Linnaean system of classification
Q. What methods are used to classify organisms?
3 Ways to classify organisms
Table of Contents
- Q. What methods are used to classify organisms?
- Q. What are two main ways that organisms can be classified?
- Q. What are the two types of cells used to classify organisms?
- Q. How are cells classified?
- Q. Why are living organisms are classified?
- Q. Which type of cell is more simple?
- Q. What are the 3 main types of cells?
- Q. Which type of cell is the oldest?
- Q. What 4 structures are found in all cells?
- Q. What structures do all cells have?
- Q. What are the 13 parts of a cell?
- Q. What structures are found in all living cells?
- Q. What are the 14 parts of a cell?
- Q. What are the 10 structures of a cell?
- Q. What are the five main parts of a cell?
- Q. How many cell types are there?
- Q. What are the 12 parts of a cell?
- Q. What are the two major parts of a cell?
- Q. What are the three main parts of a human cell What are their functions?
- Q. What are the most important parts of a cell?
- Q. What is Cytoplasms?
- Q. What is the main function of mitochondrion?
- Q. What is the main function of ribosome?
- Q. What is cytoplasm function and structure?
- Q. How many types of cytoplasm are there?
- Q. What are the major components of cytoplasm?
- Physiological Structures: Aristotle was one of the first scientists who began grouping organisms.
- Embryology and Ontogeny. Ontogeny is the development and changes that an embryo goes through as it changes from the fertilized egg to the organisms’ mature form.
- Phylogenetic Relationships:
Q. What are two main ways that organisms can be classified?
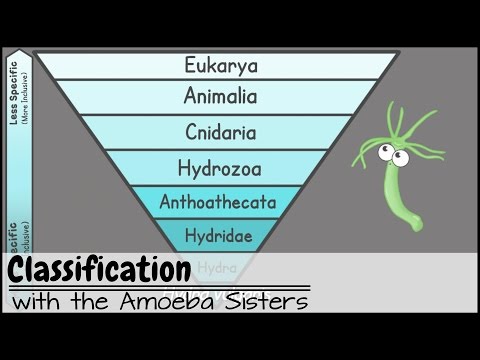
The Linnaean system of classification places organisms into groups based on their shared characteristics . These groups include kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species. These groups are hierarchical. This means that kingdom is the largest group and species is the smallest groups.
Q. What are the two types of cells used to classify organisms?
Several systems that function together form an organism (like a human being). There are many types of cells all grouped into one of two broad categories: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. For example, both animal and plant cells are classified as eukaryotic cells, whereas bacterial cells are classified as prokaryotic.
Q. How are cells classified?
Cell types. Cells are of two types: eukaryotic, which contain a nucleus, and prokaryotic, which do not. Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms, while eukaryotes can be either single-celled or multicellular.
Q. Why are living organisms are classified?
It is necessary to classify organisms because: It helps in the identification of living organisms as well as in understanding the diversity of living organisms. Classification helps us to learn about different kinds of plants and animals, their features, similarities and differences.
Q. Which type of cell is more simple?
Prokaryotic cells
Q. What are the 3 main types of cells?
Cell Types
- Stem cells. Stem cells are cells that are yet to choose what they are going to become.
- Bone cells. There are at least three primary types of bone cell:
- Blood cells. There are three major types of blood cell:
- Muscle cells.
- Sperm cells.
- Female egg cell.
- Fat cells.
- Nerve cells.
Q. Which type of cell is the oldest?
prokaryotes
Q. What 4 structures are found in all cells?
All cells share four common components: (1) a plasma membrane, an outer covering that separates the cell’s interior from its surrounding environment; (2) cytoplasm, consisting of a jelly-like region within the cell in which other cellular components are found; (3) DNA, the genetic material of the cell; and (4) …
Q. What structures do all cells have?
It includes features from all cell types. A cell consists of three parts: the cell membrane, the nucleus, and, between the two, the cytoplasm. Within the cytoplasm lie intricate arrangements of fine fibers and hundreds or even thousands of miniscule but distinct structures called organelles.
Q. What are the 13 parts of a cell?
There are 13 main parts of an animal cell: cell membrane, nucleus, nucleolus, nuclear membrane, cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, ribosomes, mitochondria, centrioles, cytoskeleton, vacuoles, and vesicles.
Q. What structures are found in all living cells?
Although cells are diverse, all cells have certain parts in common. The parts include a plasma membrane, cytoplasm, ribosomes, and DNA. The plasma membrane (also called the cell membrane) is a thin coat of lipids that surrounds a cell.
Q. What are the 14 parts of a cell?
Terms in this set (14)
- Cell Membrane. Semipermeable, controls what goes into & out of the cell.
- Nucleus. Controls cell activities, involved with reproduction & protein synthesis.
- Cytoplasm.
- Nuclear Membrane.
- Nucleoplasm.
- Nucleolus.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
- Ribosomes.
Q. What are the 10 structures of a cell?
Terms in this set (26)
- Nucleolus. A small organelle in the nucleus needed for protein manufacture.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum. A network of membranes used for storage and transport.
- Ribosomes.
- Mitochondria.
- Golgi apparatus.
- Lysozomes.
- Centrioles.
- Cilia.
Q. What are the five main parts of a cell?
List five parts of all cells and their jobs.
- Cell membrane: Surrounds the cell and holds all the parts together and allows materials to enter and exit.
- Nucleus/Chromosomes: Are made of material called DNA.
- Cytoplasm: Is all the material between the Cell membrane and Nucleus.
- Vacuoles: They act like a stomach.
- Mitochondria: They are the cells power producers.
Q. How many cell types are there?
There are about 200 different types of cells in your body. These cells make up your organs and tissues, as well as help to defend your body as a part of your immune system. Your cells are constantly being replaced as they die.
Q. What are the 12 parts of a cell?
1 Answer
- Nucleus.
- Nucleolus.
- Mitochondria.
- Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum.
- Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum.
- Centrosomes.
- Lysosomes.
- Ribosomes.
Q. What are the two major parts of a cell?
The two major parts of a cell are the cell membrane and the cytoplasm. The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, is the outer barrier of…
Q. What are the three main parts of a human cell What are their functions?
In this lesson we will learn the three basic parts of all cells. Cells have something called a cell membrane, a nucleus, and cytoplasm.
Q. What are the most important parts of a cell?
The vital parts of a cell are called “organelles.” Among the most important are the nucleus, vacuoles, and mitochondria, all of which are enclosed within the cell membrane and immersed in cytoplasm. Each organelle performs a specific task that helps keep the cell alive.
Q. What is Cytoplasms?
Cytoplasm is a thick solution that fills each cell and is enclosed by the cell membrane. It is mainly composed of water, salts, and proteins. All of the organelles in eukaryotic cells, such as the nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, and mitochondria, are located in the cytoplasm. …
Q. What is the main function of mitochondrion?
Mitochondria Mitochondria are membrane-bound cell organelles (mitochondrion, singular) that generate most of the chemical energy needed to power the cell’s biochemical reactions. Chemical energy produced by the mitochondria is stored in a small molecule called adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
Q. What is the main function of ribosome?
Ribosomes have two main functions — decoding the message and the formation of peptide bonds. These two activities reside in two large ribonucleoprotein particles (RNPs) of unequal size, the ribosomal subunits. Each subunit is made of one or more ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs) and many ribosomal proteins (r-proteins).
Q. What is cytoplasm function and structure?
The jelly-like fluid of the cytoplasm is composed of salt and water and is present within the membrane of the cells and embeds all of the parts of the cells and organelles. The cytoplasm is home to many activities of the cell as it contains molecules, enzymes that are crucial in the break down of the waste.
Q. How many types of cytoplasm are there?
The cytoplasm can be divided into two primary parts: the endoplasm (endo-,-plasm) and ectoplasm (ecto-,-plasm). The endoplasm is the central area of the cytoplasm that contains the organelles. The ectoplasm is the more gel-like peripheral portion of the cytoplasm of a cell.
Q. What are the major components of cytoplasm?
The main components of the cytoplasm are cytosol (a gel-like substance), the organelles (the cell’s internal sub-structures), and various cytoplasmic inclusions. The cytoplasm is about 80% water and usually colorless.