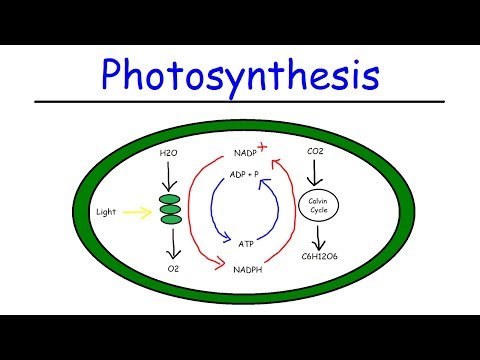
Q. What organelle does the Calvin cycle take place in?
The two parts of photosynthesis—the light-dependent reactions and the Calvin cycle—have been described, as they take place in chloroplasts.
Q. What does the Calvin cycle occur?
The Calvin cycle is a process that plants and algae use to turn carbon dioxide from the air into sugar, the food autotrophs need to grow. Energy to fuel chemical reactions in this sugar-generating process is provided by ATP and NADPH, chemical compounds which contain the energy plants have captured from sunlight.
Table of Contents
- Q. What organelle does the Calvin cycle take place in?
- Q. What does the Calvin cycle occur?
- Q. How much oxygen is produced by the Calvin cycle?
- Q. Is an anaerobic?
- Q. What are the products of anaerobic glycolysis?
- Q. How is glucose converted to lactic acid?
- Q. Why do we convert pyruvate to lactate?
- Q. How do you convert lactate to pyruvate?
- Q. Is citric acid cycle anaerobic?
Q. How much oxygen is produced by the Calvin cycle?
This is the same chemical content found in three molecules of water and three molecules of carbon dioxide, with six extra oxygen atoms. The CO2 and H2O inserted in steps two and three of the Calvin Cycle were transformed into one molecule of glyceraldehyde.
Q. Is an anaerobic?
Types of anaerobic exercises Anaerobic exercise is any activity that breaks down glucose for energy without using oxygen. Generally, these activities are of short length with high intensity. The idea is that a lot of energy is released within a small period of time, and your oxygen demand surpasses the oxygen supply.
Q. What are the products of anaerobic glycolysis?
During high intensity exercise the products of anaerobic glycolysis namely pyruvate and H+ accumulate rapidly. Lactate is formed when one molecule of pyruvate attaches to two H+ ions.
Q. How is glucose converted to lactic acid?
In glycolysis, glucose with six carbons is converted into two molecules of pyruvate, each with three carbons. In fermentation, pyruvate is reduced by NAD+ producing lactic acid.
Q. Why do we convert pyruvate to lactate?
If a cell lacks mitochondria, is poorly oxygenated, or energy demand has rapidly increased to exceed the rate at which oxidative phosphorylation can provide sufficient ATP, pyruvate can be converted to lactate by the enzyme lactate dehydrogenase.
Q. How do you convert lactate to pyruvate?
Lactate is converted to pyruvate by the enzyme lactate dehydrogenase. The standard free energy change of the reaction is -25.1 kJ/mol. Yeast and other anaerobic microorganisms convert glucose to ethanol and CO2 rather than pyruvate.
Q. Is citric acid cycle anaerobic?
Part of this is considered an aerobic pathway (oxygen-requiring) because the NADH and FADH2 produced must transfer their electrons to the next pathway in the system, which will use oxygen. If oxygen is not present, this transfer does not occur. The citric acid cycle does NOT occur in anaerobic respiration.