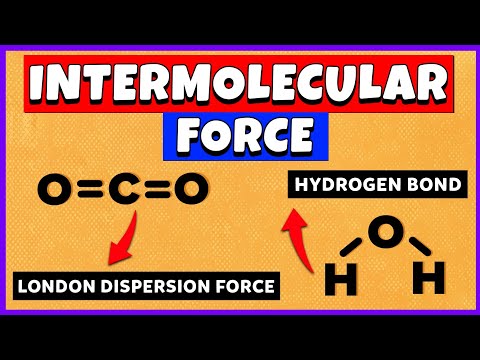
The three major types of intermolecular interactions are dipole–dipole interactions, London dispersion forces (these two are often referred to collectively as van der Waals forces), and hydrogen bonds.
Q. What force holds h2o together?
Strong linkages—called covalent bonds—hold together the hydrogen (white) and oxygen (red) atoms of individual H2O molecules. Covalent bonds occur when two atoms—in this case oxygen and hydrogen—share electrons with each other.
Table of Contents
- Q. What force holds h2o together?
- Q. What force holds substances together?
- Q. Which force keeps molecules in a fluid together quizlet?
- Q. What holds many solids and liquids together?
- Q. Do molecular solids have low melting points?
- Q. Does salt form a molecular solid?
- Q. What kind of solid tends to have the lowest melting points?
- Q. Which Crystal has highest melting?
- Q. Are solid substances with very high melting and boiling points?
- Q. Which type of solid tends to be the hardest?
- Q. What are 3 general examples of soft solids?
- Q. What type of solid is the softest?
- Q. What are hard solids?
- Q. What are the two types of solids?
- Q. What type of solid is MG?
Q. What force holds substances together?
Intermolecular forces
Q. Which force keeps molecules in a fluid together quizlet?
An intramolecular force is the force which keeps molecules together, while an intermolecular force is the attractive force between molecules and is responsible for keeping matter in a solid or liquid phase.
Q. What holds many solids and liquids together?
Gas particles have broken away from the intermolecular forces that hold liquids and solids together. An alternative name for intermolecular forces is the van der Waals forces. They include London Dispersion Forces, dipole-dipole forces, and hydrogen bonds.
Q. Do molecular solids have low melting points?
Molecular solids are composed of discrete molecules held together by intermolecular forces. Because these interactions are relatively weak, molecular solids tend to be soft and have low to moderate melting points.
Q. Does salt form a molecular solid?
An example of an ionic solid is table salt, NaCl. Molecular solids—Made up of atoms or molecules held together by London dispersion forces, dipole-dipole forces, or hydrogen bonds. Characterized by low melting points and flexibility and are poor conductors. An example of a molecular solid is sucrose.
Q. What kind of solid tends to have the lowest melting points?
The molecular solid tends to have a lower melting points. Considering its properties, the molecules of this type of solid are held together by van der Waals forces rather than by ionic or covalent bonds.
Q. Which Crystal has highest melting?
Ionic crystals have the highest melting point.
Q. Are solid substances with very high melting and boiling points?
Network solids are hard and brittle, with extremely high melting and boiling points. Being composed of atoms rather than ions, they do not conduct electricity in any state.
Q. Which type of solid tends to be the hardest?
Most covalent network solids are very hard, as exemplified by diamond, which is the hardest known substance. Covalent network solids have high melting points by virtue of their network of covalent bonds, all of which would have to be broken for them to transform into a liquid.
Q. What are 3 general examples of soft solids?
The answer lies in a type of material known as a soft solid, which can behave either like a solid or like a liquid, depending upon the stress it is subjected to. Cake batter, molten chocolate, Marmite®, custard and the foamed concrete used in oil wells are all examples of these ‘dual personality’ materials.
Q. What type of solid is the softest?
According to the Mohs scale, talc, also known as soapstone, is the softest mineral; it is composed of a stack of weakly connected sheets that tend to slip apart under pressure. When it comes to metals, scientists try to measure hardness in absolute terms.
Q. What are hard solids?
Solids can be hard like a rock, soft like fur, a big rock like an asteroid, or small rocks like grains of sand. A rock will always look like a rock unless something happens to it. The same goes for a diamond. Solids can hold their shape because their molecules are tightly packed together.
Q. What are the two types of solids?
There are two main classes of solids: crystalline and amorphous.
Q. What type of solid is MG?
Magnesium is a chemical element with symbol Mg and atomic number 12. Classified as an alkaline earth metal, Magnesium is a solid at room temperature….7.1Element Forms.
| CID | 5462224 |
|---|---|
| Name | magnesium |
| Formula | Mg |
| SMILES | [Mg] |
| Molecular Weight | 24.305 |