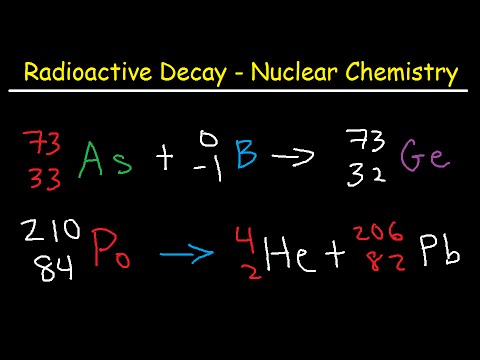
Q. What particles are emitted during beta decay?
In positron emission, also called positive beta decay (β+-decay), a proton in the parent nucleus decays into a neutron that remains in the daughter nucleus, and the nucleus emits a neutrino and a positron, which is a positive particle like an ordinary electron in mass but of opposite charge.
Q. Which process produces beta particles?
A beta particle, also called beta ray or beta radiation (symbol β), is a high-energy, high-speed electron or positron emitted by the radioactive decay of an atomic nucleus during the process of beta decay. There are two forms of beta decay, β− decay and β+ decay, which produce electrons and positrons respectively.
Table of Contents
- Q. What particles are emitted during beta decay?
- Q. Which process produces beta particles?
- Q. When a neutron decomposes by the release of a beta particle what other particle is produced?
- Q. What element will be produced if carbon 14 undergoes beta decay?
- Q. Is carbon-14 alpha emission possible?
- Q. What is the most basic building block of matter?
- Q. What is the fastest moving particle in an atom?
- Q. Which iron has the smallest mass?
- Q. Will iron ever decay?
- Q. Why is iron 56 considered as the most stable nucleus?
- Q. Is there a charge on 1+?
Q. When a neutron decomposes by the release of a beta particle what other particle is produced?
beta particle (beta decay 0/-1 e or B) formed when a neutron decomposes into a proton and an electron. Beta particles are a form of radiation called beta radiation.
Q. What element will be produced if carbon 14 undergoes beta decay?
nitrogen-14
Q. Is carbon-14 alpha emission possible?
Carbon-14 does not undergo alpha decay. It undergoes beta decay to produce nitrogen-14.
Q. What is the most basic building block of matter?
atoms
Q. What is the fastest moving particle in an atom?
Neutrinos are subatomic particles that have almost no mass and can zip through entire planets as if they are not there. Being nearly massless, neutrinos should travel at nearly the speed of light, which is approximately 186,000 miles (299,338 kilometers) a second.
Q. Which iron has the smallest mass?
Of all nuclides, iron-56 has the lowest mass per nucleon.
Q. Will iron ever decay?
Iron-60. Iron-60 is an iron isotope with a half-life of 2.6 million years, but was thought until 2009 to have a half-life of 1.5 million years. It undergoes beta decay to cobalt-60, which then decays with a half-life of about 5 years to stable nickel-60.
Q. Why is iron 56 considered as the most stable nucleus?
According to the binding energy per nucleon vs mass number graph, it is observed that iron-56 has the maximum value of binding energy per nucleon (8.75 MeV). It means that iron-56 is the most efficiently bound nucleus meaning that it has the least average mass per nucleon.
Q. Is there a charge on 1+?
A proton has positive charge of 1, that is, equal but opposite to the charge of an electron. A neutron, like the name implies, is neutral with no net charge. The charge is believed to be from the charge of the quarks that make up the nucleons (protons and neutrons).