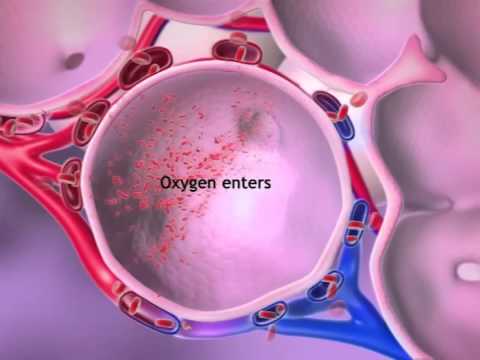
Q. Where does the exchange of carbon dioxide co2 and oxygen o2 occur?
During gas exchange oxygen moves from the lungs to the bloodstream. At the same time carbon dioxide passes from the blood to the lungs. This happens in the lungs between the alveoli and a network of tiny blood vessels called capillaries, which are located in the walls of the alveoli.
Q. What exchanges oxygen and carbon dioxide in the body?
What Are the Lungs and Respiratory System? The lungs and respiratory system allow us to breathe. They bring oxygen into our bodies (called inspiration, or inhalation) and send carbon dioxide out (called expiration, or exhalation). This exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide is called respiration.
Table of Contents
- Q. Where does the exchange of carbon dioxide co2 and oxygen o2 occur?
- Q. What exchanges oxygen and carbon dioxide in the body?
- Q. Where does o2 co2 and nutrients waste exchange take place?
- Q. What is the site of co2 & o2 gas exchange during cellular respiration?
- Q. How do the lungs get rid of all the CO2 they’ve picked up from the blood?
- Q. Why do we breathe oxygen and give off carbon dioxide?
- Q. How do you reduce CO2 in ventilation?
- Q. Does air purifier remove CO2?
- Q. How does BiPAP reduce CO2?
- Q. Does a BiPAP machine get rid of carbon dioxide?
- Q. Is BiPAP good for COPD?
- Q. What is the normal oxygen level for someone with COPD?
- Q. What does CO2 mean in a blood test?
- Q. Why is my CO2 low?
Q. Where does o2 co2 and nutrients waste exchange take place?
Exchange of Gases, Nutrients, and Waste Between Blood and Tissue Occurs in the Capillaries. Capillaries are tiny vessels that branch out from arterioles to form networks around body cells. In the lungs, capillaries absorb oxygen from inhaled air into the bloodstream and release carbon dioxide for exhalation.
Q. What is the site of co2 & o2 gas exchange during cellular respiration?
04 Dec Cellular Respiration A gas exchange takes place in the alveoli when oxygen passes into the blood and carbon dioxide passes out of the blood. This exchange occurs because the gases in the air and blood have different concentrations and are separated by very thin capillary walls that surround the alveoli.
Q. How do the lungs get rid of all the CO2 they’ve picked up from the blood?
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a waste product of cellular metabolism. You get rid of it when you breathe out (exhale). This gas is transported in the opposite direction to oxygen: It passes from the bloodstream – across the lining of the air sacs – into the lungs and out into the open.
Q. Why do we breathe oxygen and give off carbon dioxide?
When we take a breath, we pull air into our lungs that contains mostly nitrogen and oxygen. When we exhale, we breathe out mostly carbon dioxide. Oxygen helps our cells work harder by breaking down the nutrients we get from food like sugars. With sugars and oxygen, our cells can create the energy they need to function.
Q. How do you reduce CO2 in ventilation?
Hypercapnia: To modify CO2 content in blood one needs to modify alveolar ventilation. To do this, the tidal volume or the respiratory rate may be tampered with (T low and P Low in APRV). Raising the rate or the tidal volume, as well as increasing T low, will increase ventilation and decrease CO2.
Q. Does air purifier remove CO2?
Along with all this, air purifiers don’t help in reducing carbon dioxide levels. So in a sealed home or office with no ventilation, and a lot of people working in cramped spaces, carbon dioxide levels can rise rapidly.
Q. How does BiPAP reduce CO2?
This is achieved through a pressure-cycled machine known as BiPAP. The higher level of pressure assists ventilation during inspiration (IPAP) by lowering CO2 levels, while the lower level maintains airway patency during expiration (EPAP), thereby increasing oxygen levels.
Q. Does a BiPAP machine get rid of carbon dioxide?
If you have moderate to severe COPD, you may use a BiPAP machine at the hospital to help with sudden, intense symptoms. You can also use them at home to help with sleep. They’ll keep your blood oxygen levels up and remove carbon dioxide.
Q. Is BiPAP good for COPD?
BiPAP machines provide two different levels of air pressure, which makes breathing out easier than it is with a CPAP machine. For this reason, BiPAP is preferred for people with COPD. It lessens the work it takes to breathe, which is important in people with COPD who expend a lot of energy breathing.
Q. What is the normal oxygen level for someone with COPD?
Health Line Anything between 92% and 88%, is still considered safe and average for someone with moderate to severe COPD. Below 88% becomes dangerous, and when it dips to 84% or below, it’s time to go to the hospital. Around 80% and lower is dangerous for your vital organs, so you should be treated right away.
Q. What does CO2 mean in a blood test?
A CO2 blood test measures the amount of carbon dioxide in your blood. Too much or too little carbon dioxide in the blood can indicate a health problem.
Q. Why is my CO2 low?
A low CO2 level can be a sign of several conditions, including: Kidney disease. Diabetic ketoacidosis, which happens when your body’s blood acid level goes up because it doesn’t have enough insulin to digest sugars. Metabolic acidosis, which means your body makes too much acid.