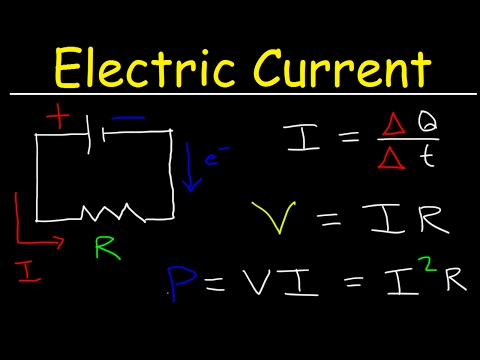
1 Answer. IN a simple circuit supply voltage and Resistance determines the current.
Q. What happens in a circuit when there is a break in the wire?
If there’s a break anywhere in the path, you have an open circuit, and the current stops flowing — and the metal atoms in the wire quickly settle down to a peaceful, electrically neutral existence. A closed circuit allows current to flow, but an open circuit leaves electrons stranded.
Table of Contents
- Q. What happens in a circuit when there is a break in the wire?
- Q. Can current still flow when the circuit is broken?
- Q. What happens to the flow of electric current if there is a break in a parallel circuit?
- Q. What type of electrical circuit has two or more switches?
- Q. How does current behave in a parallel circuit?
- Q. How does current behave in a circuit?
- Q. What happens to current in parallel?
- Q. What is the main disadvantage of parallel circuits?
- Q. What is the advantages of Series circuit?
- Q. Why are series circuits cheaper?
- Q. Which is better series or parallel connection?
- Q. Is the current the same in a series circuit?
- Q. Why is the current in a series circuit the same everywhere?
- Q. Why the current in series connection is constant?
- Q. Is current constant in series?
- Q. How do you calculate the current flow in a series circuit?
- Q. Does current stay constant in a parallel circuit?
- Q. What is the current in series connection?
- Q. What is the current in the circuit?
- Q. How many paths are there in a series circuit?
- Q. What is the difference between series connection and parallel connection?
Q. Can current still flow when the circuit is broken?
Electric current is the rate of flow of electric charge . No current can flow if the circuit is broken – for example, when a switch is open. An electric current flows when electrons move through a conductor, such as a metal wire. Electricity passes through metallic conductors as a flow of negatively charged electrons.
Q. What happens to the flow of electric current if there is a break in a parallel circuit?
(Note the open switch in the lower branch.) What happens if one device in a parallel circuit fails? A break in any one path does not interrupt the flow of current in the other paths. The reciprocal of the total resistance is equal to the sum of the reciprocals of individual resistance.
Q. What type of electrical circuit has two or more switches?
multiway switching
Q. How does current behave in a parallel circuit?
A Parallel circuit has certain characteristics and basic rules: A parallel circuit has two or more paths for current to flow through. Voltage is the same across each component of the parallel circuit. The sum of the currents through each path is equal to the total current that flows from the source.
Q. How does current behave in a circuit?
Current: The amount of current is the same through any component in a series circuit. Resistance: The total resistance of any series circuit is equal to the sum of the individual resistances. Voltage: The supply voltage in a series circuit is equal to the sum of the individual voltage drops.
Q. What happens to current in parallel?
The current in a parallel circuit splits into different branches then combines again before it goes back into the supply. When the current splits, the current in each branch after the split adds up to the same as the current just before the split.
Q. What is the main disadvantage of parallel circuits?
The major disadvantage of parallel circuits as compared to series circuits is that the power remains at the same voltage as the voltage of a single power source . parallel circuits cannot be effectively used.
Q. What is the advantages of Series circuit?
Advantages of series combination: Cells connected in series give a greater resultant voltage than individual cells. Voltage increases if the number of cells increases. Series circuits do not overheat easily.
Q. Why are series circuits cheaper?
It’s cheaper to make the series circuit. The circuit uses less power. The bulbs in the parallel circuits are brighter.
Q. Which is better series or parallel connection?
Parallel connection is better because the voltage across each appliance connected in parallel is same that means if a number of bulbs are connected in parallel then irrespective of the number no bulb will get dim, but in series as the number of bulbs increase the resistance increase voltage decrease so the bulb gets …
Q. Is the current the same in a series circuit?
The same current flows through each part of a series circuit. The total resistance of a series circuit is equal to the sum of individual resistances. The voltage drop across a resistor in a series circuit is directly proportional to the size of the resistor. If the circuit is broken at any point, no current will flow.
Q. Why is the current in a series circuit the same everywhere?
When electrons flow, they are not created nor destroyed. The current is not decreasing, it is decreased. The answer is much simpler, the current in a series circuit is the same everywhere because there are no alternate or parallel paths for it to flow in.
Q. Why the current in series connection is constant?
This is because there is continuity in the charge flowing. There is no accumulation of charge anywhere in the circuit. Hence, since, the electric charge flowing in the series circuit has to remain constant, the electric charge flowing per second in the circuit also has to remain constant.
Q. Is current constant in series?
In a series circuit the current is the same at any particular point on the circuit. The voltage in a series circuit, however, does not remain constant. 4. The voltage drops across each resistor.
Q. How do you calculate the current flow in a series circuit?
Amperage (or Amps) in a Series Circuit The equation V = I/R, known as Ohm’s Law, also holds true at each resistor in the circuit. The current flow throughout a series circuit is constant, which means it’s the same at each resistor. You can calculate the voltage drop at each resistor using Ohms’ Law.
Q. Does current stay constant in a parallel circuit?
Current remains constant in series connection and voltage remains constant in parallel connection , current is like water flowing in rivers it always flow in specific path and with constant amount but when some diversion is created it distribute and amount decrease gradually same here with current.
Q. What is the current in series connection?
In a series circuit, the current is the same for all of the elements.
Q. What is the current in the circuit?
A simple electric circuit, where current is represented by the letter i. The relationship between the voltage (V), resistance (R), and current (I) is V=IR; this is known as Ohm’s law. An electric current is a stream of charged particles, such as electrons or ions, moving through an electrical conductor or space.
Q. How many paths are there in a series circuit?
one path
Q. What is the difference between series connection and parallel connection?
Difference between series and parallel circuit A parallel circuit refers to a circuit with two or more two paths for the current to flow. In a series circuit, all the components are arranged in a single line. In a parallel circuit, all the components are arranged parallel to each other.