If all the atoms didn’t need to gain or lose electrons, there would be no chemistry, which means no molecules, no compounds, no non-gas substances, and no life.
Q. What element has 40 protons and 53 neutrons?
Zirconium – Element information, properties and uses | Periodic Table.
Table of Contents
- Q. What element has 40 protons and 53 neutrons?
- Q. What if there were no electrons?
- Q. What would happen if chemical bonds didn’t exist?
- Q. What would happen if all the electrons were removed from an atom?
- Q. What happens when you remove a core electron?
- Q. Can you remove hydrogen’s electron?
- Q. Can an atom lose protons?
- Q. Why do atoms not lose protons?
- Q. What happens if a proton is removed from an atom?
- Q. What happens when you remove a neutron to an atom?
- Q. Which part of an atom is mostly empty space?
- Q. Is empty space empty?
- Q. What percent of space is empty?
Q. What if there were no electrons?
You would become plasma as there are no electrons to form molecules. You wouldn’t exist unless you were plasma. Meaning you would die. Nothing other than plasma would exist in such a universe.
Q. What would happen if chemical bonds didn’t exist?
If chemical bonds didn’t exist, which statement would be true? Life would not exist. Substances would be limited to the elements in the periodic table. Energy would not exist.
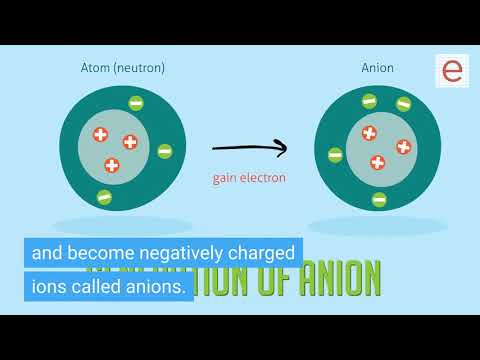
Q. What would happen if all the electrons were removed from an atom?
Originally Answered: What happens if you remove all the electrons from an atom? We have successfully ionized atoms by stripping them of their electrons. It would have a positive charge, of course, equal to how many were lost. Nitrogen losing 3 electrons has 7 protons, 4 electrons; thus, a +3 charge.
Q. What happens when you remove a core electron?
Valence electrons are the electrons orbiting the nucleus in the outermost atomic shell of an atom. Electrons that are closer to the nucleus are in filled orbitals and are called core electrons. Removing an electron (any of them) from a neutral atom turns the atom into an ion.
Q. Can you remove hydrogen’s electron?
1 Answer. Hydrogen can lose an electron meaning it can be in the +1 oxidation state. However, just like any other cation or anion it never occurs free in condensed matter, it always is in contact with solvent and/or anions. Moreover, because of extremely small size of proton, it is an extremely powerful Lewis acid.
Q. Can an atom lose protons?
The only two ways by which atoms lose protons is through radioactive decay and nuclear fission. Both processes will only occur in atoms that have unstable nuclei. It is well known that radioactively occurs naturally and spontaneously.
Q. Why do atoms not lose protons?
Atoms can have an electrical charge, positive or negative. This happens when an atom gains or loses electrons. The number of protons never changes in an atom. More electrons means a negative charge and fewer means a positive charge.
Q. What happens if a proton is removed from an atom?
Adding or removing protons from the nucleus changes the charge of the nucleus and changes that atom’s atomic number. So, adding or removing protons from the nucleus changes what element that atom is! (Actually, a few neutrons have to be added as well to make the new nucleus stable, but the end result is still helium.)
Q. What happens when you remove a neutron to an atom?
When you remove or add a neutron to the nucleus of an atom, the resulting substance is a new type of the same element and is called an isotope. It does, however, change the mass of the nucleus. …
Q. Which part of an atom is mostly empty space?
The nucleus makes up a tiny proportion of the space occupied by an atom, while the electrons make up the rest. According to quantum electrodynamics, the space is filled by an electron field around the nucleus which neutralizes its charge and fills the space defining the atom size.
Q. Is empty space empty?
Space is not empty. A point in outer space is filled with gas, dust, a wind of charged particles from the stars, light from stars, cosmic rays, radiation left over from the Big Bang, gravity, electric and magnetic fields, and neutrinos from nuclear reactions.
Q. What percent of space is empty?
0.0000000000000000000042 percent