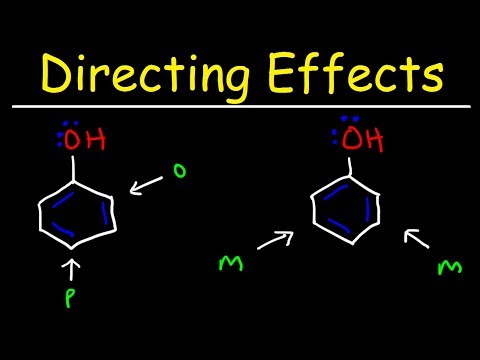
Q. Which groups are ortho para directors?
Substituents which lead to this result are called, “ortho-, para- directors”. Examples of ortho-, para– directors are hydroxyl groups, ethers, amines, alkyl groups, thiols, and halogens. Here’s a concrete example: the nitration of methoxybenzene (also known as anisole).
Q. Which functional group is meta directing?
Thus, the nitro group is a meta directing group. Ortho, para directing groups are electron-donating groups; meta directing groups are electron-withdrawing groups. The halide ions, which are electron-withdrawing but ortho, para directing, are the exception.
Table of Contents
- Q. Which groups are ortho para directors?
- Q. Which functional group is meta directing?
- Q. Why is COOH meta directing?
- Q. Which group is both ortho para directing and ring deactivating?
- Q. Which is more deactivating SO3H or NO2?
- Q. Is NO2 a meta directing group?
- Q. Why is NO2 a deactivating group?
- Q. Is NO2 a deactivating group?
- Q. Why is no ortho para directing?
- Q. Why is oh more activating than och3?
- Q. Is benzene ring an electron withdrawing group?
- Q. Why is para favored over Ortho?
- Q. Why is toluene ortho para directing?
Q. Why is COOH meta directing?
Explanation: With the exception of halogens, meta directors deactivate a benzene ring. Meta directors have little electron density at the point of contact with the benzene ring. For example, a carboxylic acid is a meta director because it experiences resonance, a delocalization of electrons.
Q. Which group is both ortho para directing and ring deactivating?
Halogens
Q. Which is more deactivating SO3H or NO2?
NO2 will higher -I effect because it has two highly electronegative atoms attached to it. Since NO2 is a strong, actually, the strongest, -R group. Hence, it decreases the electron density at ortho and para positions on a Benzene ring. SO3H is a weaker -R group as compared to NO2 and hence less deactivating.
Q. Is NO2 a meta directing group?
Since NO2 is an electron withdrawing group, a glance at the resonance structures shows that the positive charge becomes concentrated at the ortho-para positions. Thus these positions are deactivated towards electrophilic aromatic substitution. Hence, NO2 is a meta-director, as we all learned in organic chemistry.
Q. Why is NO2 a deactivating group?
The nitro group is deactivating towards EAS, as it prevents a negative charge from even existing in the benzene ring and makes the ring positively charged. The electron density is more heavily removed from the positions ortho and para to the nitro group than the position meta to the nitro group.
Q. Is NO2 a deactivating group?
Atoms with pi-bonds to electronegative groups – Strongly deactivating. NO2, CN, SO3H, CHO, COR, COOH, COOR, CONH2. All pi-acceptors. Electron withdrawing groups with no pi bonds or lone pairs – Strongly deactivating.
Q. Why is no ortho para directing?
This resonance directs the donated electrons to the ortho/para positions, making the nitroso group ortho/para directing even as the electronegativity of nitrogen and oxygen make it deactivating.
Q. Why is oh more activating than och3?
OH group is more activating than OR. Because OH group has more electron donating group . We can better understand it in he case of Phenol. Phenols have highly electron donating group i.e. hydroxyl group due to which the benzene ring has high electron density at ortho and para postions .
Q. Is benzene ring an electron withdrawing group?
The major product of a monosubstituted benzene ring with an electron withdrawing group and an additional electrophile is a product with meta substitution. In contrast to electron donating groups, electron withdrawing groups are deactivating.
Q. Why is para favored over Ortho?
Ortho and Para producst produces a resonance structure which stabilizes the arenium ion. This causes the ortho and para products for form faster than meta. Generally, the para product is preferred because of steric effects.
Q. Why is toluene ortho para directing?
In Toluene, the methyl group releases electrons towards the benzene ring partly due to inductive effect and mainly due to hyperconjugation. Thus the reactivity of the ring towards electrophilic substitution increases and the substitution is directed at ortho and para positions to the methyl group.