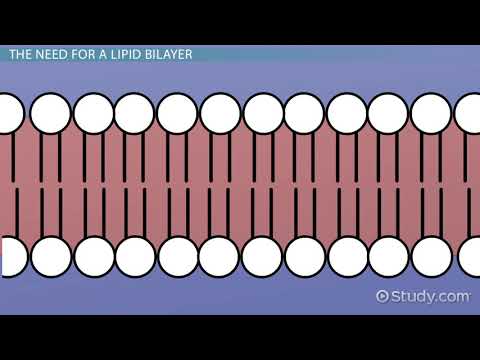
Q. What would life be like is a cell was only composed of only a phospholipid bilayer?
If a cell membrane were composed of only a phospholipid bilayer, what properties would it have? Small, uncharged molecules can easily diffuse across the cell membrane, because it will not get repelled by the membrane bc it is not charged and it is small enough to diffuse.
Q. What properties define the phospholipids that make up the lipid bilayer?
A phospholipid is a lipid made of glycerol, two fatty acid tails, and a phosphate-linked head group. Biological membranes usually involve two layers of phospholipids with their tails pointing inward, an arrangement called a phospholipid bilayer.
Table of Contents
- Q. What would life be like is a cell was only composed of only a phospholipid bilayer?
- Q. What properties define the phospholipids that make up the lipid bilayer?
- Q. What property of phospholipids makes them important in cell membranes?
- Q. What does the phospholipid bilayer do?
- Q. What allows water to move much faster across cell membranes?
- Q. Why can’t polar molecules pass through the cell membrane?
- Q. What parts of the cell membrane are polar and nonpolar?
- Q. Which is part of cell membrane?
- Q. Which part of the cell membrane is polar and allows the cell to exist in water?
- Q. How is the bilayer important for membrane activities?
- Q. How does the cell membrane work?
Q. What property of phospholipids makes them important in cell membranes?
Phospholipids are able to form cell membranes because the phosphate group head is hydrophilic (water-loving) while the fatty acid tails are hydrophobic (water-hating). They automatically arrange themselves in a certain pattern in water because of these properties, and form cell membranes.
Q. What does the phospholipid bilayer do?
Phospholipid bilayers are critical components of cell membranes. The lipid bilayer acts as a barrier to the passage of molecules and ions into and out of the cell. However, an important function of the cell membrane is to allow selective passage of certain substances into and out of cells.
Q. What allows water to move much faster across cell membranes?
Which of the following allows water to move much faster across cell membranes? pinocytosis brings only water molecules into the cell, but receptor-mediated endocytosis brings in other molecules as well.
Q. Why can’t polar molecules pass through the cell membrane?
Large, polar molecules (ex: simple sugar – glucose) and ions: The charge of an ion, and the size and charge of large polar molecules, makes it too difficult to pass through the nonpolar region of the phospholipid membrane without help.
Q. What parts of the cell membrane are polar and nonpolar?
The main component of the cell membrane is a phospholipid bi-layer or sandwich. The heads (the phospho part) are polar while the tails (the lipid part) are non-polar.
Q. Which is part of cell membrane?
(A) The plasma membrane of a cell is a bilayer of glycerophospholipid molecules. (B) A single glycerophospholipid molecule is composed of two major regions: a hydrophilic head (green) and hydrophobic tails (purple). (C) The subregions of a glycerophospholipid molecule; phosphatidylcholine is shown as an example.
Q. Which part of the cell membrane is polar and allows the cell to exist in water?
Phosphate groups
Q. How is the bilayer important for membrane activities?
The lipid bilayer is a universal component of all cell membranes. Its role is critical because its structural components provide the barrier that marks the boundaries of a cell. The structure is called a “lipid bilayer” because it is composed of two layers of fat cells organized in two sheets.
Q. How does the cell membrane work?
The cell membrane is a multifaceted membrane that envelopes a cell’s cytoplasm. It protects the integrity of the cell along with supporting the cell and helping to maintain the cell’s shape. Proteins and lipids are the major components of the cell membrane.