The reactions that do not require energy to be carried out are called thermodynamically favored reaction. In the case of the exothermic and endothermic reactions, the former is more favorable as it releases energy.
Q. How can you tell if entropy increases or decreases?
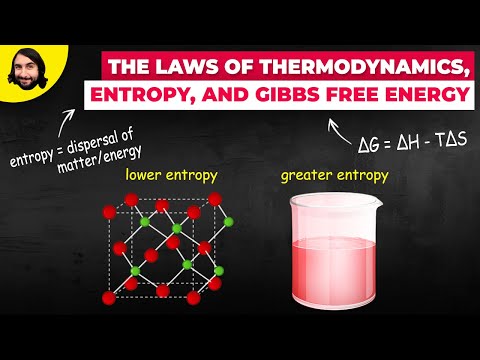
The entropy is decreasing because a solid is formed from aqueous reactants….Entropy
Table of Contents
- Q. How can you tell if entropy increases or decreases?
- Q. How do you know if a reaction is enthalpy or entropy driven?
- Q. How do you know if something is thermodynamically favored?
- Q. Is salt dissolving spontaneous?
- Q. Does dissolving salt release energy?
- Q. Is dissolving salt in water an exothermic reaction?
- Q. Does dissolving increase entropy?
- Q. What does a negative change in entropy indicate?
- Q. Why Does entropy increase from normal egg to hard boiled egg?
- Q. Which substance has the highest entropy?
- Q. Which has more entropy water or ice?
- Q. How do you know which entropy is higher?
- Q. Why Does entropy increase with mass?
- Q. Is entropy dependent on mass?
- Q. Does entropy change with mass?
- Q. Does entropy increase with volume?
- Q. What is the entropy of a system that has only a single microstate?
- Q. Is entropy a Colligative property?
- For a given substance, the entropy of the liquid state is greater than the entropy of the solid state.
- Entropy increases when a substance is broken up into multiple parts.
- Entropy increases as temperature increases.
Q. How do you know if a reaction is enthalpy or entropy driven?
A reaction with ΔH < 0 and ΔS > 0 will have ΔG = ΔH – TΔS < 0 at all temperatures. Therefore, the reaction will be spontaneous at all temperatures. Since both the negative sign of ΔH and the positive sign of ΔS lead to the reaction being favorable, the reaction is both enthalpy and entropy driven.
Q. How do you know if something is thermodynamically favored?
Reactions producing a large number of simple, gaseous products usually have a positive ΔS. The sign of ΔG indicates the direction in which a reaction moves to reach its equilibrium position. A reaction is thermodynamically favorable when its enthalpy, ΔH, decreases and its entropy, ΔS, increases.
Q. Is salt dissolving spontaneous?
The solution of NaCl in water has much less order than the pure water and the crystalline salt. Entropy increases every time a solute dissolves in a solvent. Even though the enthalpy change is a positive number, the dissolution is spontaneous because the Gibbs free energy change, G, is negative due to the entropy term.
Q. Does dissolving salt release energy?
When salt dissolves in water, sodium and chloride ions are pulled apart to form new weak bonds with water molecules. Pulling them apart takes energy, while forming new bonds with the water molecules releases energy.
Q. Is dissolving salt in water an exothermic reaction?
This means just slightly more energy must be put into the solution than is released back into the solution; therefore dissolving table salt in water is endothermic. More energy is released into the solution than is required to pull apart the ions; therefore dissolving sodium hydroxide in water is exothermic.
Q. Does dissolving increase entropy?
Dissolution of a solute normally increases the entropy by spreading the solute molecules (and the thermal energy they contain) through the larger volume of the solvent.
Q. What does a negative change in entropy indicate?
A negative change in entropy indicates that the disorder of an isolated system has decreased. For example, the reaction by which liquid water freezes into ice represents an isolated decrease in entropy because liquid particles are more disordered than solid particles.
Q. Why Does entropy increase from normal egg to hard boiled egg?
On boiling an egg entropy increases as due to denaturation the helical structure of protein become more complicated and random coiled structure. You would have thought that on boiling the liquid protein (albumin) gets solidifies and thus entropy decreases.
Q. Which substance has the highest entropy?
hydrogen
Q. Which has more entropy water or ice?
Water has a greater entropy than ice and so entropy favours melting. But ice has a lower energy than water and so energy favours freezing. Therefore, as the surroundings get hotter, they are gaining more energy and thus the entropy of the surroundings is increasing.
Q. How do you know which entropy is higher?
The entropy of a substance increases with its molecular weight and complexity and with temperature. The entropy also increases as the pressure or concentration becomes smaller. Entropies of gases are much larger than those of condensed phases.
Q. Why Does entropy increase with mass?
The greater the mass of a particle, the closer together its energy levels. The effect of closeness of energy levels on the entropy is shown in Figure 16.8. This applies in general for any number of particles and any quantity of energy. Therefore, the heavier the molecules of a substance, the larger its molar entropy.
Q. Is entropy dependent on mass?
numerically , entropy=energy of the system/kelvin. from this relation entropy depends on mass, i.e changing the mass can increase or decrease the entropy of the system.
Q. Does entropy change with mass?
If entropy is the disorder of a system, then a low entropy state is one of higher energy. As we know, mass is energy. From here we must say that the more mass something has, the lower its entropy because the mass can be converted to energy.
Q. Does entropy increase with volume?
As well, increasing the volume of a substance increases the number of positions where each molecule could be, which increases the number of microstates. Therefore, any change that results in a higher temperature, more molecules, or a larger volume yields an increase in entropy.
Q. What is the entropy of a system that has only a single microstate?
At absolute zero there is only 1 microstate possible (Ω=1) and ln(1) = 0. A more general form of the third law applies to systems such as glasses that may have more than one minimum energy state: the entropy of a system approaches a constant value as the temperature approaches zero.
Q. Is entropy a Colligative property?
Thus, colligative properties are what we would call an entropic effect (they are a result of entropy).