Q. What type of molecule is ATP synthase?
ATP synthase is a protein that catalyzes the formation of the energy storage molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP) using adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and inorganic phosphate (Pi). It is classified under ligases as it changes ADP by the formation of P-O bond (phosphodiester bond).
Q. What does ATP synthase make?
ATP synthase is a complex which makes use of the proton potential created by the action of the electron transport chain in mitochondria. It transports a proton down the gradient and uses the energy to complete the phosphorylation of ADP to ATP.
Table of Contents
- Q. What type of molecule is ATP synthase?
- Q. What does ATP synthase make?
- Q. Is ATP synthase an integral protein?
- Q. Is ATP synthase a lipid?
- Q. What part of ATP synthase rotates?
- Q. What causes rotation of ATP synthase?
- Q. What is the recovery time for the lactic acid system?
- Q. How does lactic acid affect recovery?
- Q. What fuel does the lactic acid system use?
- Q. Which energy system is the quickest?
Q. Is ATP synthase an integral protein?
The ATP synthase is bound to the inner membrane of the mitochondrion with a number of subunits being water-soluble while others are integral membrane proteins. The ATP synthase acts to convert the energy of oxidation-reduction reactions of the electron transport chain (respiration) to the phosphorylation of ADP.
Q. Is ATP synthase a lipid?
ATP synthase lipid-binding protein, mitochondrial.
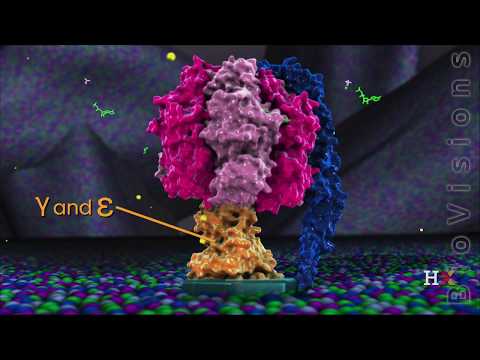
Q. What part of ATP synthase rotates?
The Fo rotor spins in response to proton (H+) flow down a concentration gradient across the membrane. This rotation causes the central stalk (axle) to rotate, altering the conformation of components of the F1 base, driving the synthesis of ATP.
Q. What causes rotation of ATP synthase?
When the magnitude of electrochemical potential of protons is large enough, downhill proton flow through Fo causes rotation of the rotor subunits (c n-γε) relative to the stator subunits (ab 2-α3β3δ), and rotation of the γ-subunit forces the β-subunits of F1 to change conformations sequentially that result in ATP …
Q. What is the recovery time for the lactic acid system?
approximately 20-60 minutes
Q. How does lactic acid affect recovery?
This often painful sensation also gets us to stop overworking the body, thus forcing a recovery period in which the body clears the lactate and other metabolites. Researchers who have examined lactate levels right after exercise found little correlation with the level of muscle soreness felt a few days later.
Q. What fuel does the lactic acid system use?
Short Term (Anaerobic Lactic) System Fuel for this system comes from glucose in the blood and stored glycogen in the muscle. Along with energy (ATP), lactic acid is produced as a byproduct of this system. As exercise intensity increases, so does the accumulation of lactic acid in the blood and muscles.
Q. Which energy system is the quickest?
Phosphagen System