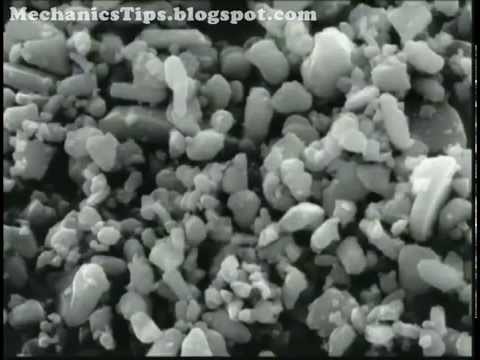
Advantages of Powders Powders are more stable than liquid dosage form. The chance of incompatibility are less as compared to liquid dosage form. The onset of action of powdered drug is rapid as compared to other solid dosage form e.g. tablet, capsules.
Q. How do you make powder metallurgy?
- Solid-State Reduction. The metal ore is crushed and then mixed with another material, usually carbon.
- Atomization. This process begins with scrap metal that is then melted.
- Electrolysis. The electrolysis process requires specific conditions to be effective, including proper:
- Chemical.
- Centrifugal Atomization.
Q. Are types of powder metallurgy process?
- Overview.
- History and capabilities.
- Powder production techniques.
- Powder compaction.
- Isostatic powder compacting.
- Sintering.
- Continuous powder processing.
- Shock (dynamic) consolidation.
Explanation: Copper is the primary metal produced by electrolysis, but iron, chromium, and magnesium powders are also produced this way. Due to its associated high energy costs, electrolysis is generally limited to high-value powders such as high-conductivity copper powders.
Table of Contents
- Q. How do you make powder metallurgy?
- Q. Are types of powder metallurgy process?
- Q. What are the advantages of powder metallurgy?
- Q. Which is an advantage of powder?
- Q. What are the different types of powder?
- Q. What are the four basic types of powder papers?
- Q. What is divided powder?
- Q. What is powder formulation?
- Q. How many types of dusting powder are there?
- Q. How are the powders administered?
- Q. How powders containing potent drugs are dispensed?
- Q. Is granules smaller than powder?
- Q. What is Efflorescent powder?
- Q. What is Deliquescence?
- Q. What are the examples of Efflorescent substances?
- Q. What does Efflorescent mean?
- Q. How do you prevent efflorescence?
- Q. Does efflorescence go away?
- Q. What is the difference between Deliquescent and Efflorescent?
- Q. What is Deliquescence and examples?
- Q. What is called Deliquescent give example?
- Q. What is hygroscopic material?
- Q. What is the most hygroscopic material?
- Q. What material does not absorb water?
- Q. How do you handle hygroscopic materials?
Q. What are the advantages of powder metallurgy?
Advantages of the Powder Metallurgy Process
- Minimizes machining by producing parts at, or close to, final dimensions.
- Minimizes scrap losses by typically using more than 97% of the starting raw material in the finished part.
- Permits a wide variety of alloy systems.
- Produces good surface finish.
Q. Which is an advantage of powder?
Q. What are the different types of powder?
Types of Powders
- Epoxy. Epoxy coatings provide a smooth, uniform appearance.
- Polyester. Polyester powders offer strong adhesion properties and excellent gloss retention when exposed to UV elements.
- Nylon. Nylon powders are generally used as a protective coating.
- Polyurethane.
- Hybrid.
- Metallic.
Q. What are the four basic types of powder papers?
34 Powder Papers – Four basic types of powder papers are available.
- Vegetable parchment, a thin semi-opaque moisture-resistant paper.
- White bond, an opaque paper with no moisture-resistant properties.
- Glassine, a glazed, transparent moisture-resistant paper.
Q. What is divided powder?
Divided powders or charts are single doses of powdered medicinals individually wrapped in cellophane, metallic foil, or paper. The divided powder is a more accurate dosage form than bulk powder because the patient is not involved in measurement of the dose.
Q. What is powder formulation?
PHARMACEUTICAL POWDERS Historically, powders represent one of the’ oldest dosage forms. A pharmaceutical powder is solid dosage form which contains mixture of finely divided drugs or chemicals in a dry form meant for internal or external use. A good powder formulation has a uniform particle size distribution.
Q. How many types of dusting powder are there?
Hence, dusting powders should be passed though sieve no 85 dusting powders are of two types:1)medical powders 2)surgical powders medical dusting powders :- medical dusting powders are used mainly for superficial skin condition, where as medical dusting powders must be free from pathogenic microorganism surgical …
Q. How are the powders administered?
Powders
- Powders are designed to be dissolved in water.
- If you have a sachet or envelope, open it and pour the contents into a small glass of water.
- If you have a tub, measure out the right amount using the scoop and pour it into a small glass of water.
Q. How powders containing potent drugs are dispensed?
If desired, powders should be micronised or passed through a sieve # 80 or 100. Dusting powders should preferably be dispensed in sifter-top containers. Such containers provide the protection from air, moisture and contamination as well as convenience of application.
Q. Is granules smaller than powder?
Granules have smaller surface area than a comparable volume of powders. This makes granules more stable physically and chemically than the corresponding powders. Granules are less likely to cake or harden upon standing than are powders. 4.
Q. What is Efflorescent powder?
Some crystalline substances liberate water of crystallization wholly or partly on exposure to humid atmosphere or during trituration and thus become wet or liquefy. Example of such substances include caffeine, citric acid, ferrous sulphate etc.
Q. What is Deliquescence?
Deliquescence, the process by which a substance absorbs moisture from the atmosphere until it dissolves in the absorbed water and forms a solution. Deliquescence occurs when the vapour pressure of the solution that is formed is less than the partial pressure of water vapour in the air.
Q. What are the examples of Efflorescent substances?
An example of an efflorescent substance is the common copper (II) sulfate crystal CuSO4. 5H2O, a blue crystalline solid that when exposed to air, slowly loses water of crystallization from its surface to crystallize to form a white layer of anhydrous copper (II) sulfate. Na2CO3.
Q. What does Efflorescent mean?
efflorescence • /ef-luh-RESS-unss/ • noun. 1 a : the action or process of developing and unfolding as if coming into flower b : an instance of such development c : fullness of manifestation : culmination 2 : the period or state of flowering 3 : the process or product of efflorescing chemically.
Q. How do you prevent efflorescence?
Clear water repellents, silicone and acrylic coatings also may help you remove efflorescence as well. The coating will absorb water across a masonry surface and prevent efflorescence from recurring. Plus, the combination of warm water and white wine vinegar has been shown to eliminate efflorescence.
Q. Does efflorescence go away?
In many cases, efflorescence will disappear on its own over time (usually after the first year of a paver or retaining wall installation). Efflorescence can also be removed with special cleaners like the Gator Efflorescence Cleaner. On average, you should wait about 60 days before applying an efflorescence cleaner.
Q. What is the difference between Deliquescent and Efflorescent?
Q17) Differentiate between an efflorescent, deliquescent & hygroscopic substance with suitable examples….Water | Exercise – I.
| Efflorescent substances | Deliquescent substances | Hygroscopic substances |
|---|---|---|
| They get crystalline when hydrated. | They are crystalline water soluble substances. | They do not change their original state. |
Q. What is Deliquescence and examples?
A deliquescent salt is a salt which absorbs the moisture from the air when exposed to air and turns into a solution. Most deliquescent substances are salts. Examples include sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, ammonium chloride, gold(III) chloride, sodium nitrate, and calcium chloride.
Q. What is called Deliquescent give example?
Delequescence: A property of some solid substance by which, they absorb a large amount of moisture from the air so that they become wet or pass into solution, is called deliquescence. The solid substance having this property, is known as deliquescent. For example, KOH, NaOH, MgCl2, CaCl2 etc.
Q. What is hygroscopic material?
A hygroscopic substance is one that readily attracts water from its surroundings, through either absorption or adsorption. Calcium chloride is so hygroscopic that it eventually dissolves in the water it absorbs: this property is called deliquescence.
Q. What is the most hygroscopic material?
Sodium chloride (NaCl) is a well-known hygroscopic material which is commonly used as an adsorbent.
Q. What material does not absorb water?
The aluminum and plastic are made from materials that do not attract water molecules. Also, the aluminum and plastic do not have spaces for the water to move into like felt and paper. Therefore, the aluminum and plastic do not absorb water.
Q. How do you handle hygroscopic materials?
Hygroscopic materials will generally be supplied in sealed bags to reduce moisture absorption but even sealed bags will pick up moisture if stored in a moist cold area. Good storage is simple common sense. Keep the material dry and keep it as warm as possible.