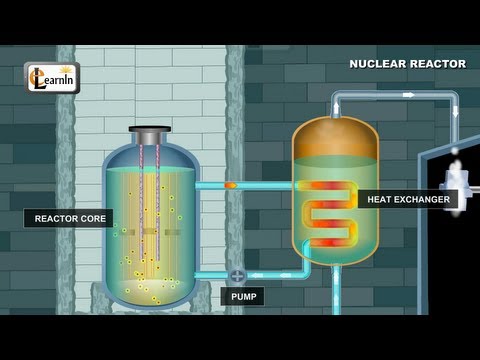
Q. Which fuel is mainly used in nuclear fission reactor?
uranium
Q. Can any element be used in fission?
The chemical element isotopes that can sustain a fission chain reaction are called nuclear fuels, and are said to be fissile. The most common nuclear fuels are 235U (the isotope of uranium with mass number 235 and of use in nuclear reactors) and 239Pu (the isotope of plutonium with mass number 239).
Table of Contents
- Q. Which fuel is mainly used in nuclear fission reactor?
- Q. Can any element be used in fission?
- Q. How was the first atom split?
- Q. Who is the father of atom?
- Q. Who first split the nucleus?
- Q. Why is Rutherford’s model important?
- Q. What are the main features of Bohr’s model?
- Q. What was the conclusion of Rutherford experiment?
- Q. Why are particles deflected bounced backwards?
- Q. Why were most alpha particles not deflected?
Q. How was the first atom split?
Walton, working jointly at the Cavendish Laboratory, were the first to split the atom when they bombarded lithium with protons generated by a type of particle accelerator (dubbed a “Cockcroft-Walton machine”) and changed the resulting lithium nucleus into two helium nuclei.
Q. Who is the father of atom?
The idea that everything is made of atoms was pioneered by John Dalton (1766-1844) in a book he published in 1808. He is sometimes called the “father” of atomic theory, but judging from this photo on the right “grandfather” might be a better term.
Q. Who first split the nucleus?
Ernest Rutherford
Q. Why is Rutherford’s model important?
Most important, he postulated the nuclear structure of the atom: experiments done in Rutherford’s laboratory showed that when alpha particles are fired into gas atoms, a few are violently deflected, which implies a dense, positively charged central region containing most of the atomic mass.
Q. What are the main features of Bohr’s model?
Salient features of Niels Bohr atomic model are:
- Electrons revolve around the nucleus in stable orbits without emission of radiant energy.
- An orbit or energy level is designated as K, L, M, N shells.
- An electron emits or absorbs energy when it jumps from one orbit or energy level to another.
Q. What was the conclusion of Rutherford experiment?
Conclusion of Rutherford’s scattering experiment: Most of the space inside the atom is empty because most of the α-particles passed through the gold foil without getting deflected. Very few particles were deflected from their path, indicating that the positive charge of the atom occupies very little space.
Q. Why are particles deflected bounced backwards?
A tiny number of alpha particles, traveling at 10% of the speed of light, hit a dense atomic center right in its middle. The collision and the repulsion cause the alpha particle to “bounce” backwards and move on a very different path. These are the reflected rays.
Q. Why were most alpha particles not deflected?
Most of the alpha particles did pass straight through the foil. The atom being mostly empty space. A small number of alpha particles were deflected by large angles (> 4°) as they passed through the foil. Like charges repel, so the positive alpha particles were being repelled by positive charges.