Q. What type of bond joins amino acids together what does a chain of amino acids form?
peptide bonds
Q. What bonds are in a polypeptide chain?
Polypeptide chains can form tightly coiled helical structures that are stabilized by hydrogen bonding between the NH proton of one amino acid and the C=O. group of the amide bond of the fourth amino acid residue in the main chain.
Table of Contents
- Q. What type of bond joins amino acids together what does a chain of amino acids form?
- Q. What bonds are in a polypeptide chain?
- Q. Where are amino acids joined together to make polypeptides?
- Q. How do amino acids join a peptide bond?
- Q. What type of bonds are formed between adjacent amino acids?
- Q. What is removed to form a peptide bond between two amino acids?
- Q. What are the three major structural components of an amino acid?
- Q. What type of reaction is responsible for linking amino acids together to form polypeptides?
- Q. What are the 5 categories of amino acids?
- Q. Which two substances are formed when two amino acid molecules join together?
- Q. What is the difference between an amino acid and a protein?
- Q. Is it better to take protein or amino acids?
- Q. Can you take too much essential amino acids?
- Q. Can amino acids hurt your kidneys?
- Q. What happens when you take too many amino acids?
- Q. How long do amino acids stay in your system?
- Q. Can too many amino acids make you gain weight?
- Q. Do amino acids burn belly fat?
- Q. Do amino acids promote weight loss?
- Q. What are the benefits of taking amino acids?
- Q. What amino acids are needed for hair growth?
- Q. What’s the best amino acids to take?
- Q. Which protein is best for hair growth?
Q. Where are amino acids joined together to make polypeptides?
Q. How do amino acids join a peptide bond?
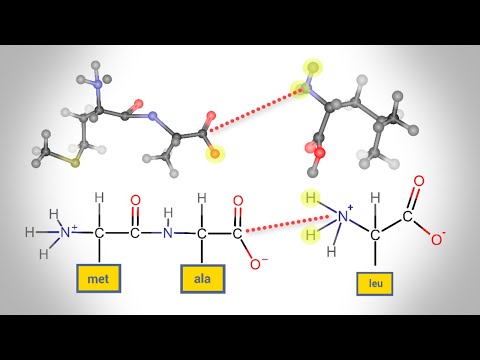
Peptide Bonds Each amino acid is attached to another amino acid by a covalent bond, known as a peptide bond. When two amino acids are covalently attached by a peptide bond, the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of the incoming amino acid combine and release a molecule of water.
Q. What type of bonds are formed between adjacent amino acids?
The bond that holds together the two amino acids is a peptide bond, or a covalent chemical bond between two compounds (in this case, two amino acids). It occurs when the carboxylic group of one molecule reacts with the amino group of the other molecule, linking the two molecules and releasing a water molecule.
Q. What is removed to form a peptide bond between two amino acids?
A peptide bond is a chemical bond formed between two molecules when the carboxyl group of one molecule reacts with the amino group of the other molecule, releasing a molecule of water (H2O).
Q. What are the three major structural components of an amino acid?
Amino acids are the monomers that make up proteins. Each amino acid has the same fundamental structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha (α) carbon, bonded to an amino group (NH2), a carboxyl group (COOH), and to a hydrogen atom.
Q. What type of reaction is responsible for linking amino acids together to form polypeptides?
Amino acids can be linked by a condensation reaction in which an ―OH is lost from the carboxyl group of one amino acid along with a hydrogen from the amino group of a second, forming a molecule of water and leaving the two amino acids linked via an amide—called, in this case, a peptide bond.
Q. What are the 5 categories of amino acids?
There are five main classes of amino acids, those whose R groups are: nonpolar and aliphatic; aromatic (generally nonpolar); polar but uncharged; negatively charged; and positively charged. Within each class there are gradations of polarity, size, and shape of the R groups.
Q. Which two substances are formed when two amino acid molecules join together?
Peptide-Bond Formation. The linking of two amino acids is accompanied by the loss of a molecule of water. A series of amino acids joined by peptide bonds form a polypeptide chain, and each amino acid unit in a polypeptide is called a residue.
Q. What is the difference between an amino acid and a protein?
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. A protein is a chain of amino acids connected together. You can think of this like a beaded necklace. The beads (amino acids) are connected together by a string (bond), which forms a long chain (protein).
Q. Is it better to take protein or amino acids?
Protein powders boost your total protein and contribute calories, so they support muscle building and can fill in gaps in your diet. Amino acids target very specific and diverse areas of your metabolism. One amino acid may affect brain chemicals, while another improves muscle performance.
Q. Can you take too much essential amino acids?
Intakes of large amounts of amino acids can produce toxicities, in which plasma concentrations of the administered amino acid rise to very high levels.
Q. Can amino acids hurt your kidneys?
Taken together, our results show that different amino acid diets given for 9 weeks exert no impact on healthy kidneys, but they suggest that in CKD, high levels of dietary BCAAs exert a deleterious effect on progression, whereas high levels of AAAs surprisingly display a protective effect.
Q. What happens when you take too many amino acids?
When your body has too much of amino acids, the following effects can occur: Gastrointestinal distress, such as bloating. Abdominal pain. Diarrhea.
Q. How long do amino acids stay in your system?
Protein degradation in human skeletal muscles estimated from the release of tyrosine in the presence of insulin and amino acids is approximately 34 nmol·h−1·g wet weight−1. This degradation rate corresponds to a half-life of approximately 20 days.
Q. Can too many amino acids make you gain weight?
Amino acids have four calories per gram. This is the same amount of calories as glucose, an element of table sugar. However, if you take amino acids as supplements, only small amounts of amino acids are consumed. So they are low in calories, and you are very unlikely to gain weight from them.
Q. Do amino acids burn belly fat?
“Essential amino acids, included as part of a meal replacement, along with whey protein, improved the synthesis of muscle and led to a greater loss of fat,” he says. Both groups lost about 7% of their total body weight. But the amino acids and whey group lost a greater percentage of fat to lean tissue.
Q. Do amino acids promote weight loss?
Branched chain amino acids (BCAA), with vitamin B6 have been reported to improve fat metabolism and muscle synthesis. We hypothesized that supplementation with BCAA and vitamin B6 would result in more weight loss and improve body composition and blood markers related to cardiovascular diseases.
Q. What are the benefits of taking amino acids?
Proper amino acid levels are important for muscle development and strength. They help control the balance between the atrophy and growth of human muscle. Supplementing your diet with essential amino acids may increase the supply of nitrogen to your body.
Q. What amino acids are needed for hair growth?
The nine essential amino acids include histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan and valine.
Q. What’s the best amino acids to take?
The 10 Best BCAA Supplements of 2020
- Best flavored powders: Thorne Amino Complex. Designs for Health BCAA Powder with L-glutamine.
- Best unflavored powder: Pure Encapsulations BCAA Powder. NOW Sports Branched-Chain Amino Acid Powder.
- Best capsules: Jarrow Branched Chain Amino Acid Complex.
- Best vegan: Naked BCAAs.
Q. Which protein is best for hair growth?
Biotin is essential for the production of a hair protein called keratin, which is why biotin supplements are often marketed for hair growth. Research has also shown that consuming more biotin can help improve hair growth in people with a biotin deficiency (2).