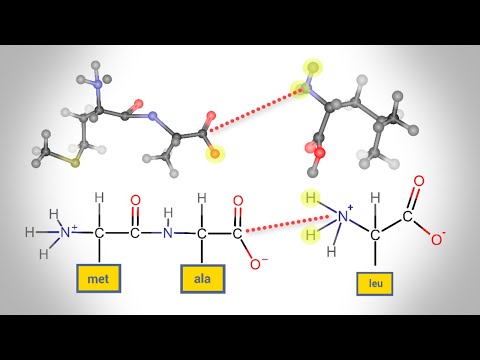
Q. What type of reaction links amino acids together?
Within a protein, multiple amino acids are linked together by peptide bonds, thereby forming a long chain. Peptide bonds are formed by a biochemical reaction that extracts a water molecule as it joins the amino group of one amino acid to the carboxyl group of a neighboring amino acid.
Q. How do 2 amino acids become linked?
Section 3.2Primary Structure: Amino Acids Are Linked by Peptide Bonds to Form Polypeptide Chains. The formation of a dipeptide from two amino acids is accompanied by the loss of a water molecule (Figure 3.18). The equilibrium of this reaction lies on the side of hydrolysis rather than synthesis.
Table of Contents
- Q. What type of reaction links amino acids together?
- Q. How do 2 amino acids become linked?
- Q. Which type of reaction forms polymers of amino acids joined together?
- Q. What type of reaction is responsible for linking amino acids together to form polypeptides?
- Q. What are the three major structural components of an amino acid?
- Q. What gives each amino acid its unique properties?
- Q. What are the three classifications of amino acids?
- Q. How are the 20 amino acids classified?
- Q. Are basic amino acids positive or negative?
- Q. Which of the following is an example of basic amino acid?
- Q. What is the basic amino acid structure?
- Q. What is the symbol for amino acid?
- Q. What is the pH of isoleucine?
- Q. What is the full chemical name for isoleucine?
- Q. What is titin full name?
- Q. What is the longest chemical name?
- Q. What does isoleucine stand for?
- Q. What are the side effects of amino acids?
- Q. Is isoleucine large or small?
- Q. Does isoleucine have special properties?
- Q. What is special about isoleucine?
Q. Which type of reaction forms polymers of amino acids joined together?
Peptide bond formation: Peptide bond formation is a dehydration synthesis reaction. The carboxyl group of one amino acid is linked to the amino group of the incoming amino acid. In the process, a molecule of water is released.
Q. What type of reaction is responsible for linking amino acids together to form polypeptides?
Amino acids can be linked by a condensation reaction in which an ―OH is lost from the carboxyl group of one amino acid along with a hydrogen from the amino group of a second, forming a molecule of water and leaving the two amino acids linked via an amide—called, in this case, a peptide bond.
Q. What are the three major structural components of an amino acid?
Each amino acid has the same fundamental structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha (α) carbon, bonded to an amino group (NH2), a carboxyl group (COOH), and to a hydrogen atom.
Q. What gives each amino acid its unique properties?
Every amino acid also has another atom or group of atoms bonded to the central atom known as the R group. This R group, or side chain, gives each amino acid proteins specific characteristics, including size, polarity, and pH.
Q. What are the three classifications of amino acids?
Amino acids are classified into three groups: Essential amino acids. Nonessential amino acids. Conditional amino acids.
Q. How are the 20 amino acids classified?
Amino acids can be classified based on the characteristics of their distinctive side chains as nonpolar, polar but uncharged, negatively charged, or positively charged. The amino acids found in proteins are L-amino acids.
Q. Are basic amino acids positive or negative?
At pH=7, two are negative charged: aspartic acid (Asp, D) and glutamic acid (Glu, E) (acidic side chains), and three are positive charged: lysine (Lys, K), arginine (Arg, R) and histidine (His, H) (basic side chains)….Charged side chains.
| Amino acid | pK of the side chain group |
|---|---|
| Histidine | 6.0 |
Q. Which of the following is an example of basic amino acid?
There are three amino acids that have basic side chains at neutral pH. These are arginine (Arg), lysine (Lys), and histidine (His). Their side chains contain nitrogen and resemble ammonia, which is a base.
Q. What is the basic amino acid structure?
An amino acid is an organic molecule that is made up of a basic amino group (−NH2), an acidic carboxyl group (−COOH), and an organic R group (or side chain) that is unique to each amino acid. Each molecule contains a central carbon (C) atom, called the α-carbon, to which both an amino and a carboxyl group are attached.
Q. What is the symbol for amino acid?
isoleucine, methionine, serine and valine. All the other amino acids share the initial letters A, G, L, P or T, so arbitrary assignments were made….Table 5. The One-Letter Symbols.
| One-letter symbol | Three-letter symbol | Amino acid |
|---|---|---|
| A | Ala | alanine |
| B | Asx | aspartic acid or asparagine |
| C | Cys | cysteine |
| D | Asp | aspartic acid |
Q. What is the pH of isoleucine?
CHEBI:58045 – L-isoleucine zwitterion
| ChEBI Name | L-isoleucine zwitterion |
|---|---|
| Definition | An L-α-amino acid zwitterion obtained by transfer of a proton from the carboxy to the amino group of L-isoleucine; major species at pH 7.3. |
| Stars | This entity has been manually annotated by the ChEBI Team. |
Q. What is the full chemical name for isoleucine?
l-Isoleucine | C6H13NO2 – PubChem.
Q. What is titin full name?
So what’s the word? Wikipedia’s says that it’s “Methionylthreonylthreonylglutaminylarginyl isoleucine” (ellipses necessary), which is the “chemical name of titin, the largest known protein.” Also, there’s some dispute about whether this is really a word.
Q. What is the longest chemical name?
The IUPAC nomenclature for organic chemical compounds is open-ended, giving rise to the 189,819-letter chemical name Methionylthreonylthreonyl… isoleucine for the protein also known as titin, which is involved in striated muscle formation.
Q. What does isoleucine stand for?
Ile
Q. What are the side effects of amino acids?
Branched-chain amino acids might also cause stomach problems, including nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and stomach bloating. In rare cases, branched-chain amino acids may cause high blood pressure, headache, or skin whitening.
Q. Is isoleucine large or small?
‘Polarity’
| Amino acid | Abbreviations | IMGT classes of the amino acids side chain properties [1] |
|---|---|---|
| Glutamic acid | Glu | medium (3) |
| Glycine | Gly | very small (1) |
| Histidine | His | medium (3) |
| Isoleucine | Ile | large (4) |
Q. Does isoleucine have special properties?
Role in structure: Being hydrophobic, Isoleucine prefers to be buried in protein hydrophobic cores. However, Isoleucine has an additional property that is frequently overlooked. Like Valine, and Threonine it is C-beta branched.
Q. What is special about isoleucine?
Role of isoleucine in the body Isoleucine has a role in the detoxification of nitrogenous waste like ammonia, which is then excreted from the body by the kidneys. Isoleucine is also essential for the production and formation of hemoglobin and the production of red blood cells.