The side opposite the right angle is the hypotenuse. The Pythagorean theorem is used to solve for the length of the hypotenuse. If a right triangle has legs measuring a and b with hypotenuse c, the Pythagorean theorem is a² + b² = c².
Q. What is the rule for the longest side of a triangle in order to make a triangle?
The longest side in a triangle is opposite the largest angle, and the shortest side is opposite the smallest angle. Triangle Inequality: In any triangle, the sum of the lengths of any two sides is greater than the length of the third side. Pythagorean Theorem: In a right triangle with hypotenuse c, a2+b2=c2.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is the rule for the longest side of a triangle in order to make a triangle?
- Q. What is the rule for finding the missing side of a triangle?
- Q. How do you find an angle with two sides?
- Q. How do you calculate A2 B2 C2?
- Q. Is a2 b2 c2 always true?
- Q. What is the formula of a2 b2?
- Q. What would be the factors of a2 b2?
- Q. What is a2 b2 identity?
- Q. What is a 2 B 2 called?
- Q. What is a 2 B 2 C 2 called?
- Q. Is a B 2 a binomial?
- Q. Why can’t you factor the sum of two squares?
- Q. Will result in a difference of two squares?
- Q. What is the perfect cube formula?
- Q. How do you solve perfect squares?
- Q. What are the perfect squares from 1 to 1000?
- Q. What are the first 20 perfect squares?
- Q. What did you do to determine whether the numbers are perfect squares?
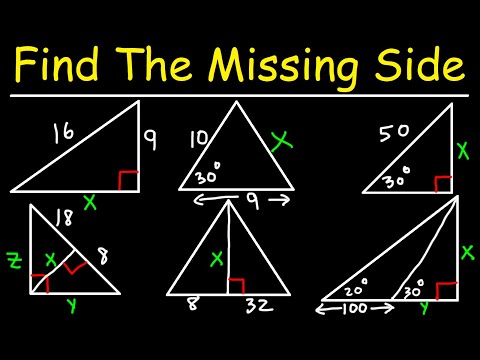
Q. What is the rule for finding the missing side of a triangle?
Finding the missing side of a right triangle is a pretty simple matter if two sides are known. One of the more famous mathematical formulas is a2+b2=c2 a 2 + b 2 = c 2 , which is known as the Pythagorean Theorem.
Q. How do you find an angle with two sides?
Example
- Step 1 The two sides we know are Opposite (300) and Adjacent (400).
- Step 2 SOHCAHTOA tells us we must use Tangent.
- Step 3 Calculate Opposite/Adjacent = 300/400 = 0.75.
- Step 4 Find the angle from your calculator using tan-1
Q. How do you calculate A2 B2 C2?
The formula is A2 + B2 = C2, this is as simple as one leg of a triangle squared plus another leg of a triangle squared equals the hypotenuse squared.
Q. Is a2 b2 c2 always true?
Note: In order for a2+b2=c2 to be true, the side length c must be the largest side length. So in order to test whether a triangle is right, you only need to plug in values where c is the largest among a,b,c.
Q. What is the formula of a2 b2?
a2 – b2 = (a + b)(a – b ) .
Q. What would be the factors of a2 b2?
2 Answers
- Whereas a2−b2=(a+b)(a−b) is very simple, to factor a2+b2 requires the use of complex numbers.
- (a+ib)(a−ib)
- So a2+b2=(a+ib)(a−ib) , but there is no other factoring with real number coefficients.
Q. What is a2 b2 identity?
Solution:- a2–b2 =(a+b)(a–b) – = ² – ² = +
Q. What is a 2 B 2 called?
It ended up very simple. And it is called the “difference of two squares” (the two squares are a2 and b2).
Q. What is a 2 B 2 C 2 called?
a2 + b2 = c2. This is known as the Pythagorean equation, named after the ancient Greek thinker Pythagoras. This relationship is useful because if two sides of a right triangle are known, the Pythagorean theorem can be used to determine the length of the third side.
Q. Is a B 2 a binomial?
BIG IDEA The square of a binomial a + b is the expression (a + b)2 and can be found by multiplying a + b by a + b as you would multiply any polynomials.
Q. Why can’t you factor the sum of two squares?
It’s true that you can’t factor A²+B² on the reals — meaning, with real-number coefficients — if A and B are just simple variables. So it’s still true that a sum of squares can’t be factored as a sum of squares on the reals.
Q. Will result in a difference of two squares?
where one perfect square is subtracted from another, is called a difference of two squares. It arises when (a − b) and (a + b) are multiplied together. This is one example of what is called a special product.
Q. What is the perfect cube formula?
Factor the Sum of Perfect Cubes: a3 + b3 = (a + b)(a2 – ab + b2) Factor the Difference of Perfect Cubes: a3 – b3 = (a – b)(a2 + ab + b2) When trying to remember these patterns, remember that the first binomial term in the factored form in each pattern keeps the same sign as the sign between the perfect cubes.
Q. How do you solve perfect squares?
A perfect square trinomial can be factored, so the equation can then be solved by taking the square root of both sides. Solve the equation x2 + 8x + 5 = 0 by completing the square. First, rewrite the equation in the form x2 + bx = c. Add the appropriate constant to complete the square, then simplify.
Q. What are the perfect squares from 1 to 1000?
There are 31 perfect squares between 1 and 1000 (inclusive.)
Q. What are the first 20 perfect squares?
So the first 20 square numbers are 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81, 100, 121, 144, 169, 196, 225, 256, 289, 324, 361 and 400.
Q. What did you do to determine whether the numbers are perfect squares?
You can also tell if a number is a perfect square by finding its square roots. Finding the square root is the inverse (opposite) of squaring a number. If you find the square root of a number and it’s a whole integer, that tells you that the number is a perfect square.