q. What metamorphic rocks form in subduction zones?
- Q. Which of the following factors describes the conditions at a zone where contact metamorphism?
- Q. What kind of metamorphism takes place at depth and in the subduction zone?
- Q. What are the seven types of metamorphism?
- Q. What is the difference between the two metamorphic process?
- Q. What does foliation mean?
- Q. What is lineation and foliation?
- Q. What is the difference between bedding and foliation?
- Q. What is another name for clastic?
- Q. What does clastic mean in science?
- Q. How are clastic sedimentary rocks named?
- Q. What are the properties of clastic sedimentary rocks?
Q. What kind of metamorphism takes place at depth and in the subduction zone?
Blueschist metamorphism occurs at convergent plate boundaries in subduction zones, either under volcanic arcs, or under continents (cordilleran type). Here cold oceanic crust and sediment is rapidly subducted.
Q. What are the seven types of metamorphism?
Metamorphic grade is a general term for describing the relative temperature and pressure conditions under which metamorphic rocks form….Some terms that describe this general bulk chemical composition are as follows:
- Pelitic.
- Quartzo-Feldspathic.
- Calcareous.
- Basic.
- Magnesian.
- Ferriginous.
- Manganiferrous.
Q. What is the difference between the two metamorphic process?
Contact Metamorphism occurs when magma comes in contact with an already existing body of rock. Regional Metamorphism occurs over a much larger area. This metamorphism produces rocks such as gneiss and schist. Regional metamorphism is caused by large geologic processes such as mountain-building.
Q. What does foliation mean?
1a : the process of forming into a leaf. b : the state of being in leaf. c : vernation. 2 : the numbering of the leaves of a manuscript or early printed book.
Q. What is lineation and foliation?
Foliation is the result of the parallel arrangement of (micas, etc.) in a plane perpendicular to the maximum principal applied stress. A lineation is caused by a similar growth of elongate minerals (eg. Slate, schist, and gneiss are three common foliated metamorphic rocks.
Q. What is the difference between bedding and foliation?
As nouns the difference between bedding and foliation is that bedding is the textiles associated with a bed, eg, sheets, pillowcases, bedspreads, blankets, etc while foliation is the process of forming into a leaf or leaves.
Q. What is another name for clastic?
What is another word for clastic rock?
| sedimentary rock | chalk |
|---|---|
| limestone | lithified sediment |
| mechanical sedimentary rock | nonclastic rock |
| sandstone | shale |
| stratified rock |
Q. What does clastic mean in science?
A clast is a fragment of geological detritus, chunks and smaller grains of rock broken off other rocks by physical weathering. Geologists use the term clastic with reference to sedimentary rocks as well as to particles in sediment transport whether in suspension or as bed load, and in sediment deposits.
Q. How are clastic sedimentary rocks named?
Clastic sedimentary rocks are named according to the grain size of the sediment particles.
Q. What are the properties of clastic sedimentary rocks?
Types of Clastic Sedimentary Rocks. Clastic sedimentary rocks are named according to the characteristics of clasts (rock and mineral fragments) that comprise them. These characteristics include grain size, shape, and sorting.