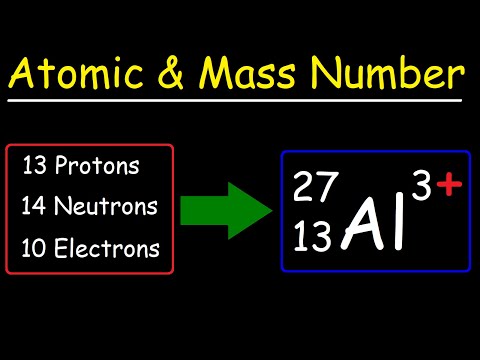
Q. What part of the atom does not account for the atomic mass?
Electrons
Q. What determines the mass of an atom?
Together, the number of protons and the number of neutrons determine an element’s mass number: mass number = protons + neutrons. If you want to calculate how many neutrons an atom has, you can simply subtract the number of protons, or atomic number, from the mass number.
Table of Contents
- Q. What part of the atom does not account for the atomic mass?
- Q. What determines the mass of an atom?
- Q. Why is atomic mass important to percent yield?
- Q. What is a good percent yield?
- Q. How is yield calculated?
- Q. What is the difference between actual yield and theoretical yield?
- Q. Can a reaction have 110 actual yield?
- Q. What if actual yield is greater than theoretical yield?
- Q. Is actual or theoretical yield bigger?
- Q. Why Is percent yield lower than 100?
- Q. What does it mean if the actual yield is too high too low?
- Q. How do you increase percentage yield?
- Q. What does a 50% percent yield mean?
- Q. What Factors Affect percent yield?
- Q. Does rate of reaction affect yield?
- Q. Is it possible to get a 100 percent yield?
- Q. Does a catalyst increase yield?
- Q. What is the name given to a catalyst in the human body?
- Q. What is catalyst examples?
- Q. What do we call a biological catalyst?
- Q. What are the 3 letters that most enzymes end with in their name?
- Q. What catalysts are not enzymes?
- Q. What is another name for enzymes?
- Q. What are 3 things that can stop an enzyme from working?
- Q. What is a good word for enzyme?
Q. Why is atomic mass important to percent yield?
Atomic mass is significant in calculating percentage yield as by using atomic mass of an element is mass of 1 mole of atom. To calculate the theoretical percentage of an element in a compound, we divide the molar mass of element by mass of compound and multiply it by 100.
Q. What is a good percent yield?
According to the 1996 edition of Vogel’s Textbook , yields close to 100% are called quantitative, yields above 90% are called excellent, yields above 80% are very good, yields above 70% are good, yields above 50% are fair, and yields below 40% are called poor.
Q. How is yield calculated?
Generally, yield is calculated by dividing the dividends or interest received on a set period of time by either the amount originally invested or by its current price: For a bond investor, the calculation is similar.
Q. What is the difference between actual yield and theoretical yield?
Theoretical yield is what you calculate the yield will be using the balanced chemical reaction. Actual yield is what you actually get in a chemical reaction.
Q. Can a reaction have 110 actual yield?
This percent yield is just a concept to measure the extent of a chemical reaction because in actual situations, reactions are rarely proceeding to completion. Thus, to put it simply, a chemical reaction can never have 110% actual yield, or anything beyond 100% for that matter.
Q. What if actual yield is greater than theoretical yield?
The percent yield is the ratio of the actual yield to the theoretical yield, expressed as a percentage. However, percent yields greater than 100% are possible if the measured product of the reaction contains impurities that cause its mass to be greater than it actually would be if the product was pure.
Q. Is actual or theoretical yield bigger?
An actual yield is the mass of a product actually obtained from the reaction. It is usually less than the theoretical yield.
Q. Why Is percent yield lower than 100?
Usually, percent yield is lower than 100% because the actual yield is often less than the theoretical value. Reasons for this can include incomplete or competing reactions and loss of sample during recovery.
Q. What does it mean if the actual yield is too high too low?
Percent yields can be higher or lower than 100%. A higher percent yield might signal that your product is being contaminated by water, excess reactant, or another substances. A lower percent yield might signal that you mis-measured a reactant or spilled a portion of your product.
Q. How do you increase percentage yield?
How to Improve Your Yield
- Flame dry or oven dry flask and stirbar.
- Use clean glassware.
- Calculate and weigh reagent amounts accurately.
- Purify reagents and solvents, if necessary.
- Be sure your reactant is pure.
- Rinse (3 times with reaction solvent) flasks and syringes used to transfer reactant and reagents.
Q. What does a 50% percent yield mean?
Percent yield is a calculation that compares how much product we actually produce with how much product that we calculate that we should produce. If we calculate a percent yield of 50%, then it means that we actually produced half of the amount of product that we calculate that we should produce.
Q. What Factors Affect percent yield?
The yield and rate of a chemical reaction depend on conditions such as temperature and pressure. In industry, chemical engineers design processes that maximise the yield and the rate at which the product is produced. They also aim to reduce waste and energy costs at all stages of the process.
Q. Does rate of reaction affect yield?
Catalysts increase the rate of reaction without affecting the yield.
Q. Is it possible to get a 100 percent yield?
Q. Does a catalyst increase yield?
Catalysts only affect the rate of reaction – they do not affect the yield of the reaction. A catalysed reaction produces the same amount of product as an uncatalysed reaction but it produces the product at a faster rate.
Q. What is the name given to a catalyst in the human body?
The most important catalysts in the human body are enzymes. An enzyme is a catalyst composed of protein or ribonucleic acid (RNA), both of which will be discussed later in this chapter. Like all catalysts, enzymes work by lowering the level of energy that needs to be invested in a chemical reaction.
Q. What is catalyst examples?
Catalyst, in chemistry, any substance that increases the rate of a reaction without itself being consumed….Catalyst.
| process | catalyst |
|---|---|
| ammonia synthesis | iron |
| sulfuric acid manufacture | nitrogen(II) oxide, platinum |
| cracking of petroleum | zeolites |
| hydrogenation of unsaturated hydrocarbons | nickel, platinum, or palladium |
Q. What do we call a biological catalyst?
Biological catalysts are called enzymes. There is, for instance, an enzyme in our saliva which converts starch to a simple sugar, which is used by the cell to produce energy, and another enzyme which degrades the excess lactic acid produced when we overexert ourselves.
Q. What are the 3 letters that most enzymes end with in their name?
The name of most enzymes end with “ase”. For example, a phosphatase is an enzyme that removes a phosphate group from a protein. …
Q. What catalysts are not enzymes?
Enzymes and catalysts both affect the rate of a reaction. In fact, all known enzymes are catalysts, but not all catalysts are enzymes. The difference between catalysts and enzymes is that enzymes are largely organic in nature and are bio-catalysts, while non-enzymatic catalysts can be inorganic compounds.
Q. What is another name for enzymes?
Different enzymes that catalyze the same chemical reaction are called isozymes. The International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology have developed a nomenclature for enzymes, the EC numbers (for “Enzyme Commission”).
Q. What are 3 things that can stop an enzyme from working?
Temperature: Raising temperature generally speeds up a reaction, and lowering temperature slows down a reaction. However, extreme high temperatures can cause an enzyme to lose its shape (denature) and stop working. pH: Each enzyme has an optimum pH range. Changing the pH outside of this range will slow enzyme activity.
Q. What is a good word for enzyme?
catalyst
- adjuvant.
- agitator.
- enzyme.
- goad.
- impetus.
- impulse.
- incendiary.
- incentive.