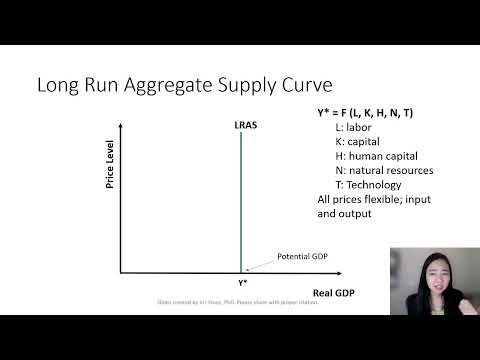
The long-run aggregate supply curve is perfectly vertical, which reflects economists’ belief that the changes in aggregate demand only cause a temporary change in an economy’s total output. In the long-run, there is exactly one quantity that will be supplied.
Q. Why is the LRAS curve vertical?
Why is the LRAS vertical? The LRAS is vertical because, in the long-run, the potential output an economy can produce isn’t related to the price level. The LRAS curve is also vertical at the full-employment level of output because this is the amount that would be produced once prices are fully able to adjust.
Table of Contents
- Q. Why is the LRAS curve vertical?
- Q. Why is the LRAS curve vertical quizlet?
- Q. Why does the sras become vertical?
- Q. What causes as curve to shift?
- Q. How do you shift the aggregate supply curve?
- Q. Which factor will shift AS1 to AS3?
- Q. Which would shift the aggregate demand curve a change in?
- Q. Which is a determinant of aggregate supply?
- Q. What percentage of the average US firm’s costs are accounted for by wages and salaries?
- Q. What percentage of an employees salary is benefits 2019?
- Q. What percentage of salary are benefits?
- Q. What percentage of expenses should payroll be?
- Q. What percentage should your overhead be?
- Q. What is the biggest expense for a company?
- Q. What are the top 5 expenses for most businesses?
- Q. What are the biggest expenses in life?
Q. Why is the LRAS curve vertical quizlet?
The long-run aggregate supply curve is vertical because in the long run wages are flexible. The level of output that the economy would produce if all prices, including nominal wages, were fully flexible is called: -potential GDP.
Q. Why does the sras become vertical?
Once idle resources are used up, then price levels increase sharply but with no corresponding increase in real GDP. Thus, the short-run aggregate supply ( SRAS ) curve slopes upward, becoming vertical, after the economy reaches full employment.
Q. What causes as curve to shift?
In the long run, the most important factor shifting the SRAS curve is productivity growth. A higher level of productivity shifts the SRAS curve to the right because with improved productivity, firms can produce a greater quantity of output at every price level.
Q. How do you shift the aggregate supply curve?
A shift in aggregate supply can be attributed to many variables, including changes in the size and quality of labor, technological innovations, an increase in wages, an increase in production costs, changes in producer taxes, and subsidies and changes in inflation.
Q. Which factor will shift AS1 to AS3?
In the diagram, a shift from AS1 to AS3 might be caused by a(n): increase in the prices of imported resources. The price level in the United States is more flexible downward than upward.
Q. Which would shift the aggregate demand curve a change in?
The aggregate demand curve shifts to the right as a result of monetary expansion. If the monetary supply decreases, the demand curve will shift to the left.
Q. Which is a determinant of aggregate supply?
A few of the determinants are size of the labor force, input prices, technology, productivity, government regulations, business taxes and subsidies, and capital. As wages, energy, and raw material prices increase, aggregate supply decreases, all else constant.
Q. What percentage of the average US firm’s costs are accounted for by wages and salaries?
Wages and salaries cost employers $26.53 and accounted for 68.7 percent of total costs, while benefits cost $12.07 and accounted for the remaining 31.3 percent.
Q. What percentage of an employees salary is benefits 2019?
Wages and salaries cost employers $26.53 and accounted for 68.7 percent of total costs, while benefits cost $12.07 and accounted for the remaining 31.3 percent. (See table 1.)
Q. What percentage of salary are benefits?
32 percent
Q. What percentage of expenses should payroll be?
30 percent
Q. What percentage should your overhead be?
In a business that is performing well, an overhead percentage that does not exceed 35% of total revenue is considered favourable. In small or growing firms, the overhead percentage is usually the critical figure that is of concern.
Q. What is the biggest expense for a company?
As any company leader knows, the biggest cost of doing business is often labor. Labor costs, which can account for as much as 70% of total business costs, include employee wages, benefits, payroll or other related taxes.
Q. What are the top 5 expenses for most businesses?
For most businesses, the five greatest expenses are: Staff, physical location, capital equipment, development costs, and Cost of Goods Sold (aka: Inventory).
Q. What are the biggest expenses in life?
The 10 Biggest Expenses in Life and How to Reduce Them
- Funerals = $10,000.
- Weddings = $33,000.
- Buying a Car = $35,000.
- Debt = Varies.
- Insurance = $50,000 +
- Vacations $60,000+
- Buying a Home = $226,000.
- Raising a Child = $233,000.