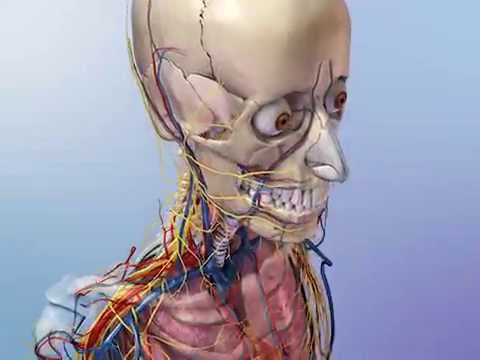
Q. What two bones protect organs?
Protection: It protects our internal organs. The skull protects the brain; the thorax (sternum, ribs and spine) protects the heart, lungs and other viscera (organs within the thorax).
Q. How do Bones support and protect the body?
Bones provide a rigid framework, known as the skeleton, that support and protect the soft organs of the body. The skeleton supports the body against the pull of gravity. The large bones of the lower limbs support the trunk when standing. The skeleton also protects the soft body parts.
Table of Contents
- Q. What two bones protect organs?
- Q. How do Bones support and protect the body?
- Q. Which bones are most important for protecting vital organs?
- Q. Does the Skeleton protect the stomach?
- Q. Which organs are protected by bones?
- Q. Which part of the body does the skull protect?
- Q. What does the skull do in the human body?
- Q. Which is the longest bone in the body?
- Q. What are the names of the skull bones?
- Q. Which part of the skull is strongest?
- Q. Why skull bones are not movable?
- Q. Can cranial bones move?
- Q. Is your skull one bone?
- Q. Where is the hardest part of your skull?
- Q. What is the most important bone in the skull?
- Q. Is the skull attached to the brain?
- Q. What is between the skull and brain?
- Q. How is brain protected in our body?
- Q. What bones protect brain?
- Q. What is the heaviest strongest bone in the body?
- Q. Which bones protect lungs?
- Q. What is the bone under your breast called?
- Q. Are your lungs attached to your ribs?
- Q. What organ is behind the chest?
Q. Which bones are most important for protecting vital organs?
The bones of the chest — namely the rib cage and spine — protect vital organs from injury, and also provide structural support for the body. The rib cage is one of the body’s best defenses against injury from impact. Flexible yet strong, the rib cage protects major vital organs such as the heart, lungs, and liver.
Q. Does the Skeleton protect the stomach?
The main bones in the abdominal region are the ribs. The rib cage protects vital internal organs. There are 12 pairs of ribs and they attach to the spine. There are seven upper ribs, known as “true” ribs, which attach to the sternum (breastbone) in the front of body.
Q. Which organs are protected by bones?
Protects and supports organs: Your skull shields your brain, your ribs protect your heart and lungs, and your backbone protects your spine. Stores minerals: Bones hold your body’s supply of minerals like calcium and vitamin D.
Q. Which part of the body does the skull protect?
the brain
Q. What does the skull do in the human body?
The skull supports the musculature and structures of the face and forms a protective cavity for the brain. The skull is formed of several bones which, with the exception of the mandible, are joined together by sutures—synarthrodial (immovable) joints.
Q. Which is the longest bone in the body?
femur
Q. What are the names of the skull bones?
There are eight cranial bones, each with a unique shape:
- Frontal bone. This is the flat bone that makes up your forehead.
- Parietal bones. This a pair of flat bones located on either side of your head, behind the frontal bone.
- Temporal bones.
- Occipital bone.
- Sphenoid bone.
- Ethmoid bone.
Q. Which part of the skull is strongest?
Some strength tests show the temporal bone in the skull to be the strongest bone. CONCLUSION: The thickest area of the skull is the parasagittal posterior parietal area in male skulls and the posterior parietal area midway between the sagittal and superior temporal line in female skulls.
Q. Why skull bones are not movable?
The skull bones are connected by fibrous joints called sutures. After birth, the bones slowly begin to fuse to become fixed, making the skull bones immovable in order to protect the brain from impact. Syndesmoses of long bones and gomphoses of teeth are also types of fibrous joints.
Q. Can cranial bones move?
Our data indicate that although the cranial bones move apart even with small (nominally 0.2 ml) increases in ICV, total cranial compliance depends more on fluid migration from the cranium when ICV increases are less than approximately 3% of total cranial volume.
Q. Is your skull one bone?
Although the cranium—the largest section of the skull—might appear to be one solid bone, there are actually 22 bones that encase the brain. Twenty-one of those pieces are fused together by sutures, which are nearly rigid, fibrous joints found only in the skull.
Q. Where is the hardest part of your skull?
temporal bones
Q. What is the most important bone in the skull?
occipital bone
Q. Is the skull attached to the brain?
The brain stem connects the brain with the spinal cord. The brain is protected by the bones of the skull and by a covering of three thin membranes called meninges. The brain is also cushioned and protected by cerebrospinal fluid.
Q. What is between the skull and brain?
Between the skull and brain is the meninges, which consist of three layers of tissue that cover and protect the brain and spinal cord.
Q. How is brain protected in our body?
The brain and spinal cord are protected by bony structures — the skull and spinal column. Meninges are membranes that cover and protect the brain and spinal cord.
Q. What bones protect brain?
Cranium. The eight bones that protect the brain are called the cranium. The front bone forms the forehead. Two parietal bones form the upper sides of the skull, while two temporal bones form the lower sides.
Q. What is the heaviest strongest bone in the body?
1. The femur bone is the longest and strongest bone in the body. Located in the thigh, it spans the hip and knee joints and helps maintain upright posture by supporting the skeleton.
Q. Which bones protect lungs?
A bony cage (commonly called the rib cage), which is formed by the sternum, ribs, and spine, protects the lungs and other organs in the chest. The 12 pairs of ribs curve around the chest from the back. Each pair is joined to the bones (vertebrae) of the spine.
Q. What is the bone under your breast called?
Your sternum is a bone that’s located in the middle of your chest. It’s also sometimes referred to as the breastbone. Your sternum protects the organs of your torso from injury and also serves as a connection point for other bones and muscles.
Q. Are your lungs attached to your ribs?
Your lungs are protected by your rib cage, which is made up of 12 sets of ribs. These ribs are connected to your spine in your back and go around your lungs to keep them safe.
Q. What organ is behind the chest?
The thymus is a small organ located just behind the breast bone (sternum) in the front part of the chest.