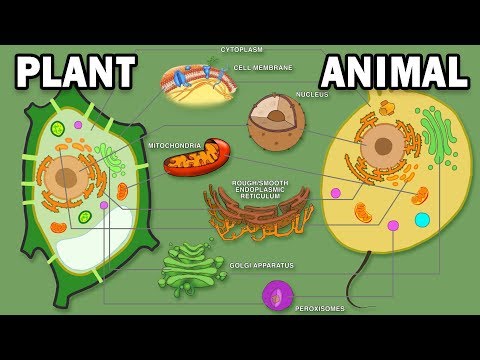
Q. What organelles are in both plant and animal?
Structurally, plant and animal cells are very similar because they are both eukaryotic cells. They both contain membrane-bound organelles such as the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and peroxisomes.
Q. Why do plant cells have organelles?
Plant Cells, Chloroplasts, and Cell Walls. In particular, organelles called chloroplasts allow plants to capture the energy of the Sun in energy-rich molecules; cell walls allow plants to have rigid structures as varied as wood trunks and supple leaves; and vacuoles allow plant cells to change size.
Table of Contents
- Q. What organelles are in both plant and animal?
- Q. Why do plant cells have organelles?
- Q. What are the 7 essential functions of animals?
- Q. What are some functions of animals?
- Q. What are the body parts of an elephant?
- Q. How do you classify animals according to their body parts and their uses?
- Q. What are the general features of animals?
Q. What are the 7 essential functions of animals?
Figure 26-2 Animals carry out seven essential functions: feeding, respiration, circulation, excretion, response, movement, and reproduction.
Q. What are some functions of animals?
There are 7 essential functions of animals:
- Feeding: Herbivore = eats plants.
- Respiration: Take in O2 and give off CO2.
- Circulation: Very small animals rely on diffusion.
- Excretion: Primary waste product is ammonia.
- Response: Receptor cells = sound, light, external stimuli.
- Movement:
- Reproduction:
Q. What are the body parts of an elephant?
Like your own, an elephant’s body has hair, skin, bones, muscles, blood vessels, eyes and ears. It also has a stomach, heart, kidney, bladder, brain and other organs. These and other parts of your body make up your anatomy.
Q. How do you classify animals according to their body parts and their uses?
Animals can be classified according to different physical characteristics, such as body covering (e.g., hair, fur, feathers, scales, shells), body shape (e.g., two main features, three main features), appendages (e.g., arms, legs, wings, fins, tails), and method of movement (e.g., walking, crawling, flying, swimming).
Q. What are the general features of animals?
All animals are eukaryotic, multicellular organisms, and almost all animals have specialized tissues. Most animals are motile, at least during certain life stages. Animals require a source of food to grow and develop. All animals are heterotrophic, ingesting living or dead organic matter.