Q. What substances does the cell membrane control?
Cell Membrane Function: Passive Transport Through Channels In this way, the cell can control the flow of just water, salts or the hydrogen ions that make a liquid acidic or not acidic. Aquaporins are protein channels that allow water to pass freely through the cell membrane.
Q. What does the cell membrane directly control?
The cell membrane controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
Table of Contents
- Q. What substances does the cell membrane control?
- Q. What does the cell membrane directly control?
- Q. Can water pass freely through cell membrane?
- Q. What happens when water flows freely through a cell membrane?
- Q. Why does water pass through the cell membrane quickly?
- Q. What is the basic character of cell?
- Q. What are the 4 characteristics of a cell?
- Q. Why does water move in and out of cells?
- Q. What is the main function of the cell membrane?
- Q. Where is the cell membrane located?
- Q. What is an example of cell membrane?
- Q. Why plasma membrane is called unit membrane?
- Q. How does the plasma membrane work?
Q. Can water pass freely through cell membrane?
Water also can move freely across the cell membrane of all cells, either through protein channels or by slipping between the lipid tails of the membrane itself. Osmosis is the diffusion of water through a semipermeable membrane (Figure).
Q. What happens when water flows freely through a cell membrane?
Diffusion of water across a membrane generates a pressure called osmotic pressure. If the pressure in the compartment into which water is flowing is raised to the equivalent of the osmotic pressure, movement of water will stop. In a hypotonic solution, water rushes into cells.
Q. Why does water pass through the cell membrane quickly?
Water, like many molecules, wants to be at equilibrium; it wants to have an equal concentration on either side of the membrane. When the concentration of water on the outside of the cell is greater than the concentration on the inside, water will quickly move into the cell to even up the concentrations.
Q. What is the basic character of cell?
Answer : Basic characteristics of a cell are as follows: (i) Cell is structural and functional unit of all living beings. (ii) Cells can replicate independently.
Q. What are the 4 characteristics of a cell?
All cells share four common components: (1) a plasma membrane, an outer covering that separates the cell’s interior from its surrounding environment; (2) cytoplasm, consisting of a jelly-like region within the cell in which other cellular components are found; (3) DNA, the genetic material of the cell; and (4) …
Q. Why does water move in and out of cells?
Water passes the membrane through osmosis. Aquaporins(channels) of the cell membrane carry out the process. If the concentration outside the cell is more than the inside, water will flow. …
Q. What is the main function of the cell membrane?
The plasma membrane, or the cell membrane, provides protection for a cell. It also provides a fixed environment inside the cell, and that membrane has several different functions. One is to transport nutrients into the cell and also to transport toxic substances out of the cell.
Q. Where is the cell membrane located?
outside
Q. What is an example of cell membrane?
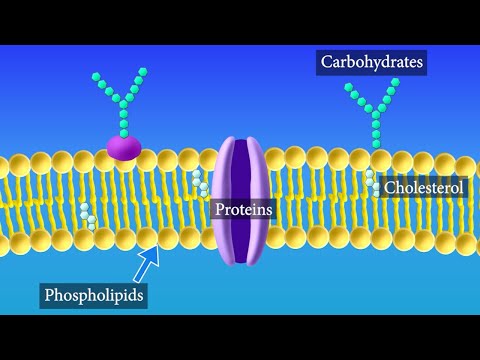
Sterol (e.g. cholesterol) is a type of lipid in the cell membrane that provides structural integrity and fluidity. Examples are transmembrane proteins (i.e. proteins that span the lipid bilayer of the membrane) and integral monotopic proteins (i.e. proteins that are permanently attached to the membrane from one side).
Q. Why plasma membrane is called unit membrane?
According to this concept, the biological membrane is a lipid bilayer surrounded on either side by proteins with a difference in their type for the outer and inner side. The external layer is a hydrophilic layer made of protein molecules of diameter 20A−25A.
Q. How does the plasma membrane work?
The primary function of the plasma membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. Composed of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins, the plasma membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and regulates the movement of substances in and out of cells.