Q. Where is MDR-TB most common?
Globally, most MDR-TB cases occur in South America, Southern Africa, India, China, and the former Soviet Union.
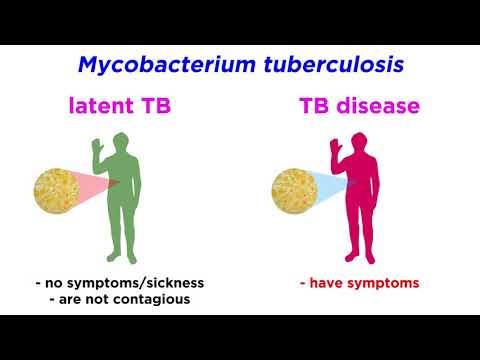
Q. Do you need to get treated for latent TB?
If they have latent TB infection, they need treatment as soon as possible to prevent them from developing TB disease. If they have TB disease, they must take medicine to treat the disease.
Table of Contents
- Q. Where is MDR-TB most common?
- Q. Do you need to get treated for latent TB?
- Q. Does latent TB weaken your immune system?
- Q. Does a chest xray show latent TB?
- Q. Will latent TB show up on xray?
- Q. Can latent TB damage lungs?
- Q. What medication is used for latent TB?
- Q. Does latent TB show up in a blood test?
- Q. How is latent TB tested?
- Q. Does latent TB show up on skin test?
- Q. What happens if you test positive for tuberculosis?
- Q. Can I marry a girl with TB?
- Q. Can you be naturally immune to TB?
- Q. Can your body fight off tuberculosis?
- Q. Can you get TB twice?
- Q. Can you test positive for TB and not have it?
- Q. What to do if TB blood test is positive?
- Q. How long can you live with untreated tuberculosis?
Q. Does latent TB weaken your immune system?
However, latent TB bacteria can ‘wake up’ and become active in the future, making you ill. This can happen many years after you first breathe in TB bacteria. Latent TB bacteria are more likely to wake up if you experience lifestyle stresses or other illnesses that weaken your immune system.
Q. Does a chest xray show latent TB?
A person has latent TB infection if they have a positive TB skin test and a normal (negative) chest x-ray. This means the person has breathed in the TB germs, but his or her body has been able to fight the germs.
Q. Will latent TB show up on xray?
The decision about treatment for latent TB infection will be based on a person’s chances of developing TB disease by considering their risk factors. TB disease is diagnosed by medical history, physical examination, chest x-ray, and other laboratory tests.
Q. Can latent TB damage lungs?
Treatment for latent TB and pulmonary TB You can still develop pulmonary TB disease in the future. You may only need one TB drug if you have latent TB. If you have pulmonary TB, your doctor may prescribe several medicines. You’ll need to take these drugs for six months or longer for the best results.
Q. What medication is used for latent TB?
You can take medicine to prevent getting active TB disease. Isoniazid and Rifapentine (INH-RPT) are medicines used together to treat LTBI.
Q. Does latent TB show up in a blood test?
A positive TB skin test or TB blood test only tells that a person has been infected with TB bacteria. It does not tell whether the person has latent TB infection (LTBI) or has progressed to TB disease. Other tests, such as a chest x-ray and a sample of sputum, are needed to see whether the person has TB disease.
Q. How is latent TB tested?
What does a test for latent TB involve? You may be offered either one of two different tests for latent TB, a TB skin test (known as a TST or Mantoux) or a blood test (known as an IGRA). The test may be taken at your local GP practice, in a specialist TB clinic or occasionally in a local community setting.
Q. Does latent TB show up on skin test?
Latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI) is often diagnosed by the tuberculin skin test (TST). The latter has several limitations with regard to its sensitivity and specificity. It may be positive in people with prior bacille Calmette-Guérin (BCG) vaccination or exposure to nontuberculous mycobacteria.
Q. What happens if you test positive for tuberculosis?
A positive TB test result means only that TB bacteria has been detected. It does not indicate whether the person has active TB or a latent infection. This requires additional testing. TB disease can be diagnosed by medical history, physical examination, chest X-ray, and other lab tests.
Q. Can I marry a girl with TB?
For example, if, due to TB and its lengthy treatment, a woman’s marriage to her cousin does not go ahead, then it is not her last opportunity to marry if she has many other as yet unmarried cousins to marry once she is in good health again.
Q. Can you be naturally immune to TB?
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease caused by a bacterium called Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB). Two thirds of the world population are infected by this mycobacterium. Nevertheless, 20 per cent of people exposed to the mycobacterium are resistant to infection and can therefore, not develop the disease.
Q. Can your body fight off tuberculosis?
If you are healthy, you probably have a strong immune system and your body can fight off infections from bacteria or viruses easily. So if you breathe in TB bacteria, your immune system would probably kill them off straight away, without you ever getting ill or knowing about it.
Q. Can you get TB twice?
Even if you successfully beat tuberculosis, you can get tuberculosis infection again. In fact, TB reinfection is becoming more common. Tuberculosis is a potentially life-threatening, airborne bacterial infection that can be found worldwide.
Q. Can you test positive for TB and not have it?
With a latent TB infection, you have the TB bacteria, but you don’t feel sick and you have no symptoms. You can’t spread TB to anyone else. The only sign that you have a TB infection is a positive TB skin test or blood test.
Q. What to do if TB blood test is positive?
A “positive” TB blood test result means you probably have TB germs in your body. Most people with a positive TB blood test have latent TB infection. To be sure, your doctor will examine you and do a chest x-ray. You may need other tests to see if you have latent TB infection or active TB disease.
Q. How long can you live with untreated tuberculosis?
Left untreated,TB can kill approximately one half of patients within five years and produce significant morbidity (illness) in others. Inadequate therapy for TB can lead to drug-resistant strains of M. tuberculosis that are even more difficult to treat. Not everyone who inhales the germ develops active TB disease.