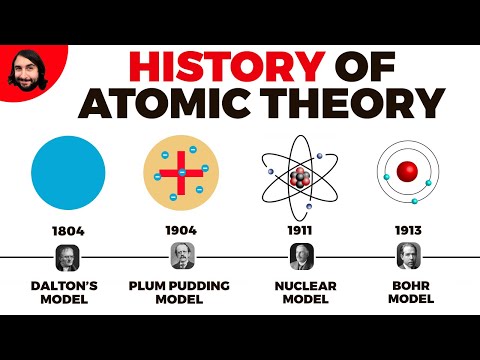
Q. What scientists were involved in the atomic theory?
John Dalton (1766-1844) is the scientist credited for proposing the atomic theory.
Q. Which experiment helped scientists gather information about the protons size charge and location?
Rutherford’s gold foil experiment
Table of Contents
- Q. What scientists were involved in the atomic theory?
- Q. Which experiment helped scientists gather information about the protons size charge and location?
- Q. What did most scientists believe about atoms?
- Q. What led scientists to think that atoms contain neutral particles?
- Q. Who invented electron?
- Q. What particle has no charge?
- Q. What gives a particle charge?
- Q. Which particle has no mass?
- Q. Is a particle with a negative charge?
- Q. What is a particle with one negative charge called?
- Q. What is the basic particle of negative charge?
- Q. What is the particle with a positive charge?
- Q. What is the neutrally charged particle?
- Q. Why is Rutherford’s experiment called the gold foil?
- Q. What is charged particle in matter?
- Q. What is charged particle called?
- Q. What is absolute charge of electron?
- Q. What do you call the positively charged ion?
- Q. What is ion give example?
- Q. How is the charge of an ion determined?
- Q. Is oxygen a cation or anion?
- Q. Is N3 a cation or anion?
- Q. How does oxygen form a anion?
- Q. Is Potassium a cation or anion?
- Q. Why does K+ move out of the cell?
- Q. How do you know if its cation or anion?
- Q. Why do anions form?
- Q. How do you form an anion?
- Q. What anion means?
- Q. Why is an anion negative?
Q. What did most scientists believe about atoms?
Democritus stated that all matter is made up of tiny particles that move around. He believed that these tiny particles were invisible and couldn’t be changed. He called them “atomos,” which means uncuttable in Greek.
Q. What led scientists to think that atoms contain neutral particles?
The only possible explanation is that atoms consist of more than just electrons. Based on the fact that atoms are neutral, and based on J. J. Thomson’s discovery that atoms contain negative subatomic particles called “electrons”, scientists assumed that atoms must also contain a positive substance.
Q. Who invented electron?
Thomson Joseph John Thomson
Q. What particle has no charge?
Neutron
Q. What gives a particle charge?
Electric charge is carried by subatomic particles. In ordinary matter, negative charge is carried by electrons, and positive charge is carried by the protons in the nuclei of atoms. The proton has a charge of +e, and the electron has a charge of −e.
Q. Which particle has no mass?
gauge bosons
Q. Is a particle with a negative charge?
Electrons are a type of subatomic particle with a negative charge. Protons are a type of subatomic particle with a positive charge. Protons are bound together in an atom’s nucleus as a result of the strong nuclear force. The positive charge on a proton is equal in magnitude to the negative charge on an electron.
Q. What is a particle with one negative charge called?
Explanation: Ions with a negative charge are called anions. A single fundamental particle in physics and chemistry with a negative charge is called an electron, though.
Q. What is the basic particle of negative charge?
Electron: A negatively charged particle found circling or orbiting an atomic nucleus. An electron, like a proton is a charged particle, although opposite in sign, but unlike a proton, an electron has negligible atomic mass. Electrons contribute no atomic mass units to the total atomic weight of an atom.
Q. What is the particle with a positive charge?
proton
Q. What is the neutrally charged particle?
All the positive charge of an atom is contained in the nucleus, and originates from the protons. Neutrons are neutrally-charged. Electrons, which are negatively-charged, are located outside of the nucleus.
Q. Why is Rutherford’s experiment called the gold foil?
Rutherford’s experiment is called the gold foil experiment because he used gold foil. 3. How did he know that an atom was mostly empty space? He knew that an atom was made of mostly empty space because most particles passed straight through the foil.
Q. What is charged particle in matter?
In physics, a charged particle is a particle with an electric charge. It may be an ion, such as a molecule or atom with a surplus or deficit of electrons relative to protons. It can also be an electron or a proton, or another elementary particle, which are all believed to have the same charge (except antimatter).
Q. What is charged particle called?
A charged particle, also called an ion, is an atom with a positive or negative charge. The particle that has the greater amount of electrons steals the other particle’s electrons. One becomes positive because it lost an electron, and the other negative because it got another electron.
Q. What is absolute charge of electron?
Electron is a negatively charged particle with an absolute mass of -1.6×10-19 coulombs. This is taken as the unit of negative charge as this is the smallest negative charge carried by a particle. The charge of the electron is equal in magnitude but opposite in sign to the charge of a proton.
Q. What do you call the positively charged ion?
Positively charged ions are called cations; negatively charged ions, anions.
Q. What is ion give example?
When a stable atom gains or loses an electron, it becomes an ion. For example, when chlorine takes an electron from sodium, and sodium gives that electron to chlorine, they become ions and form NaCl.
Q. How is the charge of an ion determined?
Since the electric charge on a proton is equal in magnitude to the charge on an electron, the net electric charge on an ion is equal to the number of protons in the ion minus the number of electrons.
Q. Is oxygen a cation or anion?
Oxygen always has a charge of negative 2, so it is an anion. Oxygen is an uncharged molecule (O2). The usual oxygen ion is oxide, O- -, which is negatively charged, therefore an anion.
Q. Is N3 a cation or anion?
The ion that has the positive charge is called a cation, while the ion which has the negative charge on it is called as an anion….Comparison Chart.
| Basis for Comparison | Cation | Anion |
|---|---|---|
| Examples | Iron (Fe2+), Sodium (Na+), Lead (Pb2+). | Fluoride (F-), Bromide (Br-), Iodide (I-), Nitride (N3-) and Hydride (H-). |
Q. How does oxygen form a anion?
Anions are the negative ions formed from the gain of one or more electrons. Oxygen has an electron arrangement of (2, 6) and needs to gain two electrons to fill the n=2 energy level and achieve an octet of electrons in the outermost shell. The oxide ion will have a charge of 2− as a result of gaining two electrons.
Q. Is Potassium a cation or anion?
It is an alkali metal cation, an elemental potassium, a monovalent inorganic cation and a monoatomic monocation. Potassium is the major cation (positive ion) inside animal cells, while sodium is the major cation outside animal cells….4.3Related Element.
| Element Name | Potassium |
|---|---|
| Atomic Number | 19 |
Q. Why does K+ move out of the cell?
The cell possesses potassium and sodium leakage channels that allow the two cations to diffuse down their concentration gradient. However, the neurons have far more potassium leakage channels than sodium leakage channels. Therefore, potassium diffuses out of the cell at a much faster rate than sodium leaks in.
Q. How do you know if its cation or anion?
Key Points
- The electronic configuration of many ions is that of the closest noble gas to them in the periodic table.
- An anion is an ion that has gained one or more electrons, acquiring a negative charge.
- A cation is an ion that has lost one or more electrons, gaining a positive charge.
Q. Why do anions form?
Anions are the negative ions formed from the gain of one or more electrons. When nonmetal atoms gain electrons, they often do so until their outermost principal energy level achieves an octet. Under typical conditions, three electrons is the maximum that will be gained in the formation of anions.
Q. How do you form an anion?
Summary. Anions are formed by the addition of one or more electrons to the outer shell of an atom. Group 17 elements add one electron to the outer shell, group 16 elements add two electrons, and group 15 elements add three electrons. Anions are named by dropping the ending of the element’s name and adding -ide.
Q. What anion means?
Anions are atoms or radicals (groups of atoms), that have gained electrons. Since they now have more electrons than protons, anions have a negative charge. For example, chloride ions Cl- , bromide Br- , iodide I-. An ion is an atom (or group of atoms) with an electrical charge.
Q. Why is an anion negative?
An anion has more electrons than protons, consequently giving it a net negative charge. For an anion to form, one or more electrons must be gained, typically pulled away from other atoms with a weaker affinity for them.