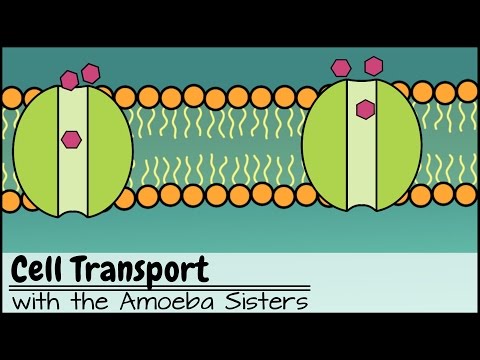
Q. What term defines the movement of materials along a concentration gradient through protein channels?
A facilitated diffusion is a term used for movement of material down their concentration gradients through protein channels, which span the membrane and facilitate the diffusion of the materials in or out the membrane.
Q. How does a cell move materials along a concentration gradient?
To move substances against a concentration or electrochemical gradient, the cell must utilize energy in the form of ATP during active transport. Primary active transport, which is directly dependent on ATP, moves ions across a membrane and creates a difference in charge across that membrane.
Table of Contents
- Q. What term defines the movement of materials along a concentration gradient through protein channels?
- Q. How does a cell move materials along a concentration gradient?
- Q. What does it mean to move with the concentration gradient?
- Q. What is the movement of particles with the concentration gradient using protein helpers?
- Q. What is the major difference between facilitated diffusion and passive diffusion *?
- Q. What is the main aim of osmosis and diffusion facilitated by plasma membrane?
- Q. What is the primary difference between diffusion and osmosis quizlet?
- Q. Which best describes the difference between osmosis and diffusion quizlet?
- Q. What statement is true regarding osmosis and diffusion?
- Q. Which correctly describes osmosis?
- Q. How do you describe diffusion?
- Q. Does diffusion require a concentration gradient?
- Q. What must happen when a concentration gradient is eliminated?
- Q. What three factors affect the concentration gradient?
- Q. Is the movement of water down a concentration gradient quizlet?
Q. What does it mean to move with the concentration gradient?
The formal definition of a concentration gradient is the process of particles, which are sometimes called solutes, moving through a solution or gas from an area with a higher number of particles to an area with a lower number of particles. The areas are typically separated by a membrane.
Q. What is the movement of particles with the concentration gradient using protein helpers?
Facilitated diffusion is a type of passive transport in which substances move across the cell membrane through helper proteins. Because it is a form of passive transport, it requires no energy to occur. In diffusion, substances move from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration.
Q. What is the major difference between facilitated diffusion and passive diffusion *?
Simple diffusion is a passive transport as thus, doesn’t require any energy. Facilitated diffusion is also a passive transport mechanism that doesn’t require any energy, but some facilitated diffusion processes can be active. The speed of simple diffusion is relatively low.
Q. What is the main aim of osmosis and diffusion facilitated by plasma membrane?
Osmosis and Semipermeable Membranes While diffusion transports materials across membranes and within cells, osmosis transports only water across a membrane. The semipermeable membrane limits the diffusion of solutes in the water.
Q. What is the primary difference between diffusion and osmosis quizlet?
The main difference between the two is osmosis is the diffusion of water and has to do with water and diffusion is the process of movement. Diffusion can be air and osmosis is water.
Q. Which best describes the difference between osmosis and diffusion quizlet?
Which best describes the difference between osmosis and diffusion? Diffusion is the movement of particles from a high to low particle concentration, while osmosis is the movement of water from a high to a low water concentration. Particles are moving into and out of the cell, but their concentrations remain stable.
Q. What statement is true regarding osmosis and diffusion?
Osmosis is specific to molecule movement and does not require energy. Osmosis is a type of diffusion and is specific to water. Diffusion is specific to water movement in cells and requires energy.
Q. Which correctly describes osmosis?
– Osmosis is an energy-demanding or “active” process. – In osmosis, solutes move across a membrane from areas of lower water concentration to areas of higher water concentration.
Q. How do you describe diffusion?
Diffusion is the process of movement of molecules under a concentration gradient. The molecules move from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration until the concentration becomes equal throughout. Liquid and gases undergo diffusion as the molecules are able to move randomly.
Q. Does diffusion require a concentration gradient?
A. Simple diffusion does not require energy: facilitated diffusion requires a source of ATP. Simple diffusion can only move material in the direction of a concentration gradient; facilitated diffusion moves materials with and against a concentration gradient.
Q. What must happen when a concentration gradient is eliminated?
Diffusion will continue until the concentration gradient has been eliminated. These molecules diffuse freely in and out of the cell, along their concentration gradient. Though water is a polar molecule, it can also diffuse through the plasma membrane.
Q. What three factors affect the concentration gradient?
Several factors affect the rate of diffusion of a solute including the mass of the solute, the temperature of the environment, the solvent density, and the distance traveled.
Q. Is the movement of water down a concentration gradient quizlet?
Passive movement of water molecules across a selectively permeable membrane down a concentration gradient.