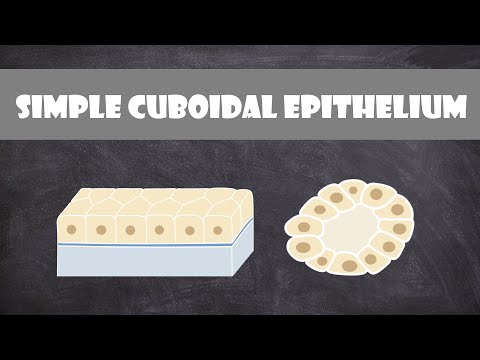
Simple cuboidal epithelia are found on the surface of ovaries, the lining of nephrons, the walls of the renal tubules, and parts of the eye and thyroid, along with the salivary glands. On these surfaces, the cells perform secretion and absorption.
Q. What is Pseudostratified epithelial tissue?
A pseudostratified epithelium is a type of epithelium that, though comprising only a single layer of cells, has its cell nuclei positioned in a manner suggestive of stratified epithelia.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is Pseudostratified epithelial tissue?
- Q. How does simple cuboidal epithelium absorb?
- Q. What are the examples of simple cuboidal epithelium?
- Q. Why is it called simple Cuboidal?
- Q. What is cuboidal epithelium Class 9?
- Q. What are the 9 types of epithelial tissue?
- Q. What are the various types of epithelial tissue explain with diagram?
- Q. What is the diagram of epithelial tissue?
Q. How does simple cuboidal epithelium absorb?
Absorption The proximal convoluted tubules and distal convoluted tubules in the kidneys, lined with the simple cuboidal epithelium remove the excess water and other waste materials and also maintain the pH and ion balance of the body.
Q. What are the examples of simple cuboidal epithelium?
Simple cuboidal epithelium occurs in many glands and glandular ducts (see Plates 37–39), various sections of the renal tubules, choroid plexus (see Plate 12), and as germinal epithelium of the ovary (see Plate 76).
Q. Why is it called simple Cuboidal?
A simple epithelium is an epithelial tissue that is composed of a single layer of epithelial cells. These cells are in direct contact with the basement membrane. The cuboidal epithelial cells, as the name implies, are cuboidal in shape, which means that they are approximately as wide as they are tall.
Q. What is cuboidal epithelium Class 9?
Cuboidal epithelium (with cube-shaped cells) forms the lining of kidney tubules and ducts of salivary glands, where it provides mechanical support. Epithelial cells often acquire additional specialisation as gland cells, which can secrete substances at the epithelial surface.
Q. What are the 9 types of epithelial tissue?
Terms in this set (9)
- Simple squamous. -air sacs of the lungs.
- Simple cuboidal. -surface of ovaries.
- Simple columnar. -lining of uterus.
- pseudostratified columnar. linings of respiratory passages.
- stratified squamous. -outer layer of skin.
- stratified cuboidal.
- stratified columnar.
- transitional.
Q. What are the various types of epithelial tissue explain with diagram?
Overview and types of epithelial tissue
| Cell shape classification | Squamous, cuboidal, columnar |
|---|---|
| Main features | Contiguous cells Polarity (apical, lateral and basal cell surfaces) Intercellular junctions Basement membrane (extracellular matrix) Supported by connective tissue (lamina propria) Avascular, innervated |
Q. What is the diagram of epithelial tissue?
Epithelial tissues line the outer surfaces of organs and blood vessels throughout the body, as well as the inner surfaces of cavities in many internal organs. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. There are three principal shapes of epithelial cell: squamous, columnar, and cuboidal.