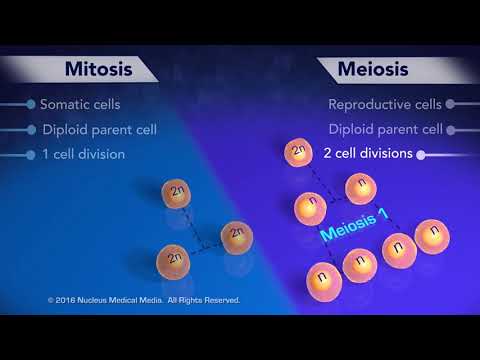
Q. Where does mitosis occur in the cell?
somatic cells
Q. Where does the cell spend most of its time in mitosis?
prophase
Table of Contents
- Q. Where does mitosis occur in the cell?
- Q. Where does the cell spend most of its time in mitosis?
- Q. What activities occur during mitosis?
- Q. What happens in a cell during mitosis?
- Q. What type of cell does mitosis create?
- Q. What kind of cells are produced at the end of mitosis?
- Q. What type of cells are made at the end of meiosis?
- Q. Does mitosis make body cells?
- Q. Does mitosis repair damaged cells?
- Q. What is the number of daughter cells in mitosis?
- Q. How does human life depend on mitosis?
- Q. What is the number of daughter cells in meiosis?
- Q. What type of daughter cells are produced in mitosis?
- Q. What are 3 difference between the daughter cells in mitosis and meiosis?
- Q. What is the correct description of the daughter cells after meiosis?
- Q. Do plants produce eggs and sperm through mitosis or through meiosis?
- Q. Does the number of chromosomes change in mitosis?
- Q. How many chromosomes are visible at the end of mitosis?
- Q. How many chromosomes are there in mitosis?
- Q. What happens to chromosomes during mitosis?
- Q. What is special about the two cells produced in mitosis?
- Q. Why do chromosomes condense during mitosis?
- Q. Why is it important for the chromosomes to condense during mitosis quizlet?
- Q. Does chromatin condense during mitosis?
- Q. Why do chromosomes coil during mitosis?
- Q. Where are chromosomes coils mitosis?
- Q. What phase are daughter cells in as a result of mitosis?
- Q. Why do chromosomes coil and condense during mitosis quizlet?
Q. What activities occur during mitosis?
These basic events of mitosis include chromosome condensation, formation of the mitotic spindle, and attachment of chromosomes to the spindle microtubules. Sister chromatids then separate from each other and move to opposite poles of the spindle, followed by the formation of daughter nuclei.
Q. What happens in a cell during mitosis?
During mitosis, a eukaryotic cell undergoes a carefully coordinated nuclear division that results in the formation of two genetically identical daughter cells. Then, at a critical point during interphase (called the S phase), the cell duplicates its chromosomes and ensures its systems are ready for cell division.
Q. What type of cell does mitosis create?
eukaryotic cells
Q. What kind of cells are produced at the end of mitosis?
At the end of mitosis, one cell produces two genetically identical daughter cells.
Q. What type of cells are made at the end of meiosis?
By the end of meiosis, the resulting reproductive cells, or gametes, each have 23 genetically unique chromosomes. The overall process of meiosis produces four daughter cells from one single parent cell. Each daughter cell is haploid, because it has half the number of chromosomes as the original parent cell.
Q. Does mitosis make body cells?
There are two types of cell division: mitosis and meiosis. Most of the time when people refer to “cell division,” they mean mitosis, the process of making new body cells. It is a two-step process that reduces the chromosome number by half—from 46 to 23—to form sperm and egg cells.
Q. Does mitosis repair damaged cells?
Replacement and regeneration of new cells- Regeneration and replacement of worn-out and damaged tissues is a very important function of mitosis in living organisms. Mitosis helps in the production of identical copies of cells and thus helps in repairing the damaged tissue or replacing the worn-out cells.
Q. What is the number of daughter cells in mitosis?
two
Q. How does human life depend on mitosis?
Mitosis affects life by directing the growth and repair of trillions of cells in the human body. Without mitosis, cell tissue would rapidly deteriorate and stop working properly.
Q. What is the number of daughter cells in meiosis?
four daughter cells
Q. What type of daughter cells are produced in mitosis?
In mitosis a cell divides to form two identical daughter cells. It is important that the daughter cells have a copy of every chromosome, so the process involves copying the chromosomes first and then carefully separating the copies to give each new cell a full set. Before mitosis, the chromosomes are copied.
Q. What are 3 difference between the daughter cells in mitosis and meiosis?
Daughter cells are the cells that are produced as a result of the division, meiosis produces genetically different cells however mitosis produces genetic clones. Meiosis includes two divisions and therefore produces four daughter cells, mitosis involves one division and produces two daughter cells.
Q. What is the correct description of the daughter cells after meiosis?
The four daughter cells resulting from meiosis are haploid and genetically distinct. The daughter cells resulting from mitosis are diploid and identical to the parent cell.
Q. Do plants produce eggs and sperm through mitosis or through meiosis?
Gametophytes produce gametes by mitosis. In animals, meiosis produces sperm and egg, but in plants, meiosis occurs to produce the gametophyte. The gametophyte is already haploid, so it produces sperm and egg by mitosis.
Q. Does the number of chromosomes change in mitosis?
A quick tip: notice that during the stages of meiosis and mitosis, the chromatid count never changes. Only the number of chromosomes changes (by doubling) during anaphase when sister chromatids are separated.
Q. How many chromosomes are visible at the end of mitosis?
At the end of mitosis, the two daughter cells will be exact copies of the original cell. Each daughter cell will have 30 chromosomes.
Q. How many chromosomes are there in mitosis?
46 chromosomes
Q. What happens to chromosomes during mitosis?
Mitosis is the process of nuclear division, which occurs just prior to cell division, or cytokinesis. During this multistep process, cell chromosomes condense and the spindle assembles. Each set of chromosomes is then surrounded by a nuclear membrane, and the parent cell splits into two complete daughter cells.
Q. What is special about the two cells produced in mitosis?
In mitosis, two cells called daughter cells are produced. It is essential that any new daughter cells produced contain genetic information that is identical to the mother cell, and that the number of chromosomes remains constant.
Q. Why do chromosomes condense during mitosis?
Chromosomes condense before mitosis to allow them the ability to move smoothly, without becoming entangled and breaking. (So, they are conveniently packaged for cell division, in which the chromosomes must move to both poles of the cell.)
Q. Why is it important for the chromosomes to condense during mitosis quizlet?
Why is it important for the chromosomes to condense during mitosis? Colchicine is a chemical that when applied to a cell during mitosis can be used to “freeze” cells in metaphase by preventing the chromosomes from moving away from the metaphase plate.
Q. Does chromatin condense during mitosis?
Chromatin condensation begins during prophase (2) and chromosomes become visible. Chromosomes remain condensed throughout the various stages of mitosis (2-5). However, when eukaryotic cells are not dividing — a stage called interphase — the chromatin within their chromosomes is less tightly packed.
Q. Why do chromosomes coil during mitosis?
Why do chromosomes coil during mitosis? E) The chromosomes are “reeled in” by the contraction of spindle microtubules, motor proteins of the kinetochores move the chromosomes along the spindle microtubules, and nonkinetochore spindle fibers serve to push chromosomes in the direction of the poles.
Q. Where are chromosomes coils mitosis?
During prophase, the complex of DNA and proteins contained in the nucleus, known as chromatin, condenses. The chromatin coils and becomes increasingly compact, resulting in the formation of visible chromosomes. Chromosomes are made of a single piece of DNA that is highly organized.
Q. What phase are daughter cells in as a result of mitosis?
Image of the cell cycle. Interphase is composed of G1 phase (cell growth), followed by S phase (DNA synthesis), followed by G2 phase (cell growth). At the end of interphase comes the mitotic phase, which is made up of mitosis and cytokinesis and leads to the formation of two daughter cells.
Q. Why do chromosomes coil and condense during mitosis quizlet?
Why do chromosomes condense during mitosis? Chromosomes condense in order to make chromosomes which consists of sister chromatids.