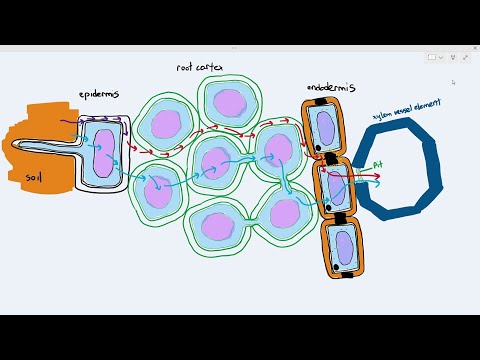
Q. What transports water and minerals up from the roots?
Just as animals, plants also contain vascular tissues (xylem), which transports water and minerals up from the roots to the leaves, and phloem, which transports sugar molecules, amino acids, and hormones both up and down through the plant. Carbohydrates move through the phloem.
Q. How do roots find water and minerals How do roots absorb water and minerals?
Plants absorb water and minerals by the roots. The roots have root hair. The root hair increase the surface area of the root for the absorption of water and mineral nutrients dissolved in water. The root hair is in contact with the water present between the soil particles.
Table of Contents
- Q. What transports water and minerals up from the roots?
- Q. How do roots find water and minerals How do roots absorb water and minerals?
- Q. What do roots take in from soil?
- Q. Why roots are called positively Geotropic?
- Q. Which is positively Geotropic?
- Q. What does positively Phototropic mean?
- Q. What are the four types of tropism?
- Q. What is Geotropism give an example?
- Q. What causes Geotropism?
- Q. What is Geotropism class 10th?
- Q. What are fossils class 10th?
- Q. What is called Geotropism?
- Q. What is negative tropism?
- Q. What are some negative tropism examples?
- Q. What happens during negative tropism?
- Q. What are the three types of tropism?
- Q. What are the 4 plant hormones?
- Q. Do plants respond to gravity?
- Q. How do plants respond to stimuli?
- Q. What are 3 stimuli that plants respond to?
- Q. How do plants respond to external stimuli?
- Q. Why do plants respond slowly to stimuli?
- Q. Do plants react to human stimuli?
- Q. Who proved plants respond to stimuli?
- Q. How do plants respond to stimuli like light and gravity?
- Q. What is plant response to gravity called?
- Q. What are the advantages of Gravitropism to plants?
Q. What do roots take in from soil?
Plants need their roots especially for three reasons: The roots take water and nutrients, a sort of food, from the soil. They also often store this food. And they fix the plants to the ground. However, most plant roots do not work at their best unless they have help from fungi.
Q. Why roots are called positively Geotropic?
The roots show positive geotropism because root always moves towards the ground in the direction of gravity. Roots are negatively phototropic and positively hydrotropic.
Q. Which is positively Geotropic?
Positive geotropism is the movement towards earth. In the case of roots, they grow towards the earth and are thus, called as positively geotropic. Whereas shoots are negatively geotropic.
Q. What does positively Phototropic mean?
Positive phototropism is growth towards a light source; negative phototropism is growth away from light. Shoots, or above-ground parts of plants, generally display positive phototropism—they bend toward the light.
Q. What are the four types of tropism?
Forms of tropism include phototropism (response to light), geotropism (response to gravity), chemotropism (response to particular substances), hydrotropism (response to water), thigmotropism (response to mechanical stimulation), traumatotropism (response to wound lesion), and galvanotropism, or electrotropism (response …
Q. What is Geotropism give an example?
(a) Geotropism is the movement or growth of plant parts in response to the force of gravity. An example of geotropism is the growth of roots towards gravity (downwards).
Q. What causes Geotropism?
Just like phototropism, geotropism is also caused by an unequal distribution of auxin. When a stem placed horizontally, the bottom side contains more auxin and grows more – causing the stem to grow upwards against the force of gravity.
Q. What is Geotropism class 10th?
Geotropism- The growth of the parts of plants in response to the force of gravity. The upward growth of plant shoots is an instance of negative geotropism; the downward growth of roots is positive geotropism.
Q. What are fossils class 10th?
Fossils are preserved remains of living organisms from remote past. Fossil mainly preserves only a portion of the dead organism (eg: skeleton, bone, teeth etc..) Layers of fossils are formed one after another over years.
Q. What is called Geotropism?
Gravitropism (also known as geotropism) is a coordinated process of differential growth by a plant in response to gravity pulling on it. That is, roots grow in the direction of gravitational pull (i.e., downward) and stems grow in the opposite direction (i.e., upwards).
Q. What is negative tropism?
Negative tropism is the movement or growth of an organism away from the stimulus. Therefore, organisms move or grow away in the direction of which the stimulus originates. Plant shoots grow away from the gravity. Hence, shoots show negative geotropism. Beetles show negative phototropism.
Q. What are some negative tropism examples?
What is Negative Tropism. Negative tropism is the growth of an organism away from a particular stimulus. Gravitropism is a common example which can be used to describe negative tropism. Generally, the shoot of the plant grows against gravity, which is a form of negative gravitropism.
Q. What happens during negative tropism?
A tropism is a growth movement whose direction is determined by the direction from which the stimulus strikes the plant. There are two forms: Positive = the plant, or a part of it, grows in the direction from which the stimulus originates. Negative = growth away from the stimulus.
Q. What are the three types of tropism?
Tropisms are growth toward or away from a stimulus. Types of tropisms include gravitropism (gravity), phototropism (light), and thigmotropism (touch).
Q. What are the 4 plant hormones?
Plant hormones include ethylene, gibberellins, cytokinins, absciscic acid, and auxins.
Q. Do plants respond to gravity?
Gravitropism is the ability of plants to perceive and respond to the gravity vector and orient themselves accordingly. Perception of the gravity signal occurs through the movement/sedimentation of starch-filled plastids (termed statoliths) in gravity sensing cells.
Q. How do plants respond to stimuli?
Plants respond to changes in the environment by growing their stems, roots, or leaves toward or away from the stimulus. This response, or behavior, is called a tropism. Examples of plant tropisms include: ○ Phototropism – The way a plant grows or moves in response to light.
Q. What are 3 stimuli that plants respond to?
Plants respond to 3 main stimuli: water. gravity. light.
Q. How do plants respond to external stimuli?
Plants respond to the external factors with the help of receptors and hormones. The receptors help the plants to sense the external stimulus and act accordingly. As a result of these stimuli, various growth hormones are produced which result in the movement or directed growth of the plant.
Q. Why do plants respond slowly to stimuli?
The plants respond to various stimuli very slowly by growing due to lack of nervous system. So, in most of the cases, the response of a plant to a stimulus cannot be observed immediately. It usually takes a considerable time to observe the effect of a stimulus on a plant.
Q. Do plants react to human stimuli?
Scientists already know that plants are highly sensitive to touch of any kind, and even have a word for this phenomenon, “thigmomorphogenesis.” If you’ve ever touched a Mimosa pudica (also known as the “sensitive plant”) you have already witnessed this phenomenon first hand—the Mimosa’s fan-like leaves close up like.
Q. Who proved plants respond to stimuli?
However, like most pioneering scientists, Bose was famed for his more controversial pursuits – his experiments in plant physiology during the 1900s that drew some startling inferences. On his 158th birth anniversary, we bring you the story of J C Bose’s path-breaking work on the discovery of plant stimuli.
Q. How do plants respond to stimuli like light and gravity?
Plants respond directly to Earth’s gravitational attraction, and also to light. Roots grow downward, or towards the center of Earth, and away from light. These responses to external stimuli are called tropisms. Plants’ growth response to gravity is known as gravitropism; the growth response to light is phototropism.
Q. What is plant response to gravity called?
Gravitropism is the ability of plants to perceive and respond to the gravity vector and orient themselves accordingly.
Q. What are the advantages of Gravitropism to plants?
Plants sense and respond to gravity – gravitropism. In roots, this is positive gravitropism and they grow towards gravity deeper into the soil. This helps anchor the plant, as well as allowing the roots to obtain water and mineral ions.