At resonance in series RLC circuit, both inductive and capacitive reactance cancel each other and we know that in series circuit, the current flowing through all the elements is same, So the voltage across inductor and capacitor is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction and thereby they cancel each other.
Q. How the RLC series circuit behaves for the frequencies above and below the resonant frequencies?
How the RLC series circuit behaves for the frequencies above and below the resonant frequencies. For frequencies below resonant frequency, the capacitive reactance is more than the inductive reactance. Therefore the equivalent reactance is equal to capacitive and the circuit behaves like a RC circuit.
Table of Contents
- Q. How the RLC series circuit behaves for the frequencies above and below the resonant frequencies?
- Q. What happens at resonant frequency in an RLC circuit?
- Q. How do you find the resonant frequency of an RLC circuit?
- Q. What is resonant frequency formula?
- Q. How do you calculate the resonant frequency?
- Q. How do you solve for resonance?
- Q. Do humans have a resonant frequency?
- Q. What is the unit of resonant frequency?
- Q. What is the use of resonant frequency?
- Q. How do you increase resonant frequency?
- Q. What is the resonance condition?
- Q. What are some examples of resonance in everyday life?
- Q. What happens at resonance frequency?
- Q. What is the difference between frequency and natural frequency?
- Q. What is the difference between natural frequency and resonant frequency?
- Q. What is natural frequency and resonance?
- Q. What is meant by natural frequency?
- Q. How can you prevent natural frequency?
- Q. What is the unit of natural frequency?
- Q. What is the root of frequency?
Q. What happens at resonant frequency in an RLC circuit?
In complex form, the resonant frequency is the frequency at which the total impedance of a series RLC circuit becomes purely “real”, that is no imaginary impedance’s exist. Then at resonance the impedance of the series circuit is at its minimum value and equal only to the resistance, R of the circuit.
Q. How do you find the resonant frequency of an RLC circuit?
Resonant Frequency In series RLC circuit resonance occurs, when the imaginary term of impedance Z is zero, i.e., the value of XL−XC should be equal to zero. Substitute XL=2πfL and XC=12πfC in the above equation. Where, L is the inductance of an inductor and C is the capacitance of a capacitor.
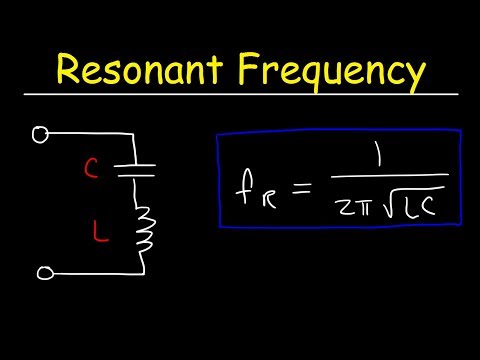
Q. What is resonant frequency formula?
The resonance is obtained when the capacitive impedance and the inductive impedance are equal. Resonant frequency = 1/ 2*pi* squere root (Inductance * Capacitance) The equation is written. We have: fr: resonant frequency.
Q. How do you calculate the resonant frequency?
This resonant frequency is represented by the following equation:
- f = 1 / (2π √L C)
- f = 1 / (2π √L C) Resonant Frequency [Hz]
- L = 1 / (4π2 f2 C) Inductance [H]
- C = 1 / (4π2 f2 L) Capacitance [F]
Q. How do you solve for resonance?
Use the formula v = λf to find the resonance frequency of a single continuous wave. The letter “v” stands for the wave velocity, whereas “λ” represents the distance of the wavelength. This formula states that the wave velocity equals the distance of the wavelength multiplied by the resonance frequency.
Q. Do humans have a resonant frequency?
By testing the response of the human body on a vibrating platform, many researchers found the human whole-body fundamental resonant frequency to be around 5 Hz. However, in recent years, an indirect method has been prosed which appears to increase the resonant frequency to approximately 10 Hz.
Q. What is the unit of resonant frequency?
hertz
Q. What is the use of resonant frequency?
Chapter 6 – Resonance One use for resonance is to establish a condition of stable frequency in circuits designed to produce AC signals. Usually, a parallel (tank) circuit is used for this purpose, with the capacitor and inductor directly connected together, exchanging energy between each other.
Q. How do you increase resonant frequency?
Adding stiffness increases the natural frequency. Adding mass decreases the natural frequency. Increasing damping reduces the peak response but widens the response range. Decreasing damping increases the peak response but narrows the response range.
Q. What is the resonance condition?
Resonance describes the phenomenon of increased amplitude that occurs when the frequency of a periodically applied force (or a Fourier component of it) is equal or close to a natural frequency of the system on which it acts.
Q. What are some examples of resonance in everyday life?
Let’s see the examples of resonance that occur in our everyday life.
- Swing. A playground swing is one of the familiar examples of resonance.
- Guitar. A guitar produces sound entirely by vibration.
- Pendulum.
- Singer Breaking A Wine Glass.
- Bridge.
- Music system playing on the high heavy beat.
- Singing in shower.
- Radio.
Q. What happens at resonance frequency?
Resonant frequency is the oscillation of a system at its natural or unforced resonance. Resonance occurs when a system is able to store and easily transfer energy between different storage modes, such as Kinetic energy or Potential energy as you would find with a simple pendulum.
Q. What is the difference between frequency and natural frequency?
In a natural vibration, you just excite the object once. Then it will vibrate for a while. Natural frequency pertains to a resonant system, refers to any resonant frequency of the system. Fundamental frequency, or simply frequency, is sometimes used to refer to the natural frequency with the highest amplitude.
Q. What is the difference between natural frequency and resonant frequency?
Natural frequency is the frequency pocessed by any body which is natural and is an basic property but Resonant frequency is the frequency at which it matches the frequency of medium travelling in.
Q. What is natural frequency and resonance?
The natural frequency is the frequency at which an object will remain vibrating after hitting it. What happens when you excite that object at the same frequency as its natural frequency? Well, that is resonance.
Q. What is meant by natural frequency?
Natural frequency, also known as eigenfrequency, is the frequency at which a system tends to oscillate in the absence of any driving or damping force. The motion pattern of a system oscillating at its natural frequency is called the normal mode (if all parts of the system move sinusoidally with that same frequency).
Q. How can you prevent natural frequency?
- Stiffening without adding mass raises the natural frequency.
- Adding mass without stiffening lowers the natural frequency.
- Increasing damping lowers the response, but widens the range of the response.
- Decreasing damping raises the response, but in a narrower range.
- Reducing the forcing function reduces the response.
Q. What is the unit of natural frequency?
Q. What is the root of frequency?
First recorded in 1545–55, frequency is from the Latin word frequentia assembly, multitude, crowd.