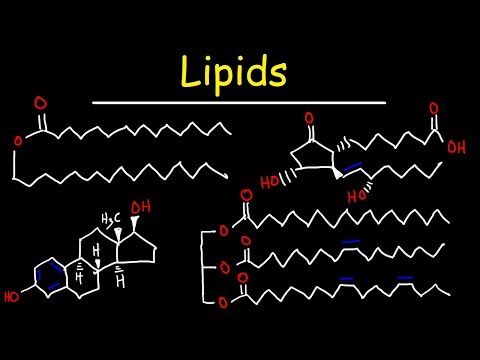
Q. What type of lipid molecule includes testosterone and cholesterol?
Steroids are another class of lipids. Their basic structure has four fused carbon rings. Cholesterol is a type of steroid and is an important constituent of the plasma membrane, where it helps to maintain the fluid nature of the membrane. It is also the precursor of steroid hormones such as testosterone.
Q. What type of lipids is testosterone?
Examples of steroid hormones include estradiol, which is an estrogen, or female sex hormone, and testosterone, which is an androgen, or male sex hormone.
Table of Contents
- Q. What type of lipid molecule includes testosterone and cholesterol?
- Q. What type of lipids is testosterone?
- Q. What are 4 functions of lipids in the body?
- Q. What is the biological importance of lipids in the body?
- Q. What functions does fat serve in the body?
- Q. What are two functions of lipids in bacterial cells?
- Q. What are the major types of lipids present in cell membrane?
- Q. Why does the nucleus have a double membrane?
- Q. What is the difference between Nucleoplasm and nucleolus?
- Q. Does the nucleus hold DNA?
- Q. Why is a double membrane important?
- Q. What role does the double membrane play in the mitochondria?
- Q. Why does the mitochondria have both an inner and outer membrane?
Q. What are 4 functions of lipids in the body?
Within the body, lipids function as an energy reserve, regulate hormones, transmit nerve impulses, cushion vital organs, and transport fat-soluble nutrients.
Q. What is the biological importance of lipids in the body?
The lipids of physiological importance for humans serve as structural components of biological membranes; provide energy reserves, predominantly in the form of triglycerides, serve as biologically active molecules exerting a wide range of regulatory functions, and the lipophilic bile acids aid in lipid emulsification …
Q. What functions does fat serve in the body?
Fat Functions Triglycerides, cholesterol and other essential fatty acids–the scientific term for fats the body can’t make on its own–store energy, insulate us and protect our vital organs. They act as messengers, helping proteins do their jobs.
Q. What are two functions of lipids in bacterial cells?
They maintain a selective permeability for the import and export of water-soluble compounds, enabling the living cell to maintain a stable chemical environment for biological processes.
Q. What are the major types of lipids present in cell membrane?
There are three major classes of membrane lipid molecules—phospholipids, cholesterol, and glycolipids.
Q. Why does the nucleus have a double membrane?
A nuclear membrane is a double membrane that encloses the cell nucleus. It serves to separate the chromosomes from the rest of the cell. The nuclear membrane includes an array of small holes or pores that permit the passage of certain materials, such as nucleic acids and proteins, between the nucleus and cytoplasm.
Q. What is the difference between Nucleoplasm and nucleolus?
The nucleus stores chromatin (DNA plus proteins) in a gel-like substance called the nucleoplasm. The nucleolus is a condensed region of chromatin where ribosome synthesis occurs. The nucleus (plural = nuclei) houses the cell’s DNA and directs the synthesis of ribosomes and proteins.
Q. Does the nucleus hold DNA?
The nucleus (plural, nuclei) houses the cell’s genetic material, or DNA, and is also the site of synthesis for ribosomes, the cellular machines that assemble proteins. Inside the nucleus, chromatin (DNA wrapped around proteins, described further below) is stored in a gel-like substance called nucleoplasm.
Q. Why is a double membrane important?
The membranes create two compartments. The intermembrane space, as implied, is the region between the inner and outer membranes. It has an important role in the primary function of mitochondria, which is oxidative phosphorylation. The matrix contains the enzymes that are responsible for the citric acid cycle reactions.
Q. What role does the double membrane play in the mitochondria?
The mitochondrion has a primary role in energy metabolism, a role that is intimately connected with its double-membrane structure (outer and inner, each comprising a lipid bilayer). Formation of mitochondria (mitochondrial biogenesis) is under the dual control of the nuclear and mitochondrial genetic systems.
Q. Why does the mitochondria have both an inner and outer membrane?
As previously mentioned, mitochondria contain two major membranes. In contrast, the inner membrane has much more restricted permeability, much like the plasma membrane of a cell. The inner membrane is also loaded with proteins involved in electron transport and ATP synthesis.