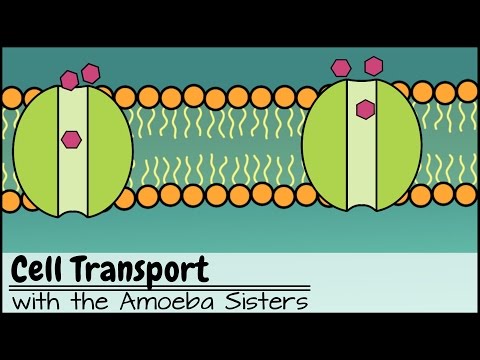
When proteins help transport molecules in and out of the cell, it is called active transport.
Q. Which of the following best explains the type of cell transport observed by the scientist?
Which of the following best explains the type of cell transport observed by the scientist? Osmosis because the molecules were moving against the concentration gradient. Membrane proteins provide a pathway for larger particles to move across the cell membrane and bring the cell and environment closer to equilibrium.
Table of Contents
- Q. Which of the following best explains the type of cell transport observed by the scientist?
- Q. Which best describes the type of cellular transport that the student is investigating?
- Q. When molecules pass through a cell membrane using transport proteins?
- Q. What are the two main types of transport proteins?
- Q. What are the 3 classes of transport proteins?
- Q. What is an example of coupled transport?
- Q. What is required for active transport?
- Q. Why does a cell need active transport?
- Q. How do cells transport?
- Q. Which of the following is an example of active transport in a cell?
Q. Which best describes the type of cellular transport that the student is investigating?
The correct answer is A The student is investigating the passive transport of diffusion.
Q. When molecules pass through a cell membrane using transport proteins?
Facilitated diffusion is the diffusion of solutes through transport proteins in the plasma membrane. Channel proteins, gated channel proteins, and carrier proteins are three types of transport proteins that are involved in facilitated diffusion.
Q. What are the two main types of transport proteins?
Carrier proteins and channel proteins are the two major classes of membrane transport proteins.
Q. What are the 3 classes of transport proteins?
Types
- 1: Channels/pores.
- 2: Electrochemical potential-driven transporters.
- 3: Primary active transporters.
- 4: Group translocators.
- 5: Electron carriers.
Q. What is an example of coupled transport?
What is an example of coupled transport? Glucose-Na+ symporter. It captures the energy from Na+ diffusion to move glucose against the concentration gradient.
Q. What is required for active transport?
During active transport, substances move against the concentration gradient, from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration. This process is “active” because it requires the use of energy (usually in the form of ATP). It is the opposite of passive transport.
Q. Why does a cell need active transport?
Active transport: moving against a gradient To move substances against a concentration or electrochemical gradient, a cell must use energy. Active transport mechanisms do just this, expending energy (often in the form of ATP) to maintain the right concentrations of ions and molecules in living cells.
Q. How do cells transport?
Cell transport is movement of materials across cell membranes. Cell transport includes passive and active transport. Passive transport does not require energy whereas active transport requires energy to proceed. Passive transport proceeds through diffusion, facilitated diffusion and osmosis.
Q. Which of the following is an example of active transport in a cell?
Because energy is required in this process, it is known as ‘active’ transport. Examples of active transport include the transportation of sodium out of the cell and potassium into the cell by the sodium-potassium pump. Active transport often takes place in the internal lining of the small intestine.