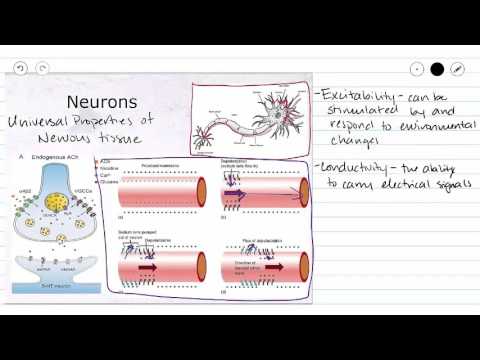
Q. What shows irritability and conductivity?
Schwann cells and satellite cells are only found here. Show irritability and conductivity. Conducts impulses away from cell body; called nerve fiber.
Q. Which type of nerve cell demonstrates irritability and conductivity and thus transmits electrical messages from one area of the body to another area?
Neuroglia
Table of Contents
- Q. What shows irritability and conductivity?
- Q. Which type of nerve cell demonstrates irritability and conductivity and thus transmits electrical messages from one area of the body to another area?
- Q. Why are Neurotubules important in neurons?
- Q. What is mitotic and responsible for most brain neoplasms?
- Q. Which is the principal molecule of nervous tissue?
- Q. Which system is the master controlling and communicating system of the body?
- Q. Which system controls all the functions of your body?
- Q. What is the main role of the peripheral nervous system?
- Q. Why do we need both endocrine and nervous system?
- Q. What is the difference between endocrine system and nervous system?
- Q. What hormones are released by the parasympathetic nervous system?
- Q. What is an example of a parasympathetic response?
- Q. Why am I always fight-or-flight mode?
- Q. Which hormone is responsible for fight or flight response?
- Q. How do you know if your fight or flight?
- Q. What are four common psychosomatic responses?
- Q. What is an example of a psychosomatic response to stress?
- Q. What is a psychosomatic response?
- Q. What are the types of psychosomatic disorder?
- Q. How do you control psychosomatic symptoms?
- Q. What is the difference between hypochondria and psychosomatic?
- Q. Can hypochondriacs create symptoms?
- Q. What is another word for psychosomatic?
- Q. Can anxiety cause weird body sensations?
Q. Why are Neurotubules important in neurons?
Neurotubules are crucial in various cellular processes in neurons. Together with neurofilaments, they help to maintain the shape of a neuron and provide mechanical support.
Q. What is mitotic and responsible for most brain neoplasms?
Neurons are highly mitotic and therefore are responsible for most brain neoplasms (tumors). Microglia 6. Astrocytes engulf invading microorganisms and dead neural tissue.
Q. Which is the principal molecule of nervous tissue?
myelin: A substance produced by cells of the neuroglia that increases the speed of impulses along the axon of the neuronal fiber. nervous tissue: The principal constituent of the central and peripheral nervous system, comprised neurons and neuroglia cells.
Q. Which system is the master controlling and communicating system of the body?
The nervous system
Q. Which system controls all the functions of your body?
The brain is like a computer that controls the body’s functions, and the nervous system is like a network that relays messages to parts of the body.
Q. What is the main role of the peripheral nervous system?
The PNS has three basic functions: (1) conveying motor commands to all voluntary striated muscles in the body; (2) carrying sensory information about the external world and the body to the brain and spinal cord (except visual information: the optic nerves, which convey information from the retina to the brain, are in …
Q. Why do we need both endocrine and nervous system?
Along with the nervous system, the endocrine system coordinates the body’s functions to maintain homeostasis during rest and exercise. The nervous and endocrine systems also work together to initiate and control movement, and all the physiological processes movement involves.
Q. What is the difference between endocrine system and nervous system?
The primary difference between nervous system and endocrine system is in nervous system electrical impulses are used, whereas the endocrine system involves chemical signal called hormones. Secondly, the nervous system is formed by a collection of neuron cells, glands and organs operate the endocrine system.
Q. What hormones are released by the parasympathetic nervous system?
The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) releases the hormones (catecholamines – epinephrine and norepinephrine) to accelerate the heart rate. The parasympathetic nervous system (PNS) releases the hormone acetylcholine to slow the heart rate.
Q. What is an example of a parasympathetic response?
Examples of parasympathetic responses Salivation: As part of its rest-and-digest function, the PSNS stimulates production of saliva, which contains enzymes to help your food digest. Lacrimation: Lacrimation is a fancy word for making tears. Tears keep your eyes lubricated, preserving their delicate tissues.
Q. Why am I always fight-or-flight mode?
When you feel threatened and afraid, the amygdala automatically activates the fight-or-flight response by sending out signals to release stress hormones that prepare your body to fight or run away. This response is triggered by emotions like fear, anxiety, aggression, and anger.
Q. Which hormone is responsible for fight or flight response?
These glands respond by pumping the hormone epinephrine (also known as adrenaline) into the bloodstream.
Q. How do you know if your fight or flight?
What Happens to Your Body During the Fight or Flight Response?
- Your heart rate and blood pressure increases.
- You’re pale or have flushed skin.
- Blunt pain response is compromised.
- Dilated pupils.
- You’re on edge.
- Memories can be affected.
- You’re tense or trembling.
- Your bladder might be affected.
Q. What are four common psychosomatic responses?
Cards
| Term stress | Definition the reaction of the body adn mind to everyday challenges and demands |
|---|---|
| Term what are four common psychosomatic responses | Definition headache, high blood pressure, asthma, weakened immune system |
| Term anxiety | Definition the condition of feeling uneasy or worried about what may happen. |
Q. What is an example of a psychosomatic response to stress?
Psychosomatic disorders resulting from stress may include hypertension, respiratory ailments, gastrointestinal disturbances, migraine and tension headaches, pelvic pain, impotence, frigidity, dermatitis, and ulcers.
Q. What is a psychosomatic response?
A psychosomatic response was a reflex that was triggered by an incorrect belief or stress.
Q. What are the types of psychosomatic disorder?
Psychosomatic illnesses can be classified in three general forms. The first form includes those who experience both a mental illness and a medical one; these illnesses complicate the symptoms and management of each other….Symptoms
- Hypochondriasis.
- Conversion disorder.
- Somatization disorder.
- Body dysmorphic disorder.
Q. How do you control psychosomatic symptoms?
Cognitive Behavior Therapy (CBT) is often the treatment of choice for a psychosomatic disorder. This therapy helps patients learn new ways to cope with and solve their problems as they gain a deeper understanding of their condition or circumstances.
Q. What is the difference between hypochondria and psychosomatic?
Unlike hypochondria, people with psychosomatic illness present with symptoms that are real, but have no medical explanation.
Q. Can hypochondriacs create symptoms?
A little indigestion means heart disease. Often dismissed as neurotic time-wasters, hypochondriacs’ constant fixation and anxiety about their health can be as disabling as a real physical illness. “Hypochondriacs become their symptoms.
Q. What is another word for psychosomatic?
What is another word for psychosomatic?
| psychic | mental |
|---|---|
| psychological | cognitive |
| intellectual | spiritual |
| cerebral | psychogenic |
| emotional | intellective |
Q. Can anxiety cause weird body sensations?
Certain physical symptoms associated with anxiety can cause weird feelings in the head as well. Symptoms that affect the body’s circulatory system, like heart palpitations and temporary spikes in blood pressure, can cause feelings in the head like: dizziness. a choking sensation.