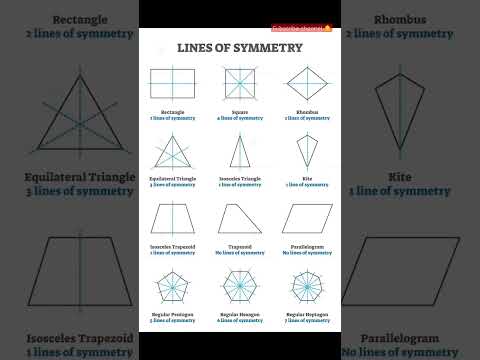
Q. Which number has a vertical line of symmetry?
8
Q. What figure has exactly 3 lines of symmetry?
equilateral triangle
Table of Contents
- Q. Which number has a vertical line of symmetry?
- Q. What figure has exactly 3 lines of symmetry?
- Q. Is the number 3 symmetrical?
- Q. What is vertically symmetrical?
- Q. What has both vertical and horizontal symmetry?
- Q. What is the shape of horizontal and vertical?
- Q. Does a straight line have symmetry?
- Q. What does a symmetrical graph mean?
- Q. What does symmetry mean in statistics?
- Q. How do you describe symmetry in statistics?
- Q. What is symmetrical curve?
- Q. Why is normal distribution symmetrical?
- Q. Is a normal distribution always symmetrical?
- Q. Why is it called skewed left?
- Q. Why is right skewed to the left?
- Q. How do you interpret a right skewed histogram?
- Q. What is skewed left and right?
- Q. How do you know if a graph is skewed right or left?
- Q. Can a normal distribution be skewed?
- Q. Can a bimodal distribution be skewed?
- Q. What is positive and negative skewness?
Q. Is the number 3 symmetrical?
The numbers 0, 3, and 8 are symmetrical. The number 1 is symmetrical only if it is written without the flag. 0 has 2 lines of symmetry (one horizontal and one vertical).
Q. What is vertically symmetrical?
If the line passes through the pattern from top to bottom, hence dividing the pattern into identical halves, then such line is the vertical line of symmetry. It is a standing line that divides the pattern into their replicating halves.
Q. What has both vertical and horizontal symmetry?
Answer: The letter ‘X’ has both horizontal and vertical lines of symmetry,i.e. when a vertical or horizontal line is made to pass through the letter, it gets divided into two equal halves. A line of symmetry is one that divides a figure into two halves which are mirror images of each other.
Q. What is the shape of horizontal and vertical?
Anything parallel to the horizon is called horizontal. As vertical is the opposite of horizontal, anything that makes a 90-degree angle (right angle) with the horizontal or the horizon is called vertical. So, the horizontal line is one that runs across from left to right….What is Horizontal?
| Horizontal | Vertical |
|---|---|
| 24 + 33 = 57 | 24 + 33 = 57 |
Q. Does a straight line have symmetry?
The straight lines are called the lines of symmetry of the respective figures. In the above pictures or figures the lines of symmetry are both horizontal and vertical. In the above figure the straight lines shown are not lines of symmetry. These are the basic and main points to understand line symmetry.
Q. What does a symmetrical graph mean?
What Is Symmetrical Distribution? A symmetrical distribution occurs when the values of variables appear at regular frequencies and often the mean, median, and mode all occur at the same point. If a line were drawn dissecting the middle of the graph, it would reveal two sides that mirror one other.
Q. What does symmetry mean in statistics?
Symmetry is an attribute used to describe the shape of a data distribution. When it is graphed, a symmetric distribution can be divided at the center so that each half is a mirror image of the other.
Q. How do you describe symmetry in statistics?
A symmetric distribution is a type of distribution where the left side of the distribution mirrors the right side. By definition, a symmetric distribution is never a skewed distribution. The normal distribution is symmetric. It is also a unimodal distribution (it has one peak). Standard normal distribution.
Q. What is symmetrical curve?
A symmetric curve can have one midpoint that is located on the mirror plane. In a symmetric curve, the curve continues to the mirror plane from the last defined point, and the curve is mirrored across the plane. So the direction of the points in a curve is significant, specifically the first point and last point.
Q. Why is normal distribution symmetrical?
A normal distribution comes with a perfectly symmetrical shape. This means that the distribution curve can be divided in the middle to produce two equal halves. The symmetric shape occurs when one-half of the observations fall on each side of the curve.
Q. Is a normal distribution always symmetrical?
A normal distribution is the proper term for a probability bell curve. In a normal distribution the mean is zero and the standard deviation is 1. Normal distributions are symmetrical, but not all symmetrical distributions are normal. In reality, most pricing distributions are not perfectly normal.
Q. Why is it called skewed left?
A left-skewed distribution has a long left tail. Left-skewed distributions are also called negatively-skewed distributions. That’s because there is a long tail in the negative direction on the number line. The mean is also to the left of the peak.
Q. Why is right skewed to the left?
Data skewed to the right is usually a result of a lower boundary in a data set (whereas data skewed to the left is a result of a higher boundary). So if the data set’s lower bounds are extremely low relative to the rest of the data, this will cause the data to skew right. Another cause of skewness is start-up effects.
Q. How do you interpret a right skewed histogram?
The mean of right-skewed data will be located to the right side of the graph and will be a greater value than either the median or the mode. This shape indicates that there are a number of data points, perhaps outliers, that are greater than the mode.
Q. What is skewed left and right?
For skewed distributions, it is quite common to have one tail of the distribution considerably longer or drawn out relative to the other tail. A “skewed right” distribution is one in which the tail is on the right side. A “skewed left” distribution is one in which the tail is on the left side.
Q. How do you know if a graph is skewed right or left?
So when data are skewed right, the mean is larger than the median. An example of such data would be NBA team salaries where star players make a lot more than their teammates. If most of the data are on the right, with a few smaller values showing up on the left side of the histogram, the data are skewed to the left.
Q. Can a normal distribution be skewed?
The skewness for a normal distribution is zero, and any symmetric data should have a skewness near zero. Negative values for the skewness indicate data that are skewed left and positive values for the skewness indicate data that are skewed right.
Q. Can a bimodal distribution be skewed?
Bimodal: A bimodal shape, shown below, has two peaks. This shape may show that the data has come from two different systems. If this shape occurs, the two sources should be separated and analyzed separately. A skewed distribution can result when data is gathered from a system with has a boundary such as zero.
Q. What is positive and negative skewness?
These taperings are known as “tails.” Negative skew refers to a longer or fatter tail on the left side of the distribution, while positive skew refers to a longer or fatter tail on the right. The mean of positively skewed data will be greater than the median.