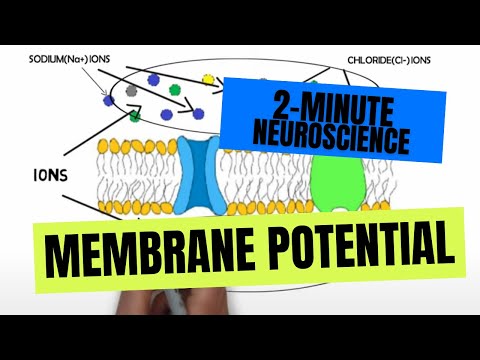
What is happening to the membrane potential? For depolarization the voltage gated sodium channels are open and the potassium channels are closed. The Na+ ions are flowing into the cell. the membrane potential is becoming more positive towards +30mV.
Q. What is depolarization and repolarization?
Action potential in a neuron, showing depolarization, in which the cell’s internal charge becomes less negative (more positive), and repolarization, where the internal charge returns to a more negative value.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is depolarization and repolarization?
- Q. What is depolarization and hyperpolarization?
- Q. What happens if Na+ channels open and sodium ions diffuse into the cell?
- Q. What causes depolarization?
- Q. What is depolarization of muscle?
- Q. Is potassium needed for muscle contraction?
- Q. Is calcium needed for muscle contraction?
- Q. Why is sodium important for muscle contraction?
- Q. What mineral is important for muscle contraction?
- Q. How many steps are in a muscle contraction?
- Q. What are the 3 phases of muscle contraction?
- Q. What are the 8 steps of muscle contraction?
- Q. What are the steps of muscle relaxation?
- Q. How do muscles work together to move bones?
Q. What is depolarization and hyperpolarization?
Hyperpolarization and depolarization Hyperpolarization is when the membrane potential becomes more negative at a particular spot on the neuron’s membrane, while depolarization is when the membrane potential becomes less negative (more positive).
Q. What happens if Na+ channels open and sodium ions diffuse into the cell?
Ligand gated sodium ion channels open and sodium diffuses in. These channels open, allowing Na+ to enter the cell and K+ to leave. As Na+ enters the cell, it spreads out along the inside of the plasma membrane and depolarizes it, producing a local potential called the postsynaptic potential.
Q. What causes depolarization?
Depolarization is caused when positively charged sodium ions rush into a neuron with the opening of voltage-gated sodium channels. Repolarization is caused by the closing of sodium ion channels and the opening of potassium ion channels.
Q. What is depolarization of muscle?
muscle contraction In muscle: Release of acetylcholine from the nerve terminal. The channels are opened by depolarization (an increase in membrane potential) of the nerve terminal membrane and selectively allow the passage of calcium ions.
Q. Is potassium needed for muscle contraction?
We need potassium to keep the electrochemical balance across cell membranes. This is vital to transmit nerve signals. This leads to skeletal muscle contraction, hormone release, and smooth muscle and heart contraction.
Q. Is calcium needed for muscle contraction?
Calcium triggers contraction in striated muscle. (A) Actomyosin in striated muscle. (1) Striated muscle in the relaxed state has tropomyosin covering myosin-binding sites on actin.
Q. Why is sodium important for muscle contraction?
The sodium influx also sends a message within the muscle fiber to trigger the release of stored calcium ions. The calcium ions diffuse into the muscle fiber. The relationship between the chains of proteins within the muscle cells changes, leading to the contraction.
Q. What mineral is important for muscle contraction?
Macrominerals
| Mineral | Function |
|---|---|
| Potassium | Needed for proper fluid balance, nerve transmission, and muscle contraction |
| Calcium | Important for healthy bones and teeth; helps muscles relax and contract; important in nerve functioning, blood clotting, blood pressure regulation, immune system health |
Q. How many steps are in a muscle contraction?
12 Steps to Muscle Contraction. A nerve impulse travels to the neuromuscular junction on a muscle cell.
Q. What are the 3 phases of muscle contraction?
The contraction generated by a single action potential is called a muscle twitch. A single muscle twitch has three components. The latent period, or lag phase, the contraction phase, and the relaxation phase.
Q. What are the 8 steps of muscle contraction?
Terms in this set (8)
- an action potential travels along a neuron to a synapse at a muscle fiber.
- acetylcholine (neurotransmitter) is released from a neuron.
- acetylcholine (neurotransmitter) binds to muscle cell membrane.
- sodium ions diffuse into the muscle fiber starting an action potential.
Q. What are the steps of muscle relaxation?
Muscle relaxation occurs when ________.
- calcium ions are actively transported out of the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
- calcium ions diffuse out of the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
- calcium ions are actively transported into the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
- calcium ions diffuse into the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
Q. How do muscles work together to move bones?
Muscles move body parts by contracting and then relaxing. Muscles can pull bones, but they can’t push them back to the original position. So they work in pairs of flexors and extensors. The flexor contracts to bend a limb at a joint.