Q. Which 2 phases do the centrioles move to opposite sides of the cell and spindle fibers begin to form?
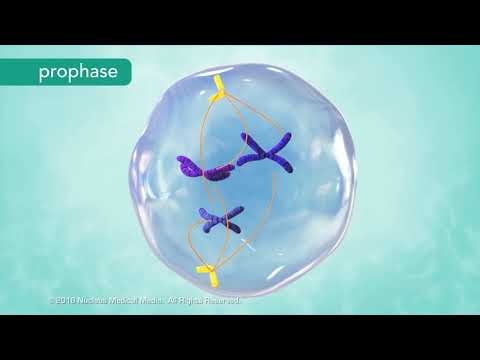
At the beginning of the first mitotic stage, prophase, the thread-like doubled chromosomes contract and become visible. The two centrioles move to opposite sides of the nucleus. At the same time, the nuclear membrane begins to break down.
Q. Do spindle fibers shorten and pull the chromosomes apart?
After the pairs of chromosomes are aligned, anaphase I begins. During this stage, the microtubules, or spindle fibers, pull the homologous chromosomes apart and move them to opposite ends of the cell.
Table of Contents
- Q. Which 2 phases do the centrioles move to opposite sides of the cell and spindle fibers begin to form?
- Q. Do spindle fibers shorten and pull the chromosomes apart?
- Q. What attaches a chromatid to a spindle fiber?
- Q. What would happen if one of the sets of sister chromatids didn’t separate during anaphase 2?
- Q. What would happen if one of the sets of sister chromatids did not separate during anaphase 2?
- Q. Why is it important to keep sister chromatids together?
- Q. What color should the sister chromatids be for each pair?
- Q. What is the difference between sister and non sister chromatids?
- Q. Why do sister chromatids not differ from each other?
- Q. Why do sister chromatids separate in anaphase 2?
- Q. How are sister chromatids connected to each other?
- Q. Which offspring will inherit all their mitochondrial DNA from their mother?
- Q. What are sister chromatids called after they separate?
- Q. How many sister chromatids are passed on to each daughter cell?
- Q. How do daughter cells obtain their DNA?
- Q. What phases of mitosis are sister chromatids visible?
Q. What attaches a chromatid to a spindle fiber?
chromosome duplication …of a set of duplicate chromatids that are held together by the centromere. The centromere is the point of attachment of the kinetochore, a protein structure that is connected to the spindle fibres (part of a structure that pulls the chromatids to opposite ends of the cell).
Q. What would happen if one of the sets of sister chromatids didn’t separate during anaphase 2?
When nondisjunction occurs in meiosis II, cells divide normally during anaphase I (homologous chromosomes separate correctly), but sister chromatids fail to separate during anaphase II (as seen in the diagram above, on the left). This again results in four possible haploid gametes.
Q. What would happen if one of the sets of sister chromatids did not separate during anaphase 2?
Sometimes during anaphase, chromosomes will fail to separate properly. This is called nondisjunction. Nondisjunction results in cells with abnormal numbers of chromosomes. Instead, one pair of sister chromatids failed to split, resulting in one cell with 5 chromosomes and one cell with 3 chromosomes.
Q. Why is it important to keep sister chromatids together?
In cell division, after replication of the cell’s chromosomes, the two copies, called sister chromatids, must be kept together to ensure that each daughter cell receives an equal complement of chromosomes. In higher organisms, DNA is packaged into chromosomes.
Q. What color should the sister chromatids be for each pair?
Duplicate the chromosome for DNA duplication (S synthesis) What color should the sister chromatids be for each pair? Yellow and red 4.
Q. What is the difference between sister and non sister chromatids?
Sister chromatids are two identical copies of a chromatid. When we say “identical,” they are exact replicas of the parent chromatid. Sister chromatids have the same genes and the same alleles. Non-sister chromatids are also called as homologues.
Q. Why do sister chromatids not differ from each other?
Sister chromatids are by and large identical (since they carry the same alleles, also called variants or versions, of genes) because they derive from one original chromosome. Homologous chromosomes might or might not be the same as each other because they derive from different parents.
Q. Why do sister chromatids separate in anaphase 2?
Anaphase II is the stage when sister chromatids of every chromosome separate and begin to move towards the opposite ends of the cell. The separation and the movement is due to the shortening of the kinetochore microtubules.
Q. How are sister chromatids connected to each other?
The sister chromatids are identical to one another and are attached to each other by proteins called cohesins. The attachment between sister chromatids is tightest at the centromere, a region of DNA that is important for their separation during later stages of cell division.
Q. Which offspring will inherit all their mitochondrial DNA from their mother?
maternal lineage
Q. What are sister chromatids called after they separate?
anaphase
Q. How many sister chromatids are passed on to each daughter cell?
one sister
Q. How do daughter cells obtain their DNA?
How do daughter cells obtain their DNA? The DNA in the parent cell nucleus makes a copy of itself and is then split between the two daughter cells during mitosis. The cell grows and makes a copy of its genetic material.
Q. What phases of mitosis are sister chromatids visible?
Prophase: the nuclear envelope breaks down, chromosomes condense, and spindle fibers connect to sister chromatids. Metaphase: spindle fibers pull sister chromatids to the metaphase plate at the equator of the cell. Anaphase: spindle fibers separate sister chromatids to opposite poles of the cell.